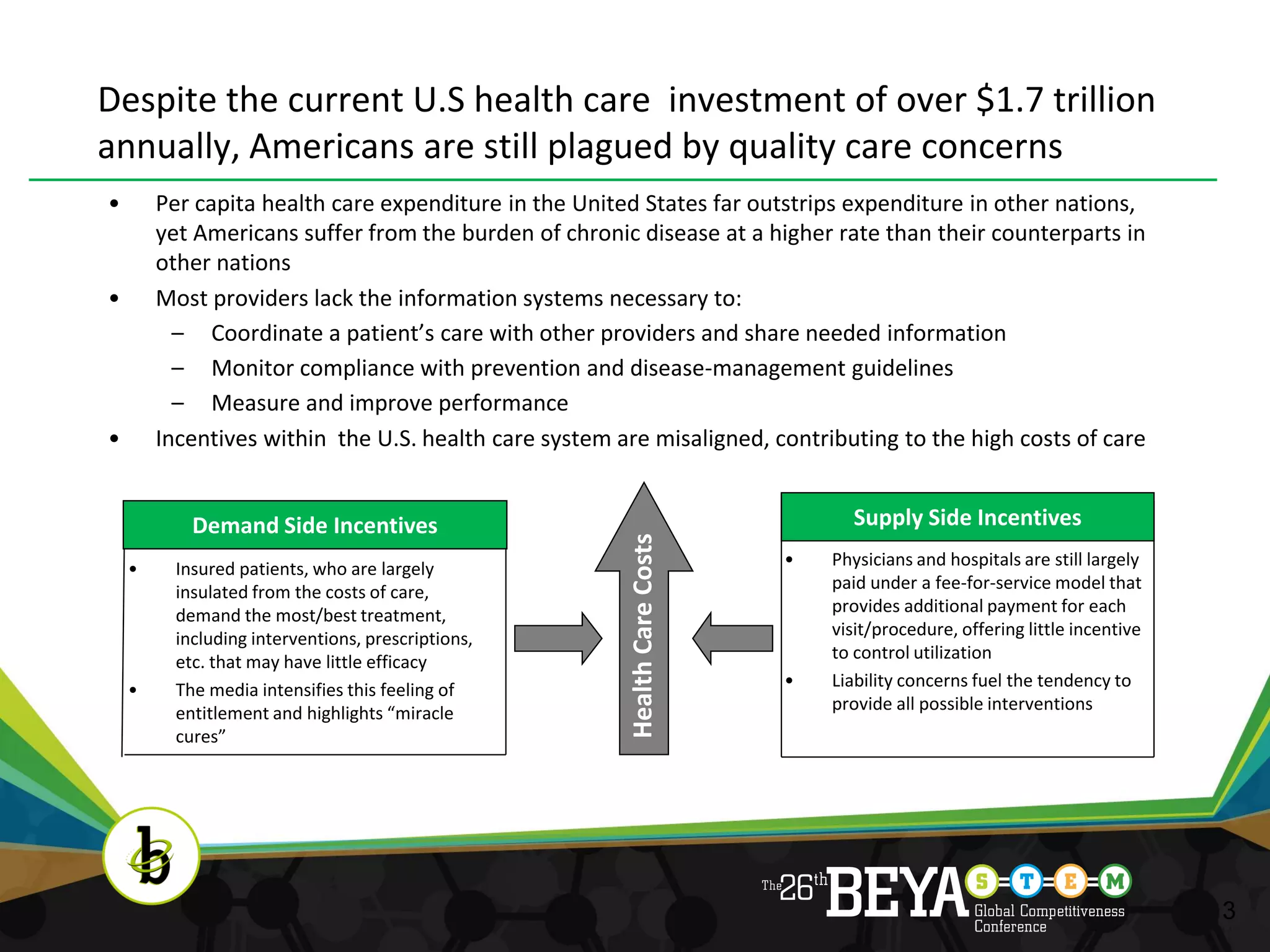
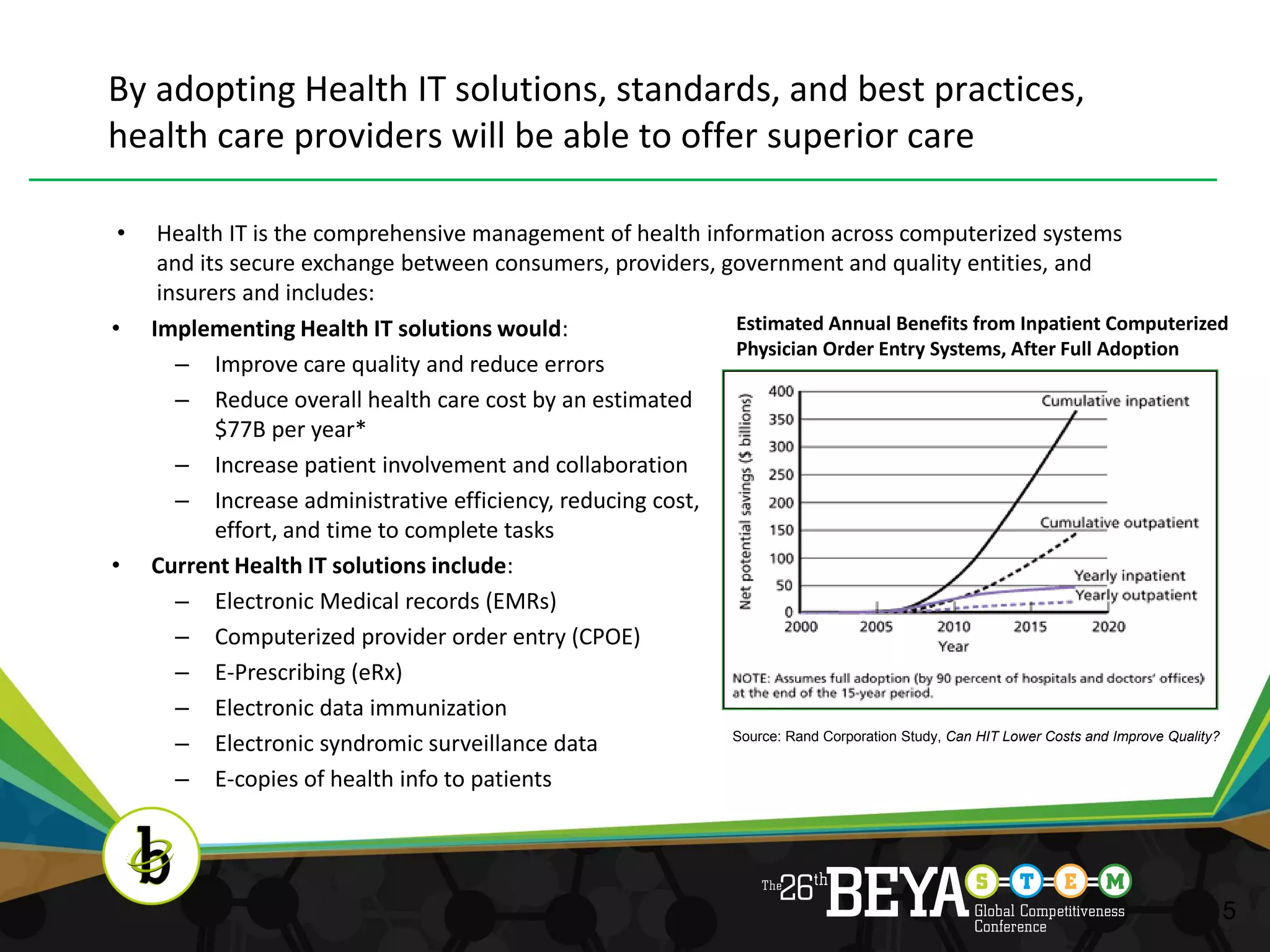
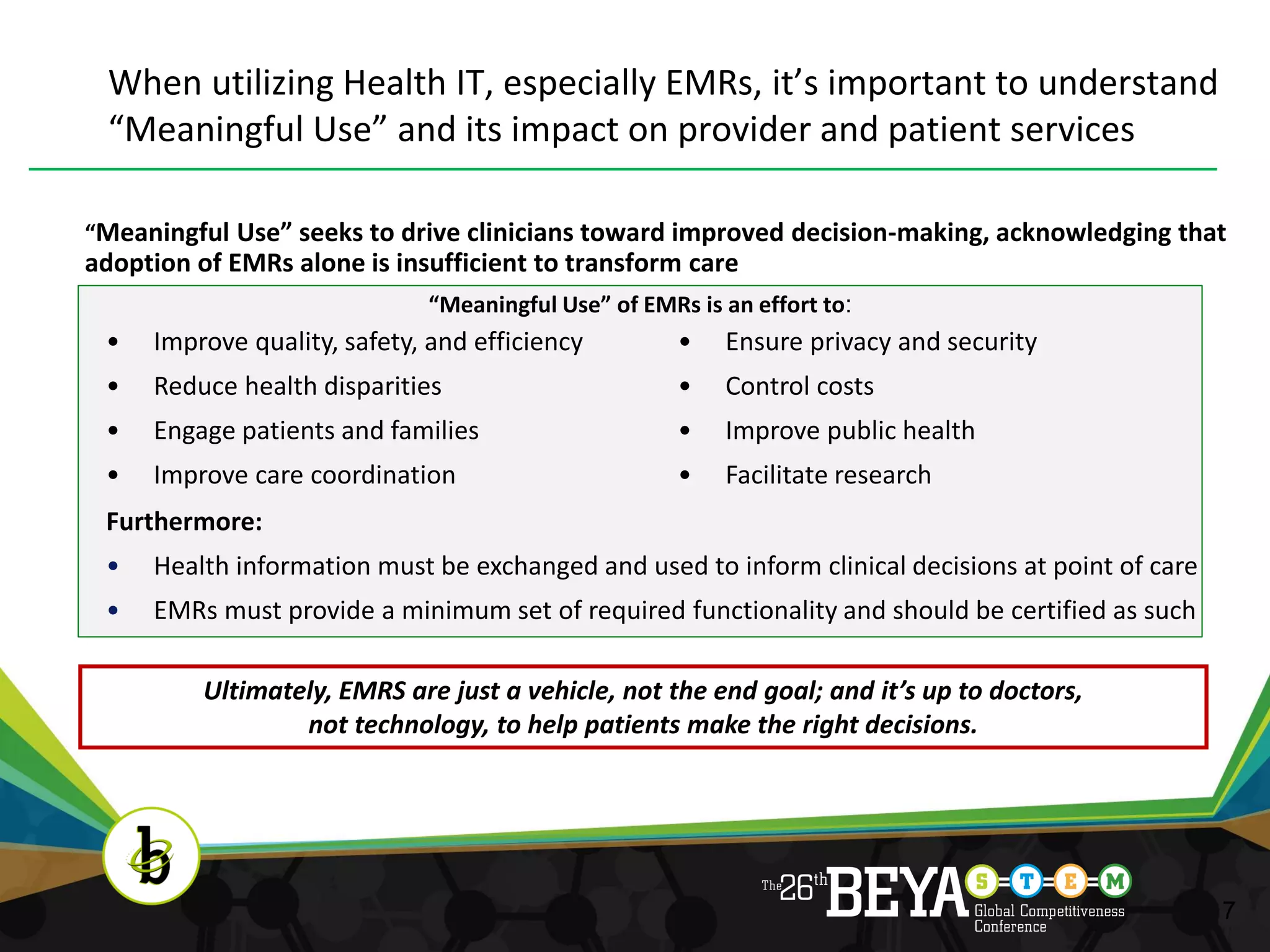
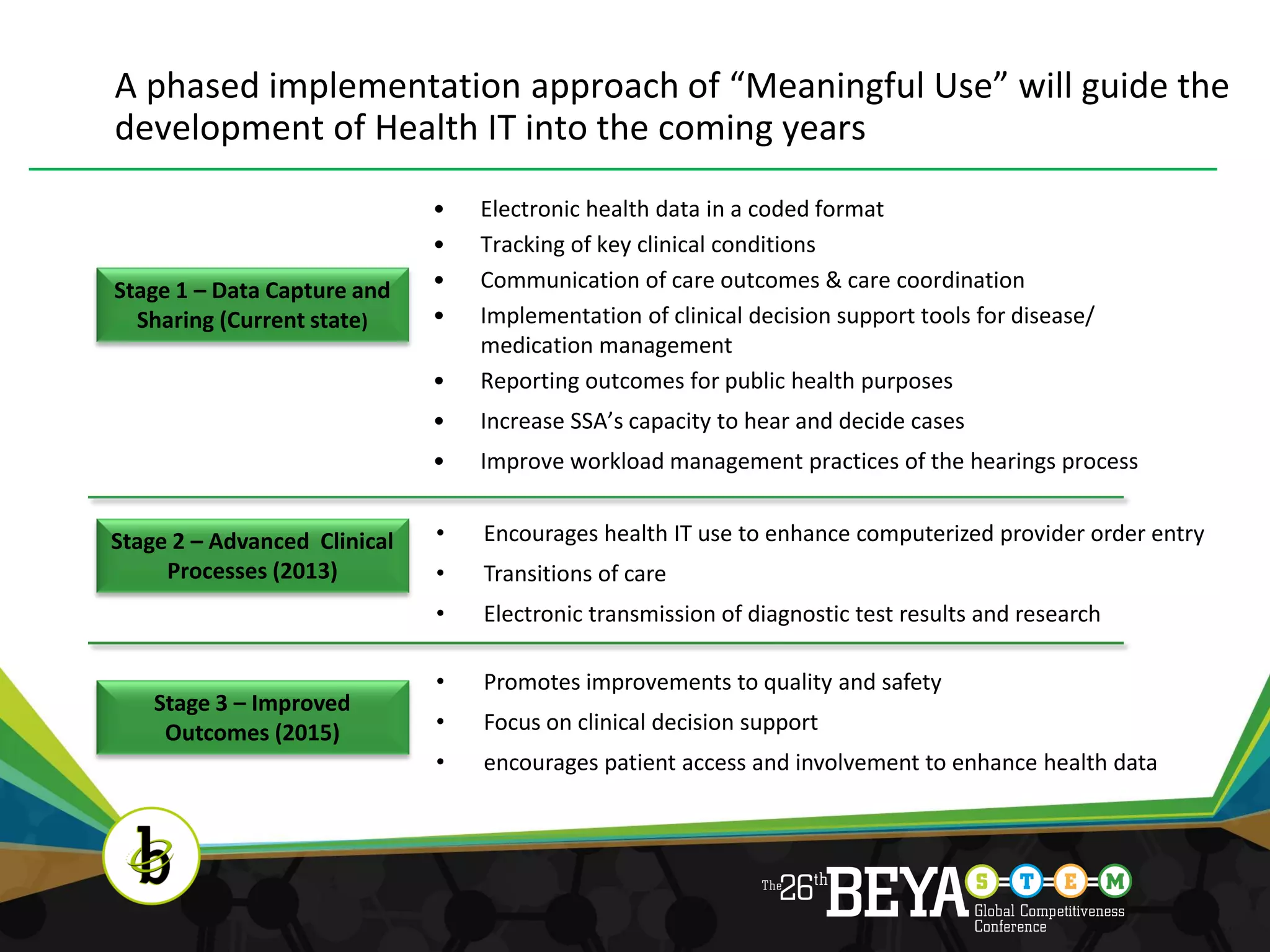
The document discusses advancements in health information technology (IT) and electronic medical records (EMRs). It notes that while the US spends over $1.7 trillion annually on healthcare, Americans still face quality issues. EMRs and health IT can help by improving care coordination, monitoring guidelines, and measuring performance. The document outlines recent legislation promoting health IT adoption and the benefits of EMRs, such as reduced costs and errors. It explains what EMRs are and their role in supplementing technologies like e-prescribing. Finally, it discusses the concept of "meaningful use" to ensure EMRs improve care, safety, efficiency and engage patients rather than just being adopted.