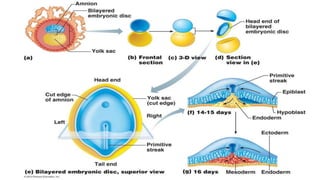
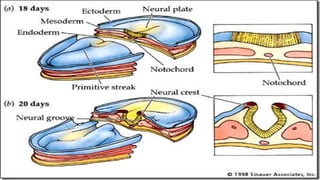
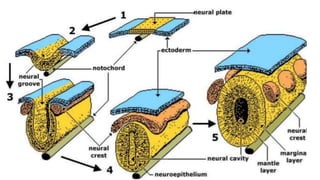
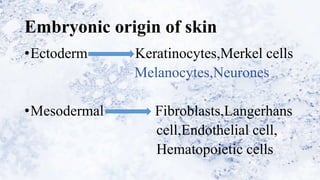
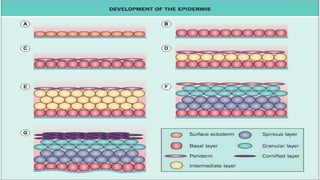
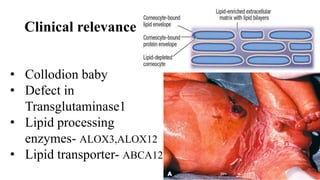
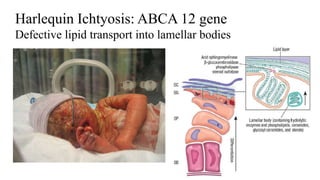
1) The skin develops from surface ectoderm and underlying mesoderm. Key stages include specification, morphogenesis, and differentiation as the epidermis stratifies and cornification occurs.
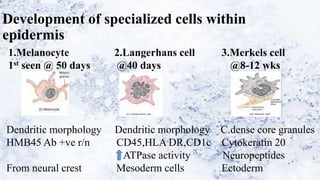
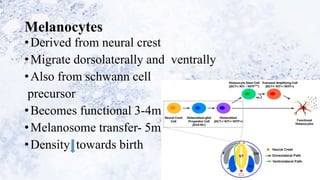
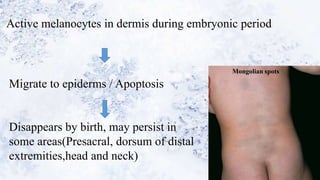
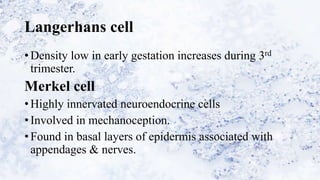
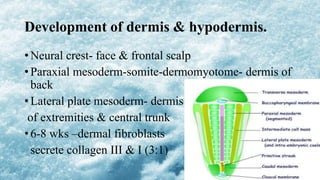
2) Specialized cells like melanocytes and Langerhans cells arise and mature according to defined timelines. Dermal components also develop from distinct embryonic origins.
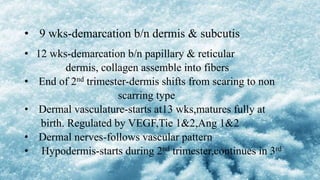
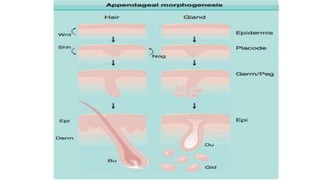
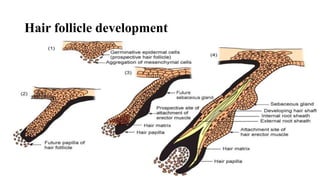
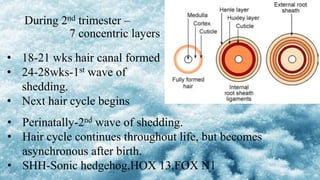
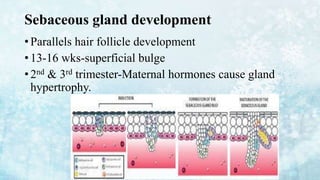
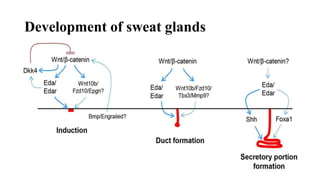
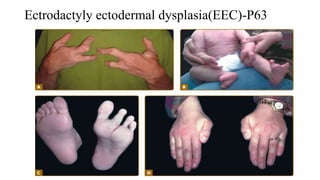
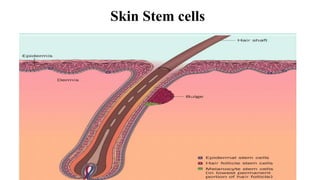
3) Skin appendages form through epithelial-mesenchymal interactions, with hair follicles, sebaceous glands, nails, and sweat glands developing in parallel through gestation. The dermal-epidermal junction also acquires mature structures by 12 weeks.