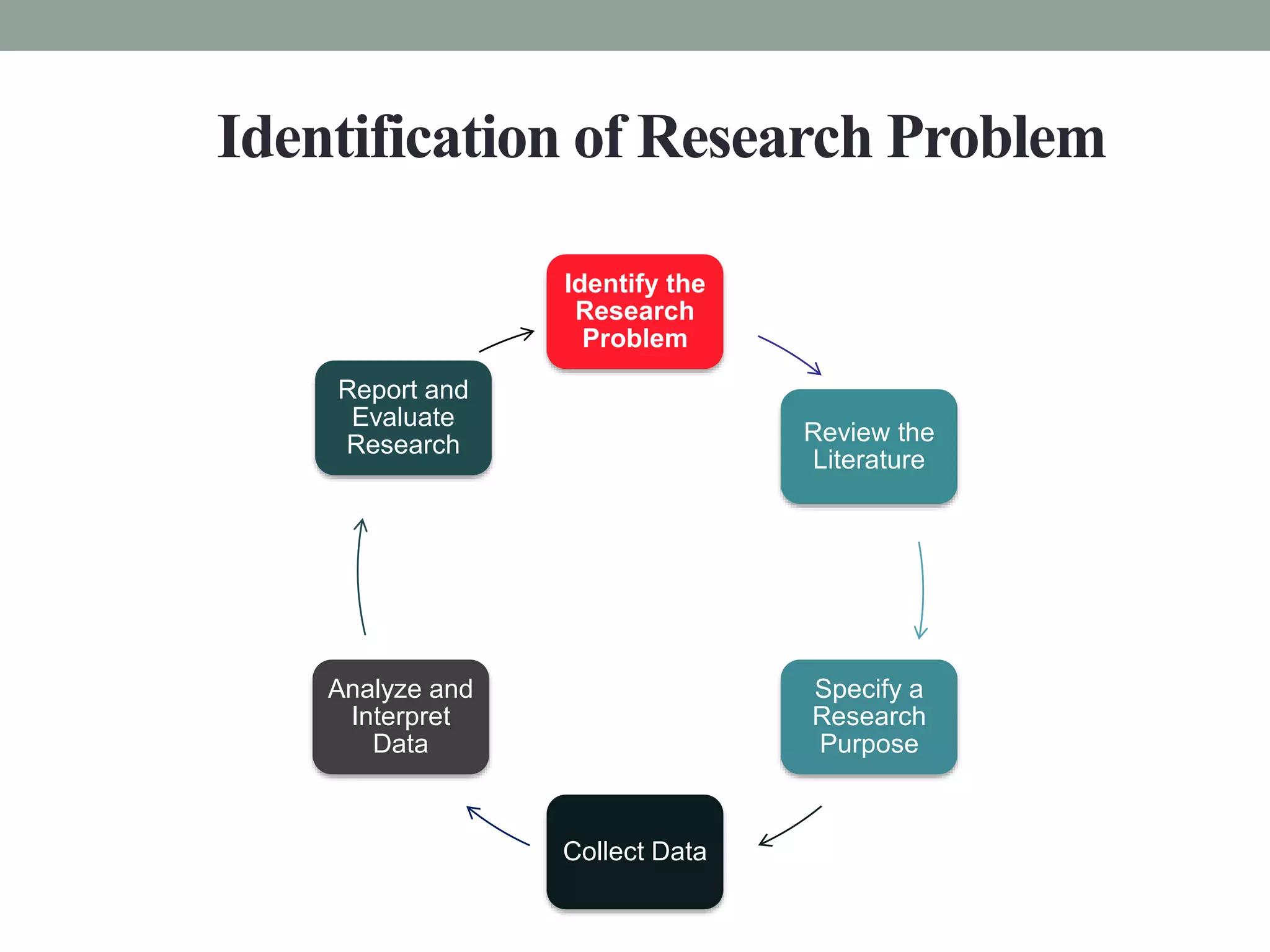
This document discusses selecting and defining a research problem. It explains that a research problem needs to be clearly defined and operationalized using measurable variables. The selection process involves evaluating potential problems based on criteria like the researcher's background and available resources. Problems should be novel, solve a current issue, and allow further research. The document provides guidance on refining broad topics into narrow, specific research problems suitable for different research methods like historical, descriptive or experimental studies.