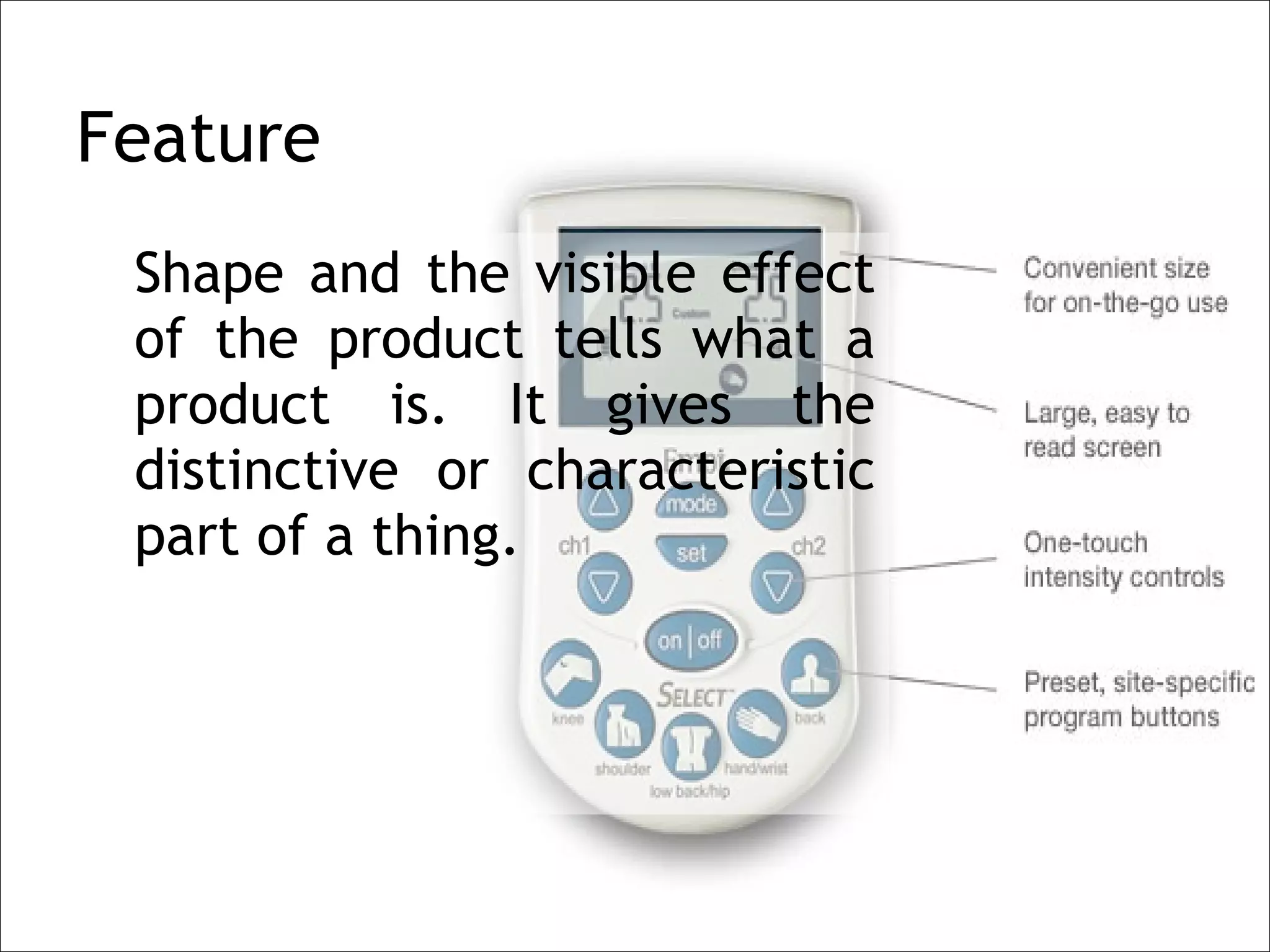
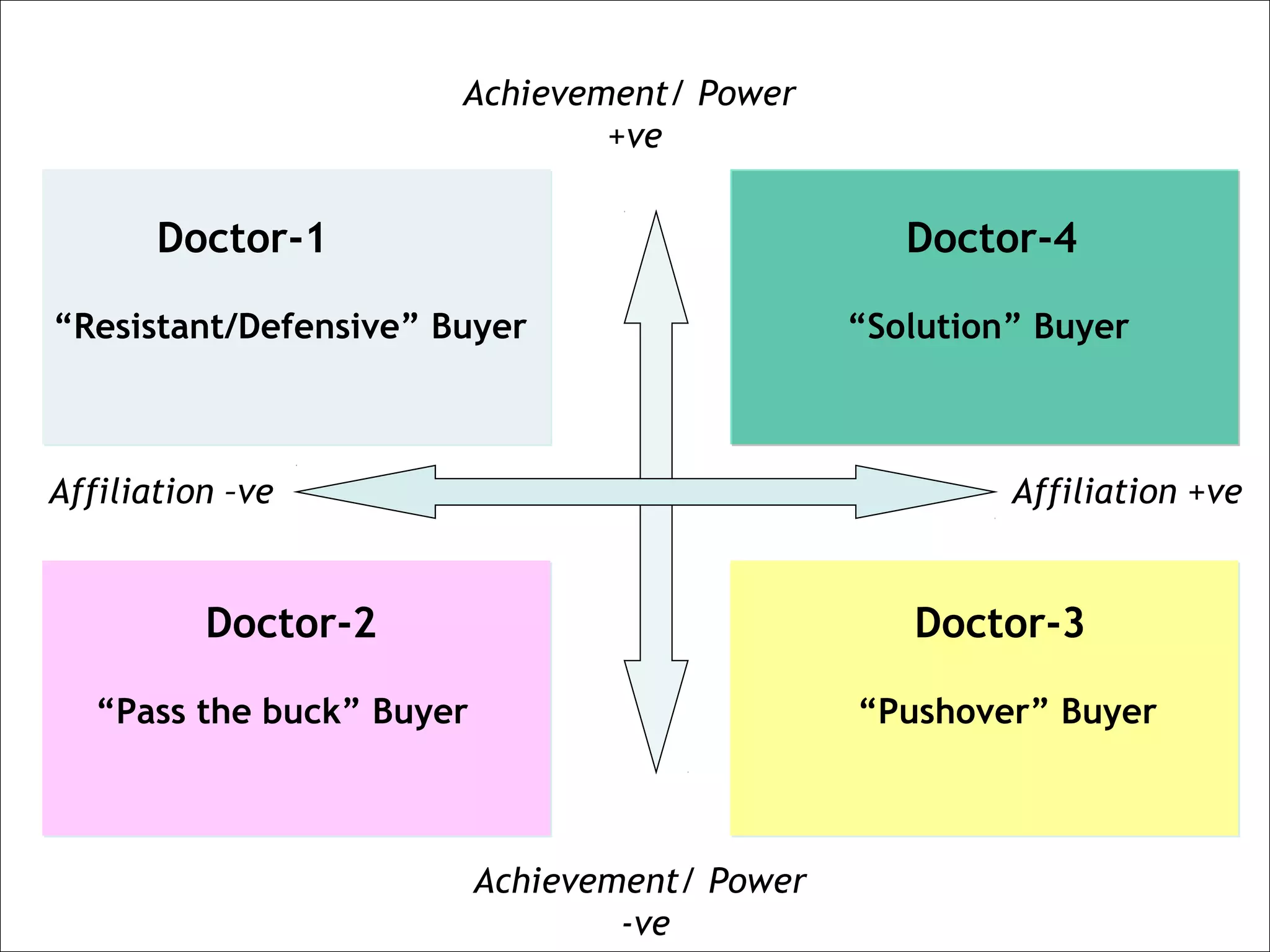
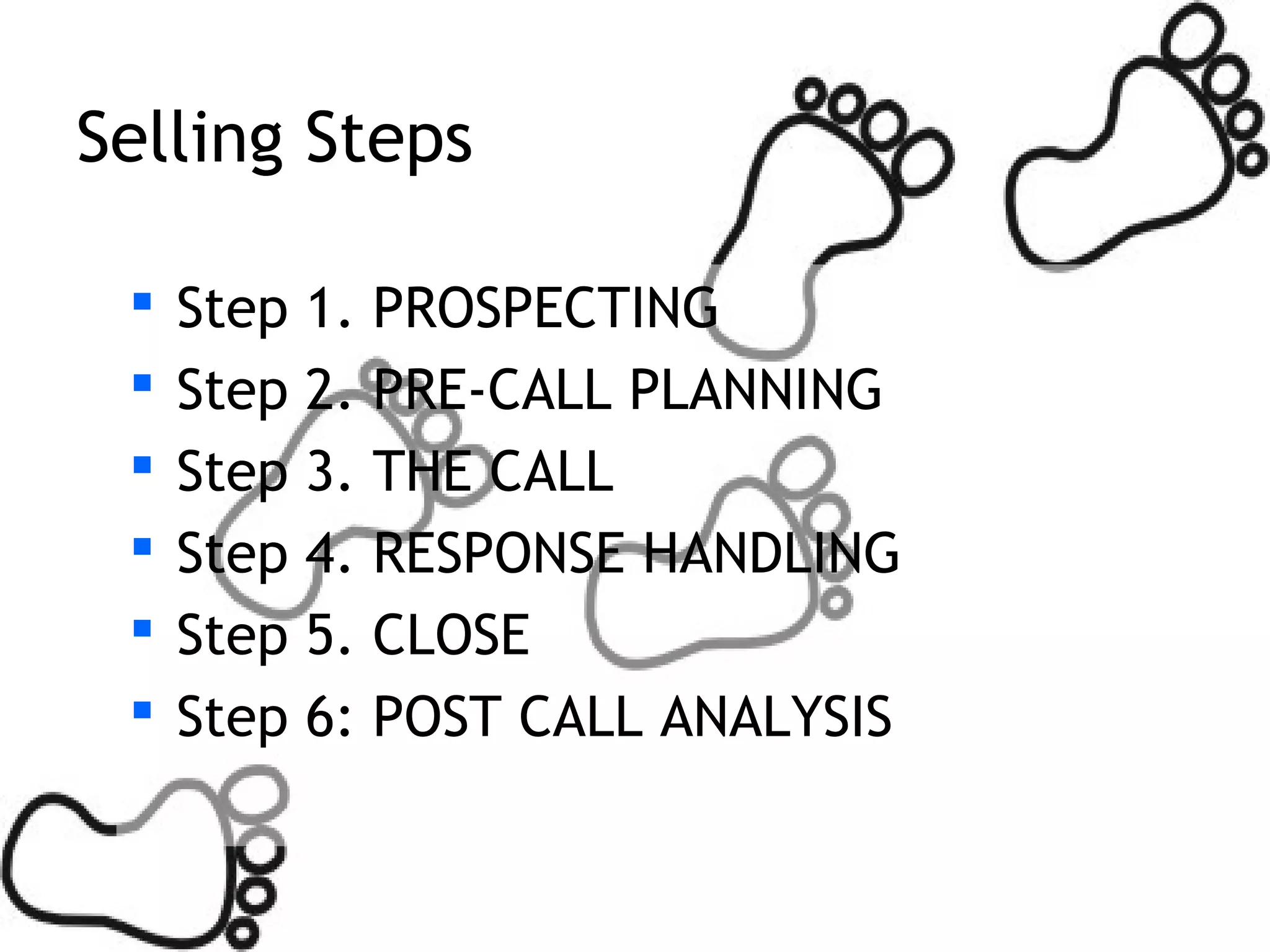
The document provides guidance on developing selling skills for pharmaceutical sales representatives. It outlines the selling procedure in 6 steps: 1) prospecting, 2) pre-call planning, 3) the call, 4) response handling, 5) closing, and 6) post-call analysis. Key aspects covered include identifying customer needs, presenting product benefits to satisfy needs, dealing with potential objections, and getting commitments. The overall approach is to gradually develop prescription potential with doctors through repeated calls over the long term.