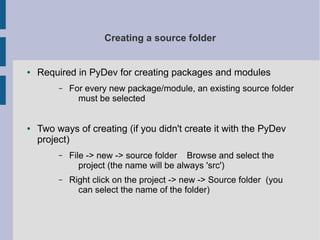
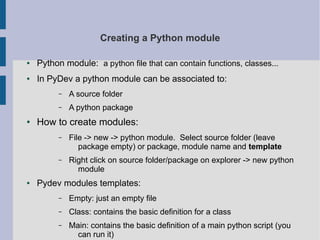
The document describes a Python Object Oriented Programming session that covers using the Eclipse IDE and PyDev plugin to create Python projects, packages, and modules. It provides instructions for setting up a project structure with the CLTL group's packages and assigning a task to create specific modules and functions within that structure.