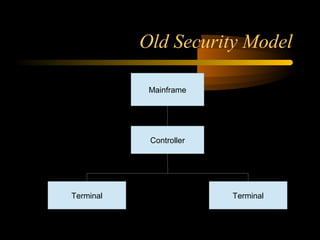
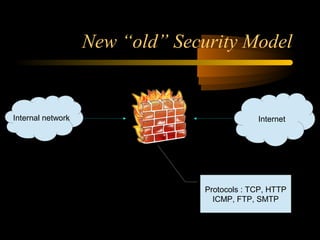
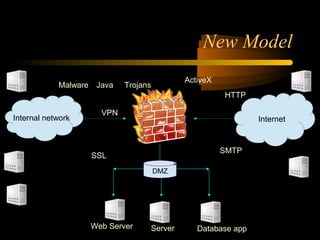
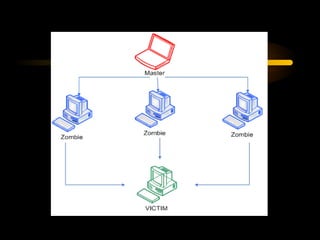
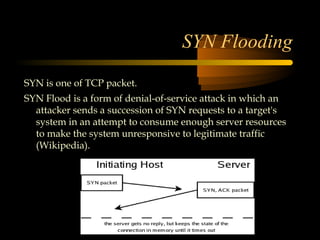
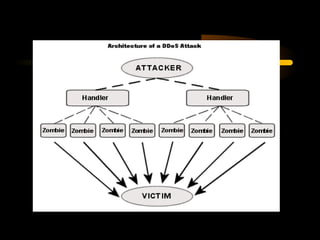
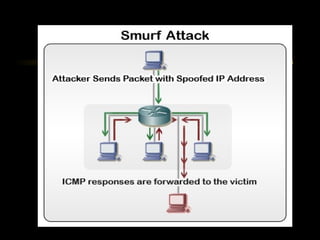
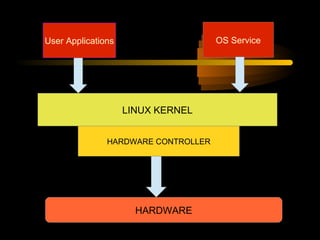
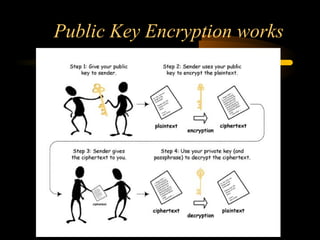
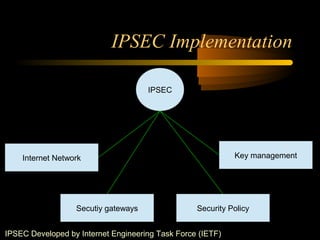
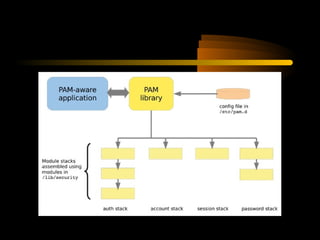
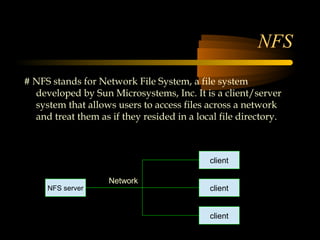
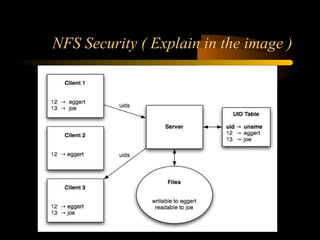
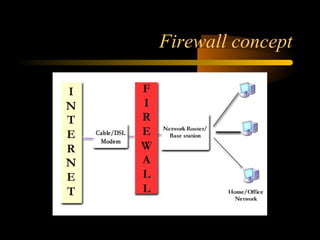
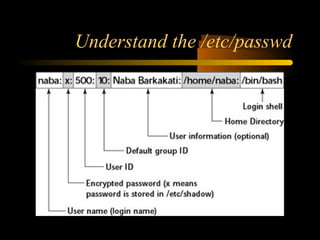
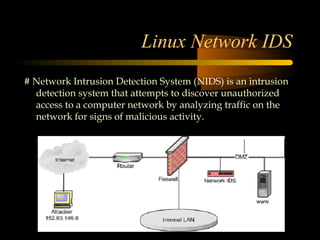
The document summarizes a presentation on network security and Linux security. The presentation covered introduction to security, computer security, and network security. It discussed why security is needed, who is vulnerable, common security attacks like dictionary attacks, denial of service attacks, TCP attacks, and packet sniffing. It also covered Linux security topics like securing the Linux kernel, file and filesystem permissions, password security, and network security using firewalls, IPSEC, and intrusion detection systems. The presentation concluded with a reference to an ID-CERT cybercrime report and a call for questions.