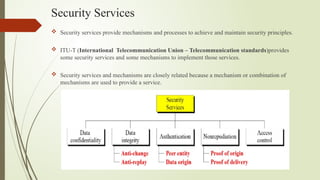
The document discusses the definition and significance of security, emphasizing the importance of confidentiality, integrity, and availability in protecting systems and data. It outlines standard measures to establish these principles, including encryption, 2FA, and data backups, while providing examples of their application. Additionally, it describes security services aimed at achieving these principles, such as authentication, access control, and non-repudiation.