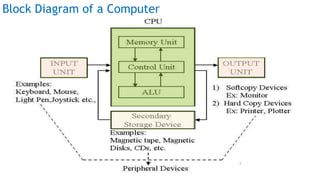
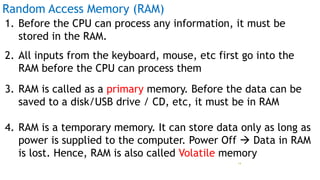
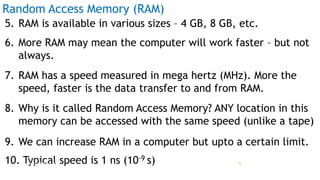
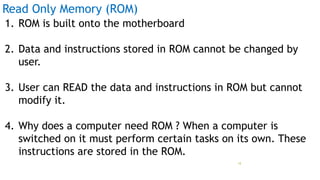
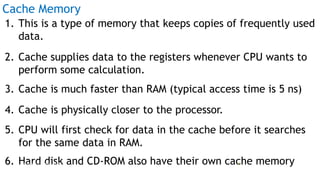
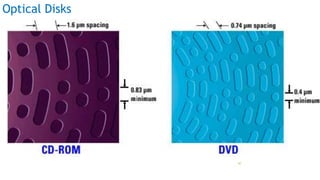
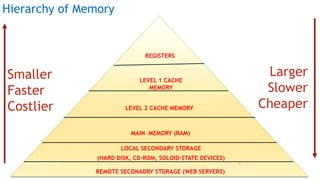
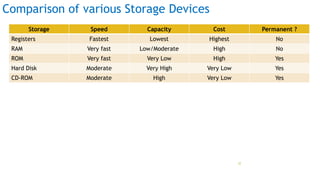
The document serves as an introduction to computer systems, covering critical components such as hardware and software, the central processing unit (CPU), memory types (RAM, ROM, and cache), and storage devices. It explains how these elements interact and highlights commonly used computer terms. The content is aimed at providing foundational knowledge of computer organization and functionality.