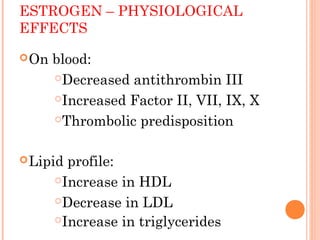
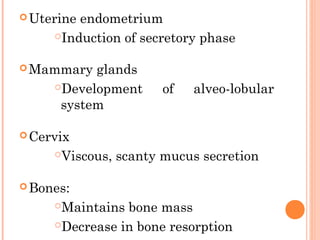
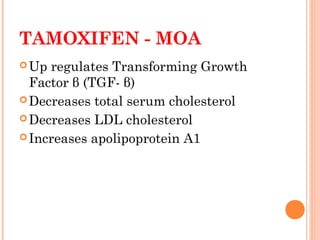
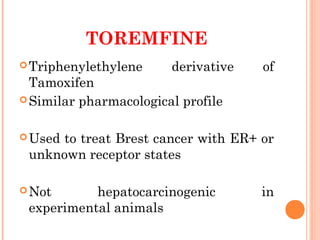
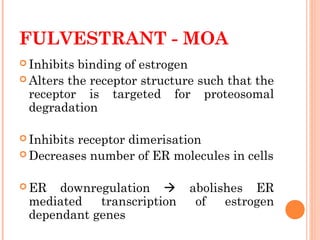
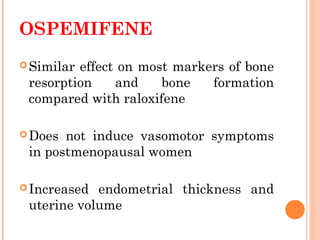
This document discusses selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) and selective estrogen receptor downregulators (SERDs), which are drugs that act as agonists or antagonists of estrogen receptors in a tissue-selective manner. It provides details on commonly used SERMs like tamoxifen, clomiphene, raloxifene, and newer drugs. It also discusses the prototype SERD fulvestrant and its mechanism of downregulating estrogen receptors. The document summarizes the pharmacological properties, mechanisms of action, uses and side effects of these estrogen-modulating drugs.