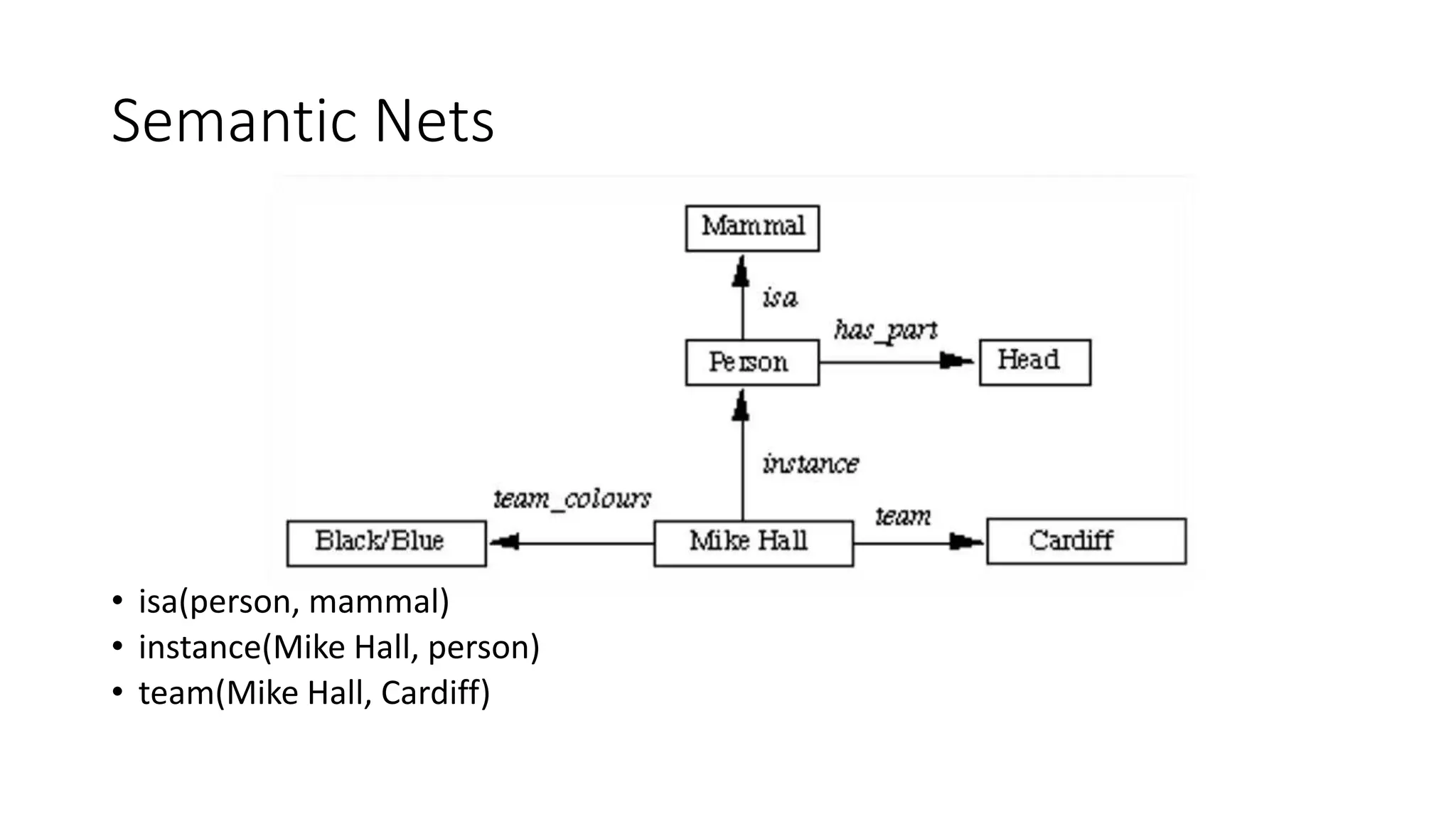
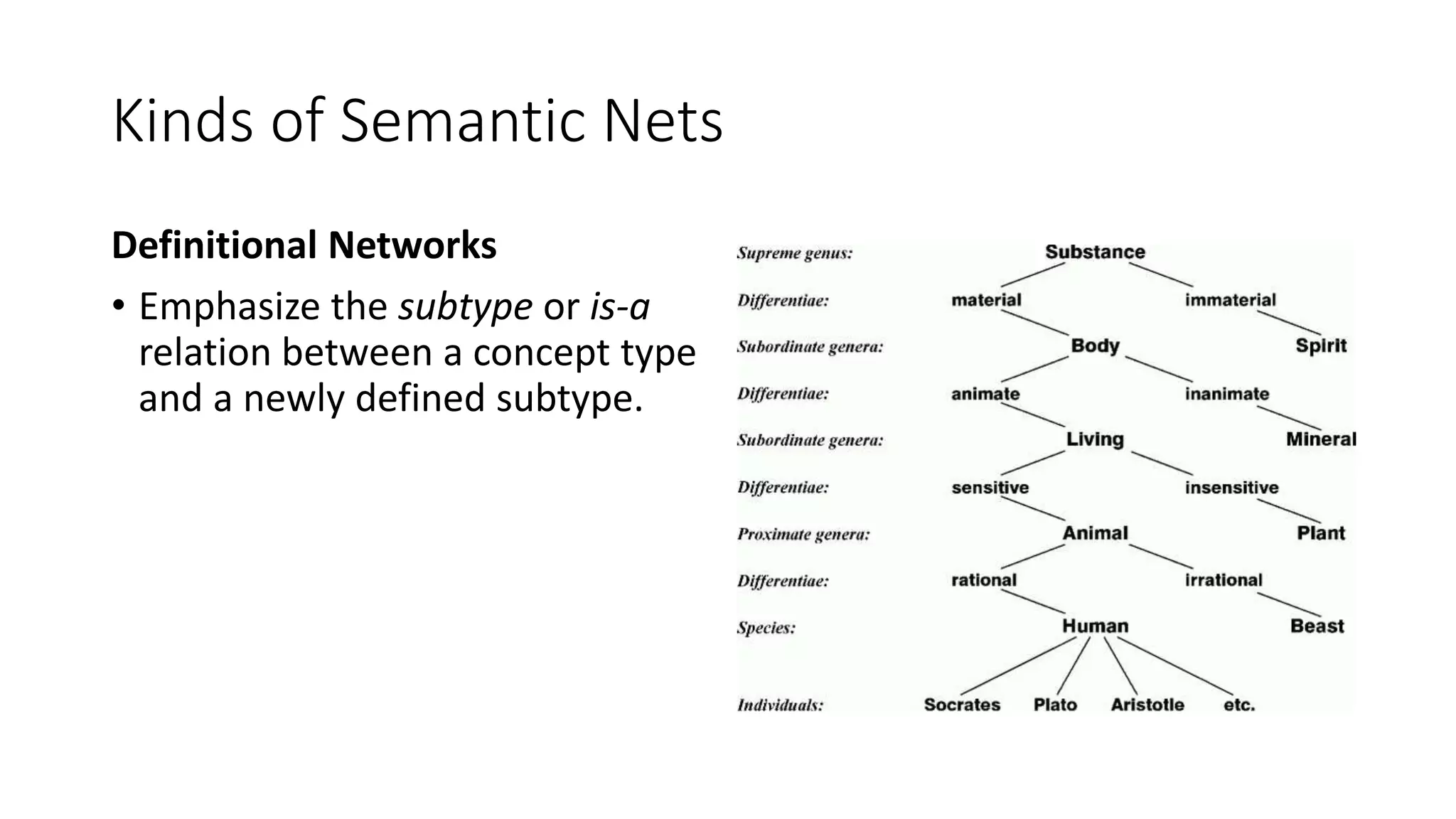
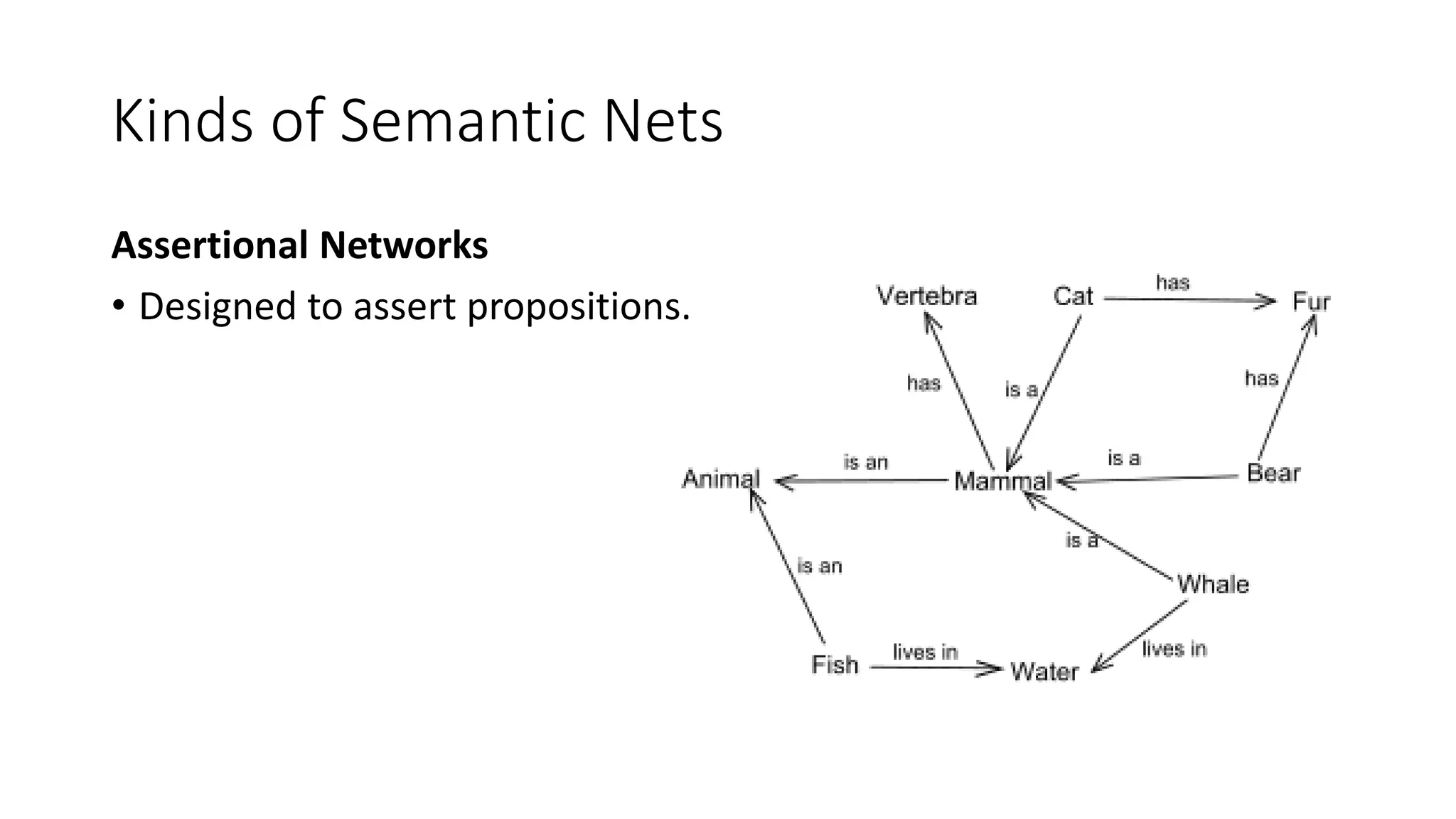
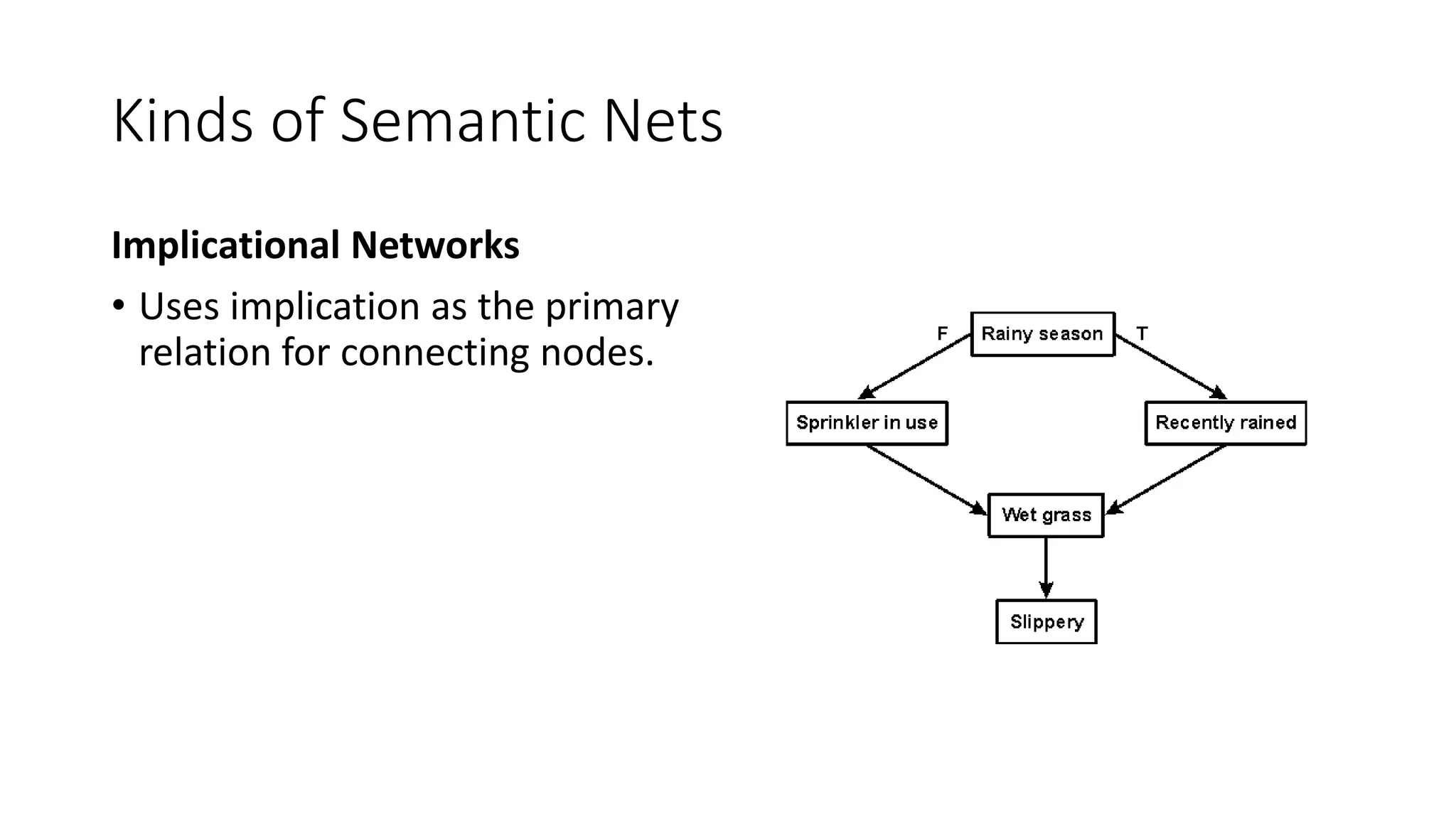
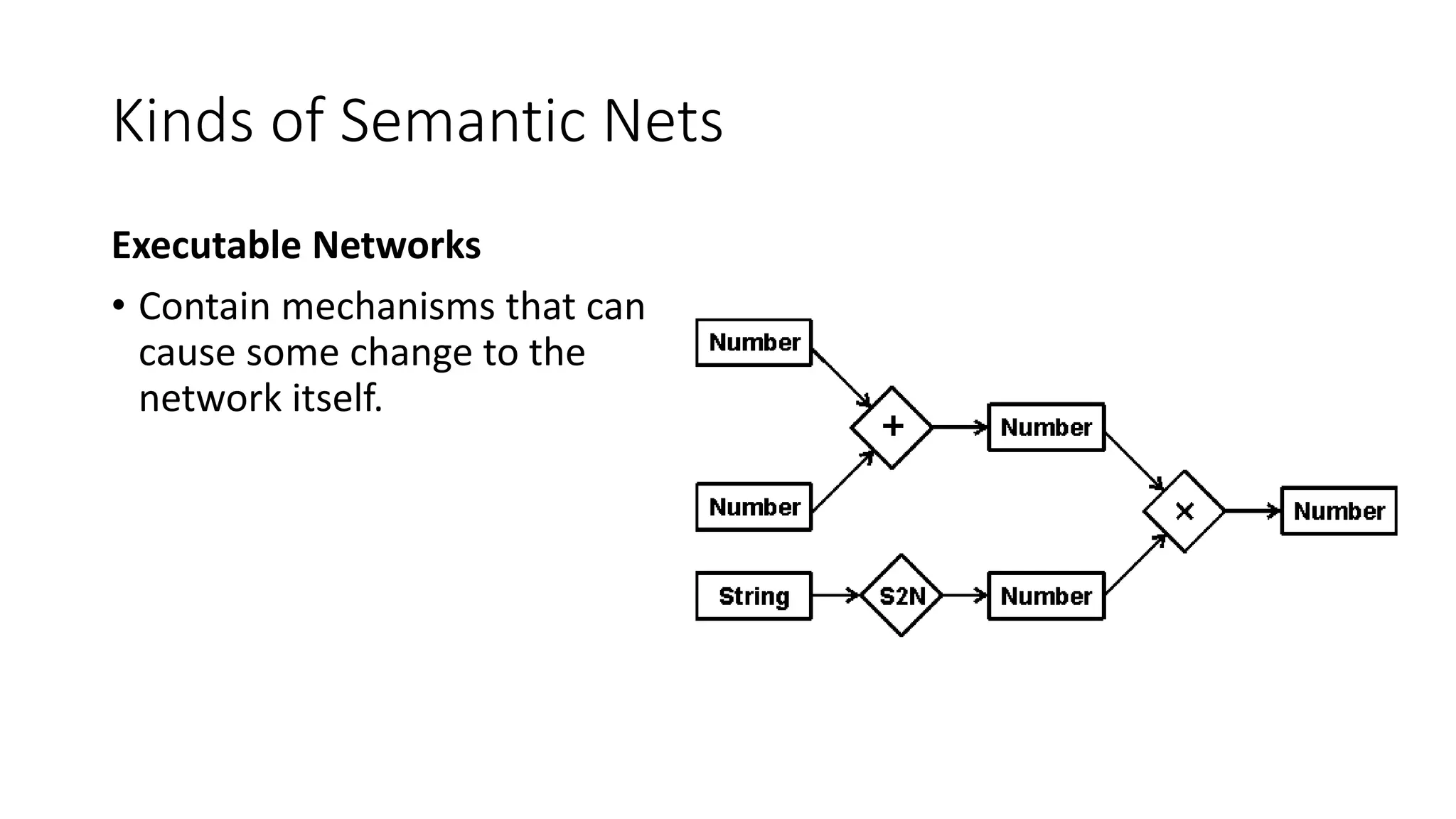
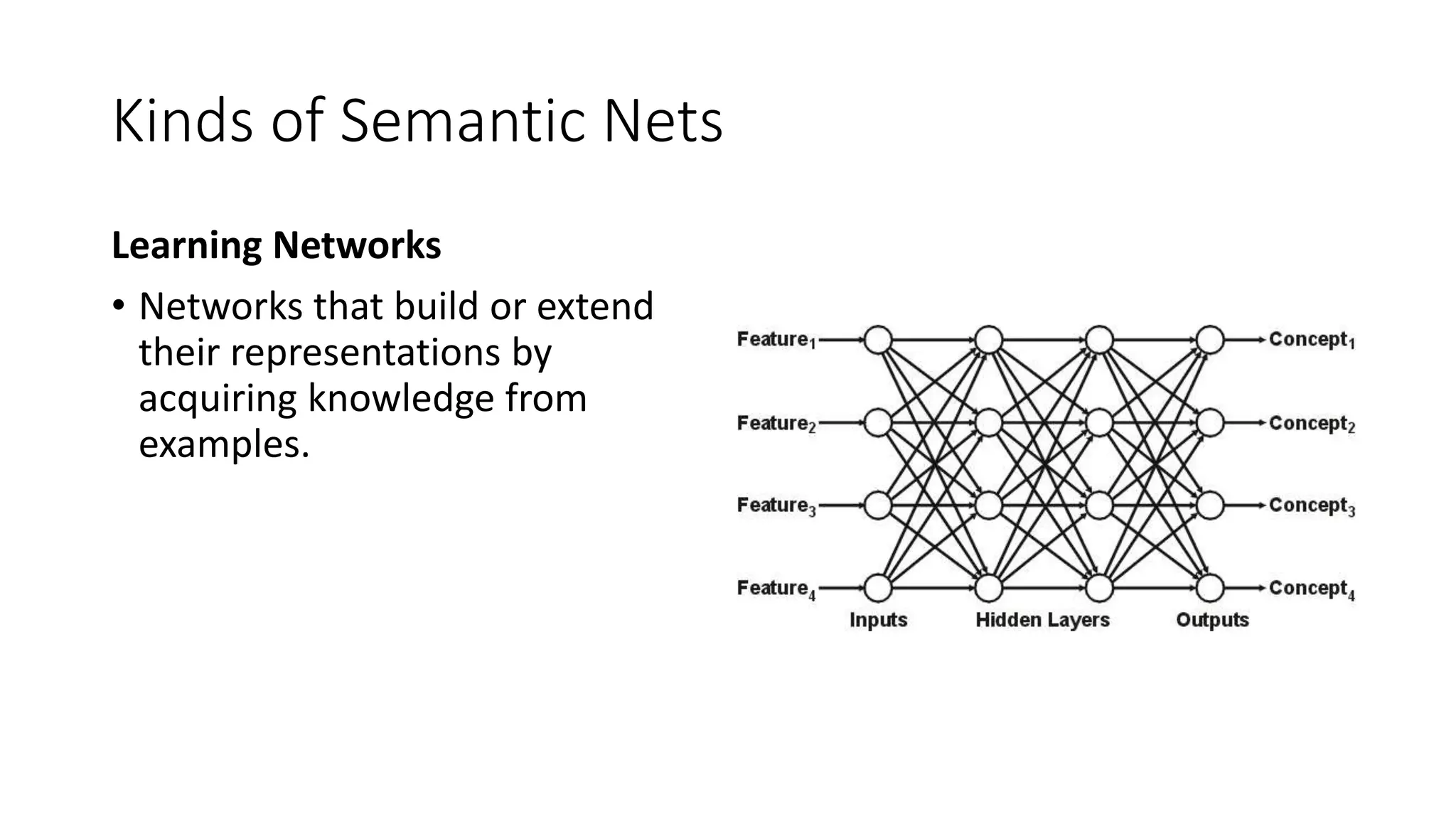
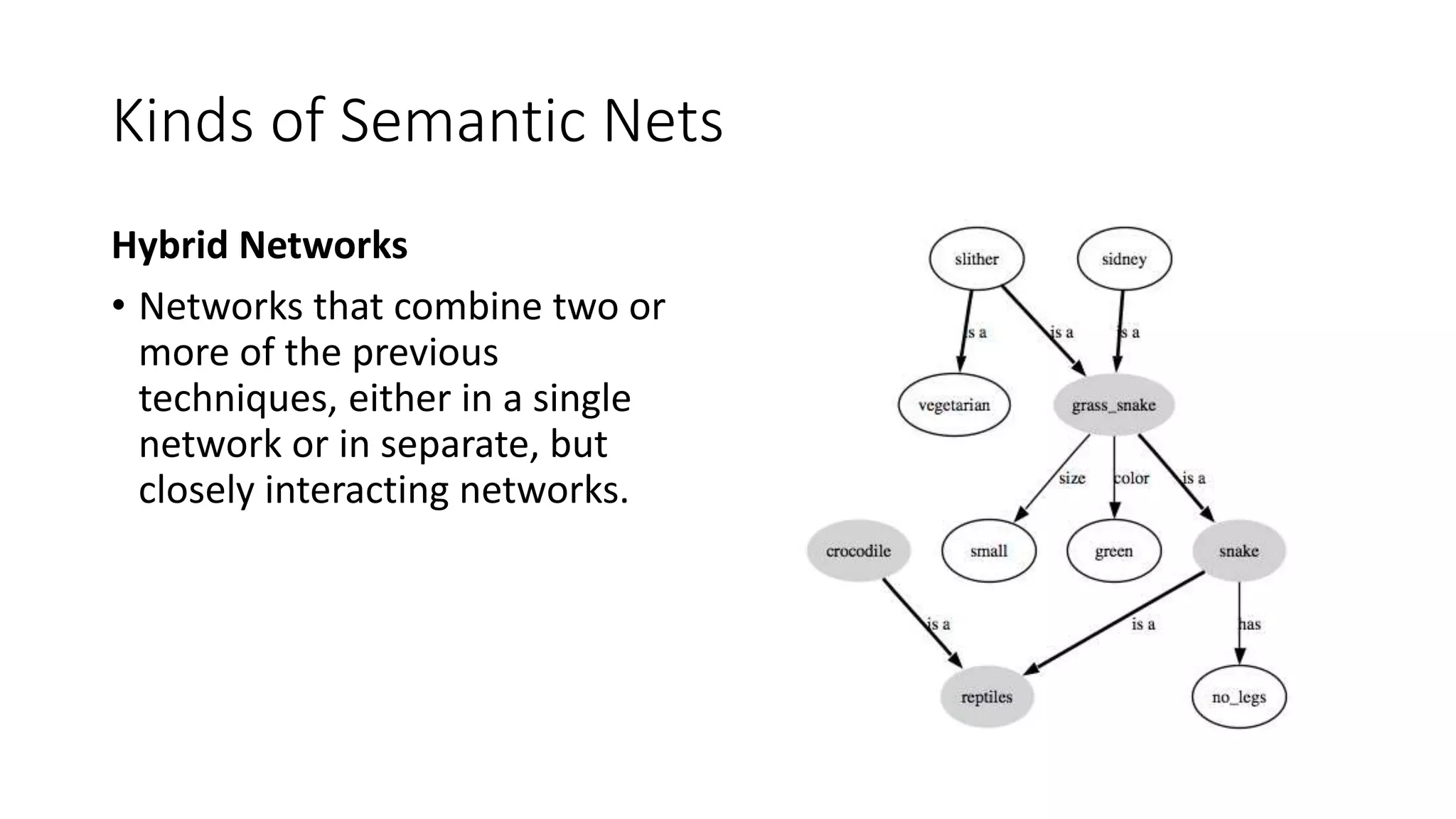
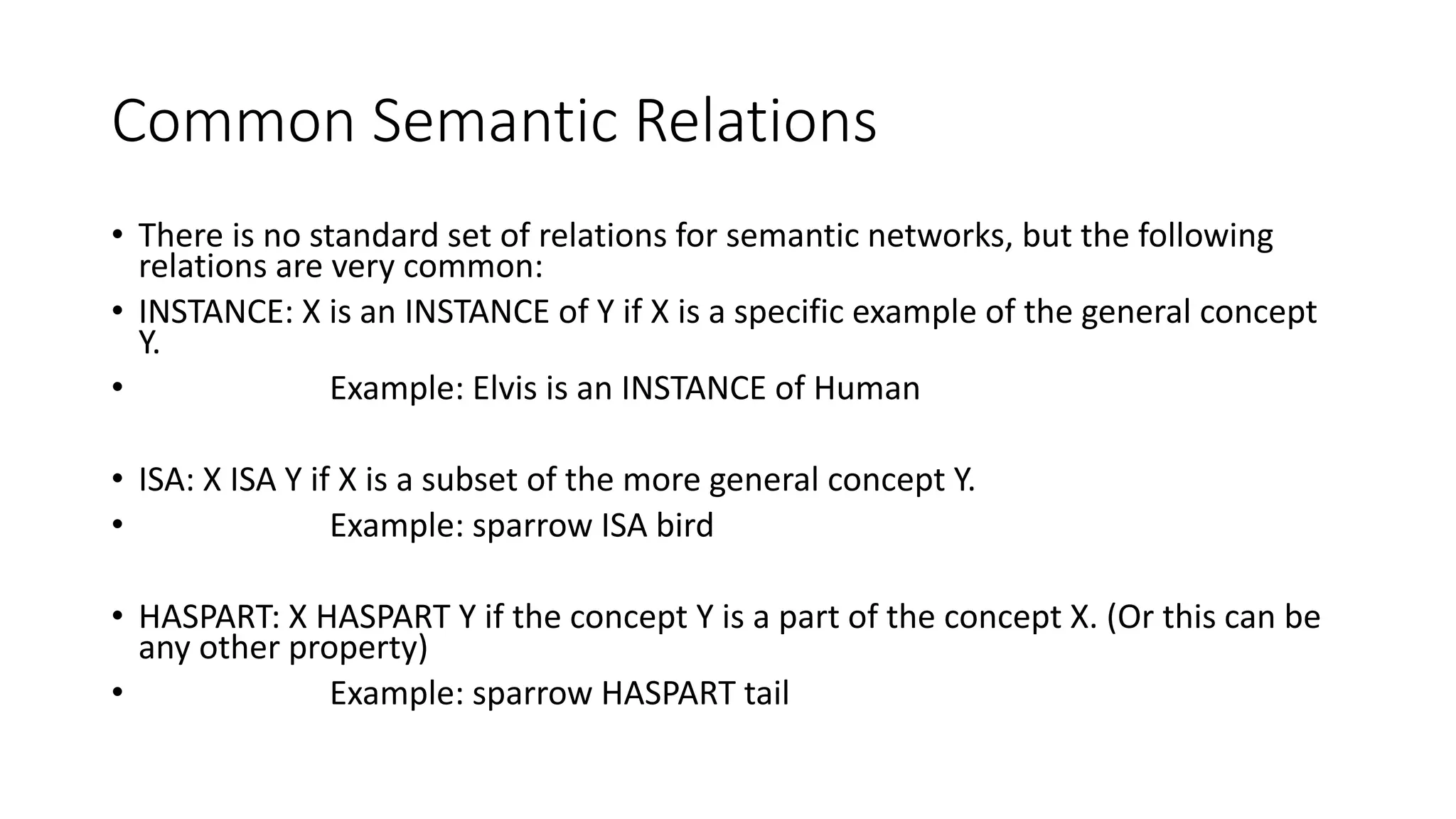
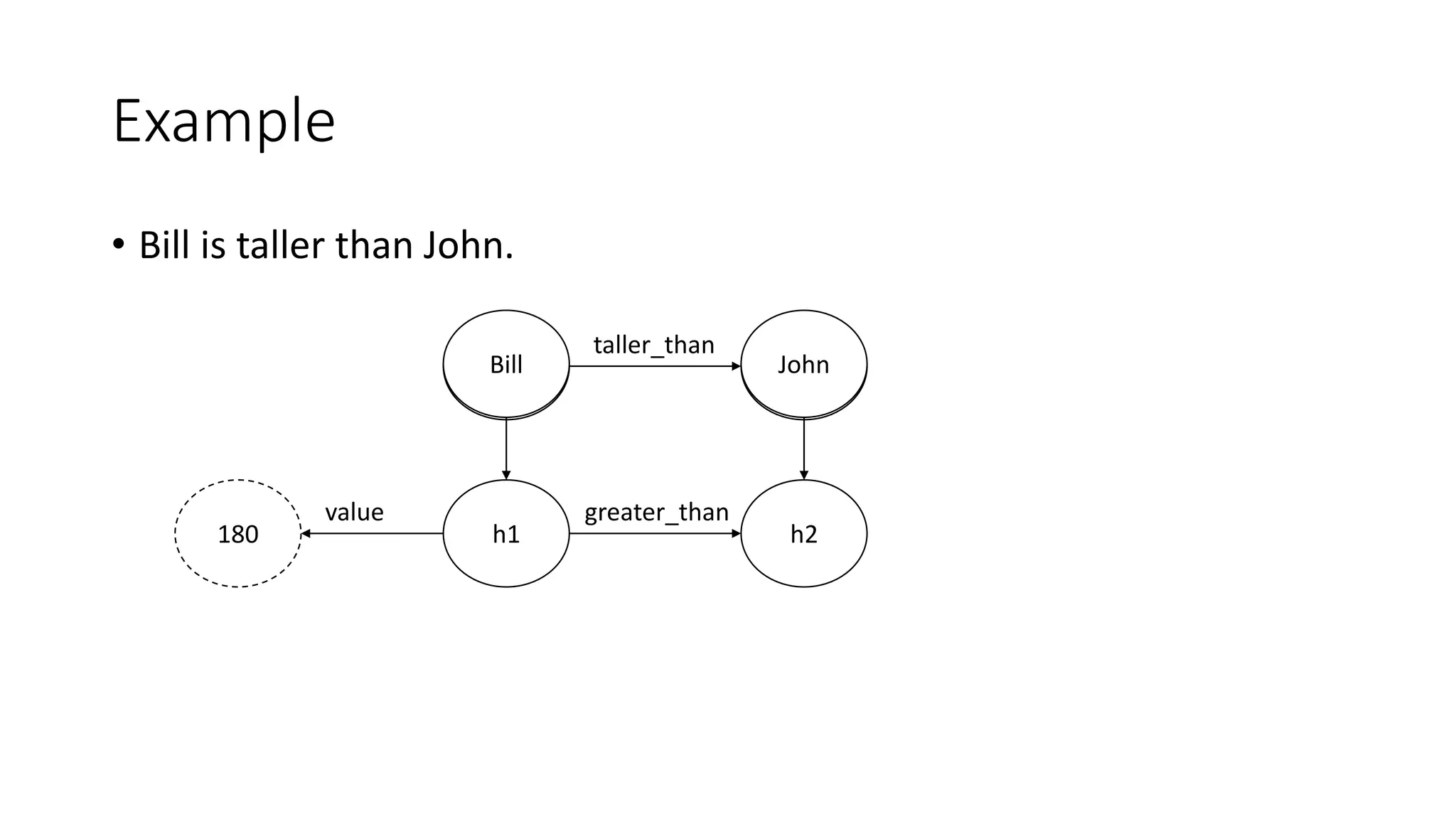
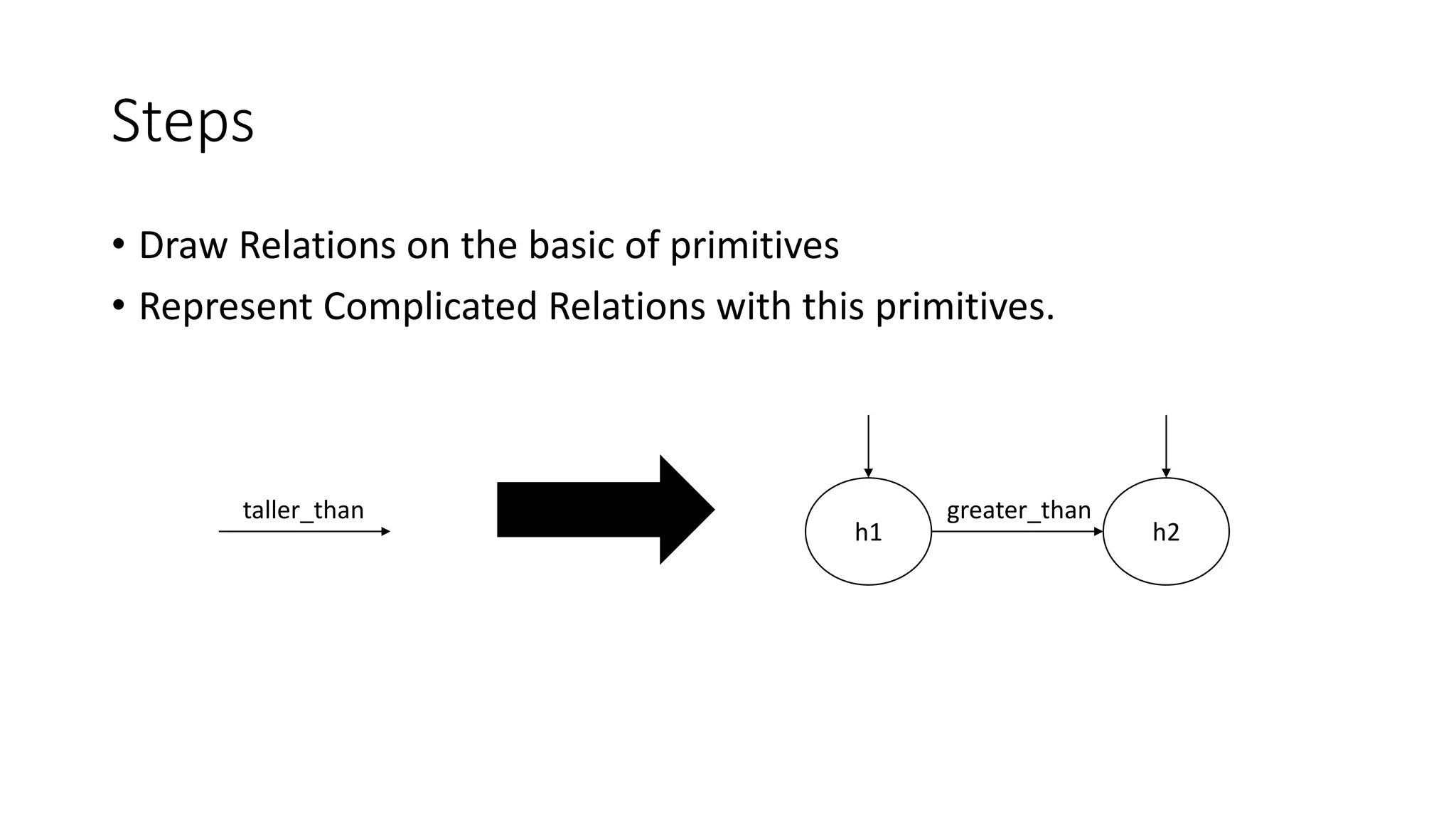
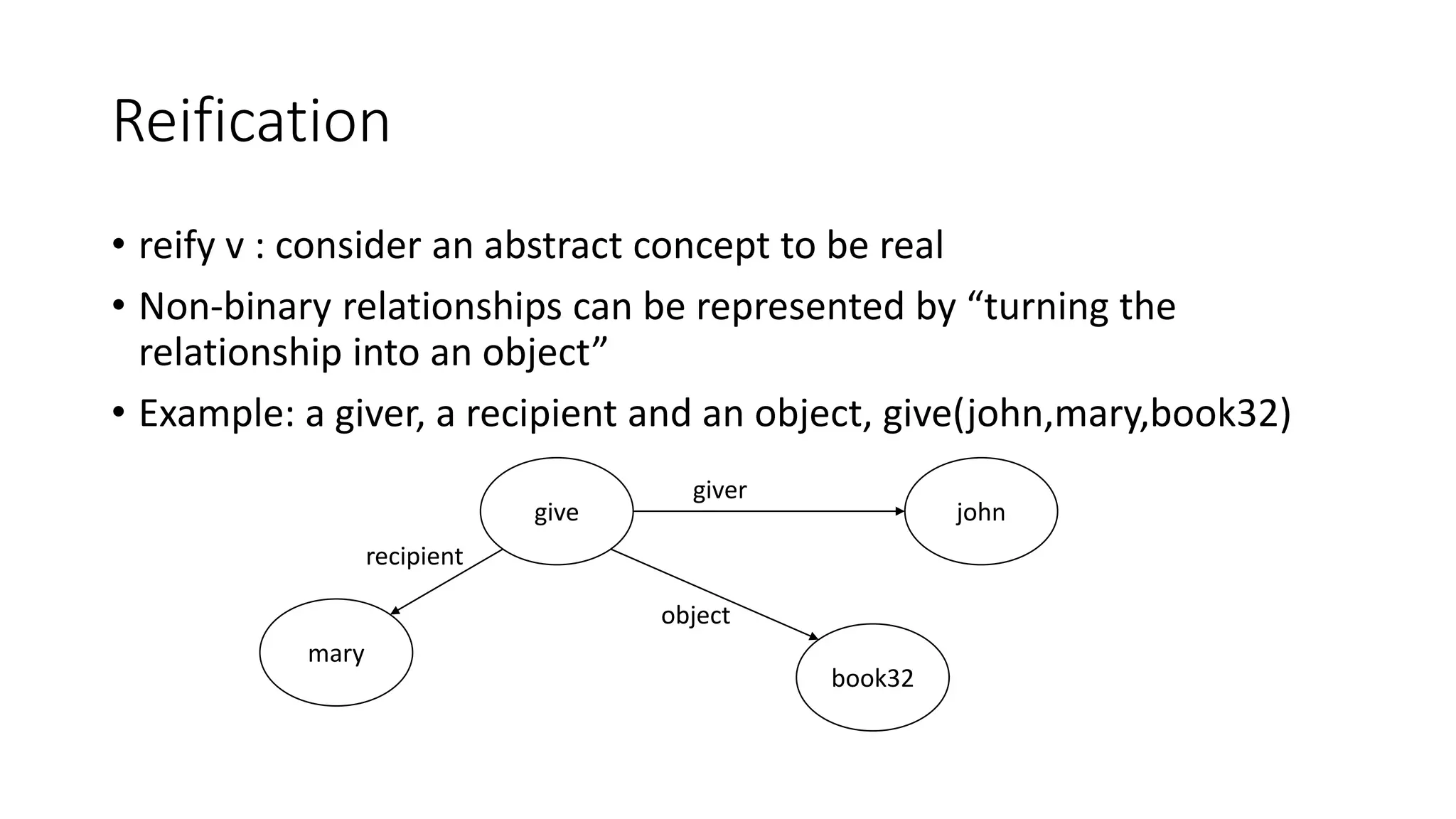
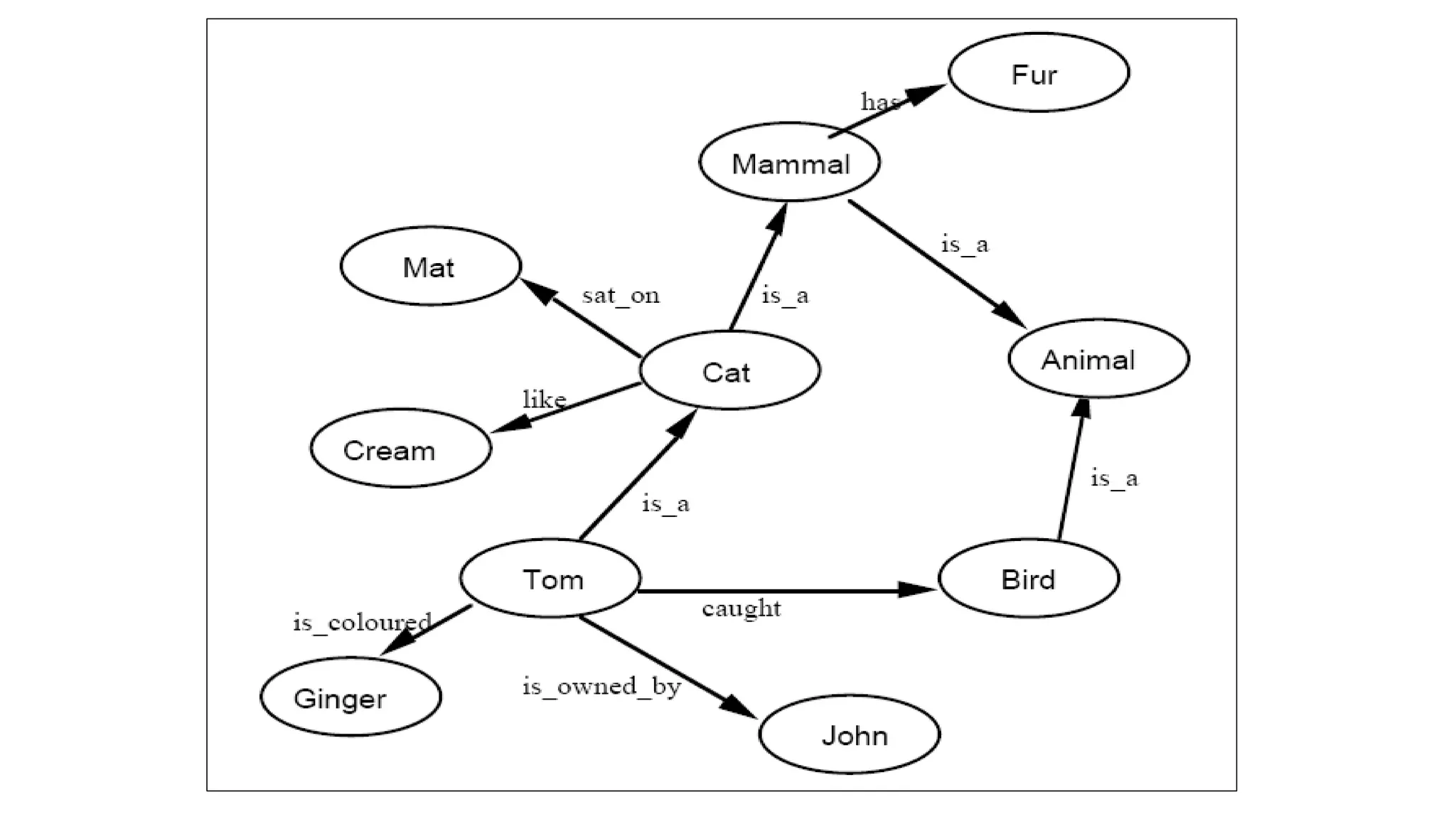
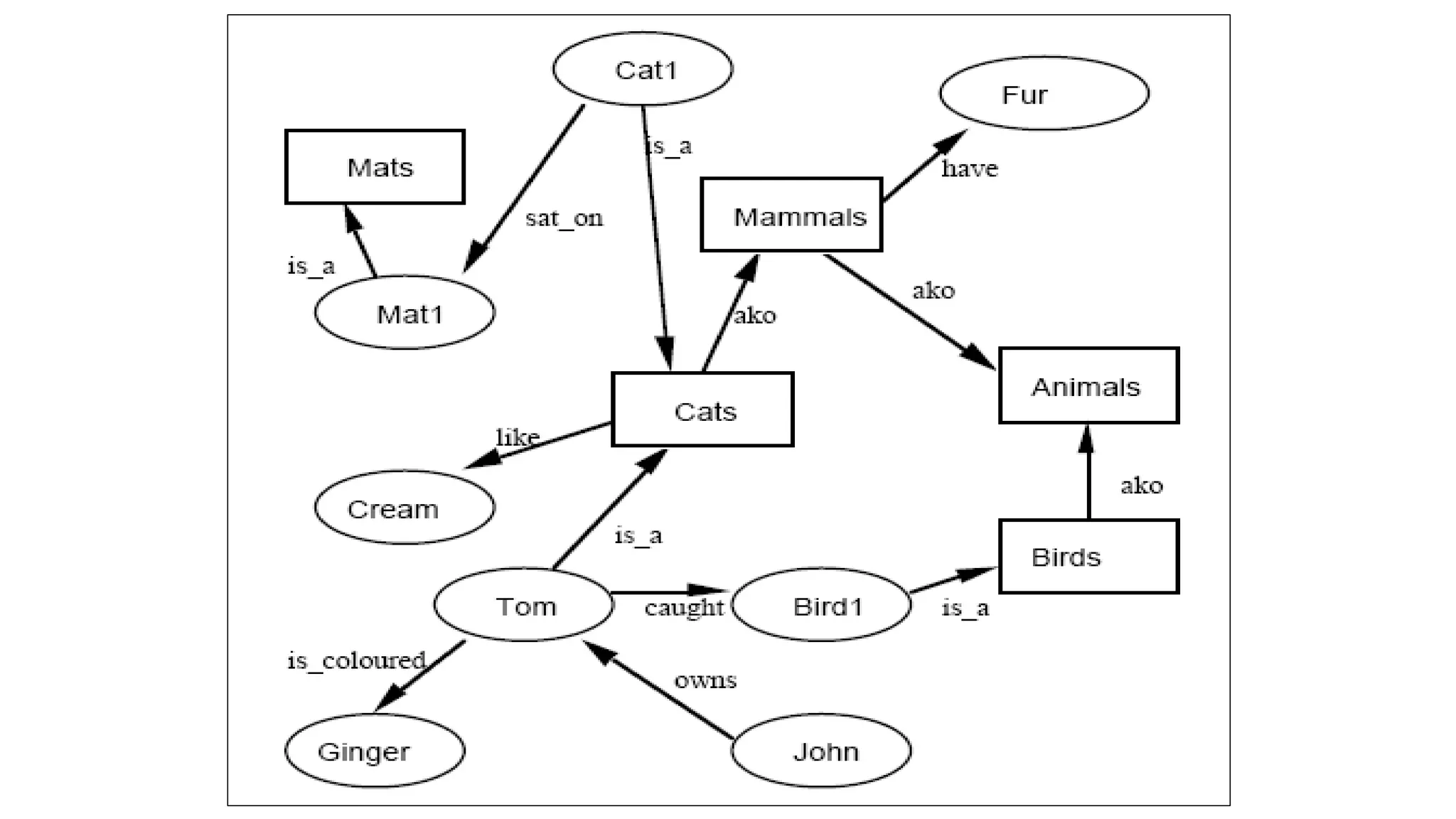
Semantic networks are a knowledge representation technique where concepts are represented as nodes in a graph, and relationships between concepts are represented as links between nodes. There are different types of semantic networks, including definitional networks that emphasize subclass relationships, assertional networks for making propositions, and executable networks that can change based on operations. Common semantic relations include IS-A for subclasses, INSTANCE for examples, and HAS-PART for components. While semantic networks provide a natural representation of relationships, they have disadvantages like lack of standard link names and difficulty representing some logical constructs.