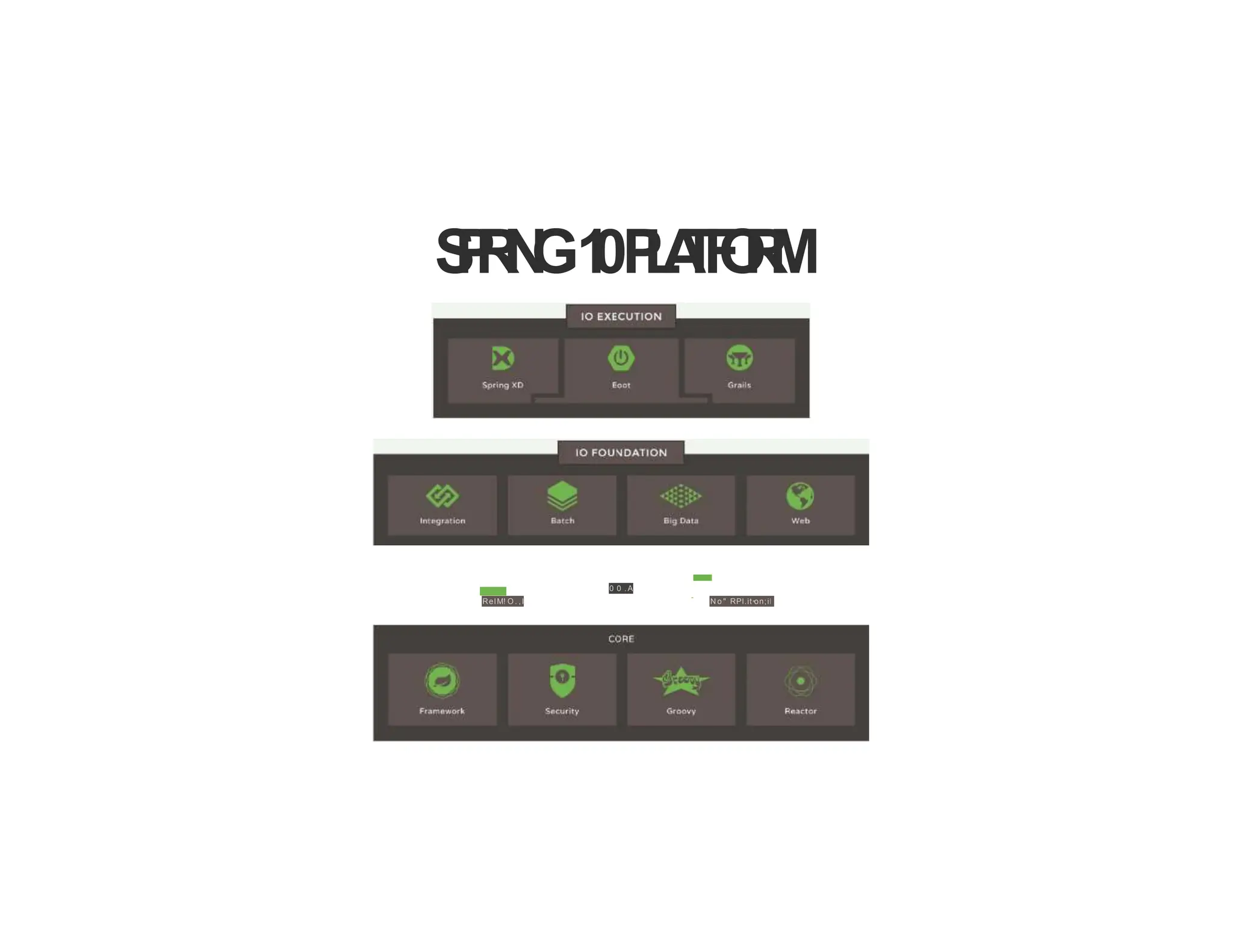
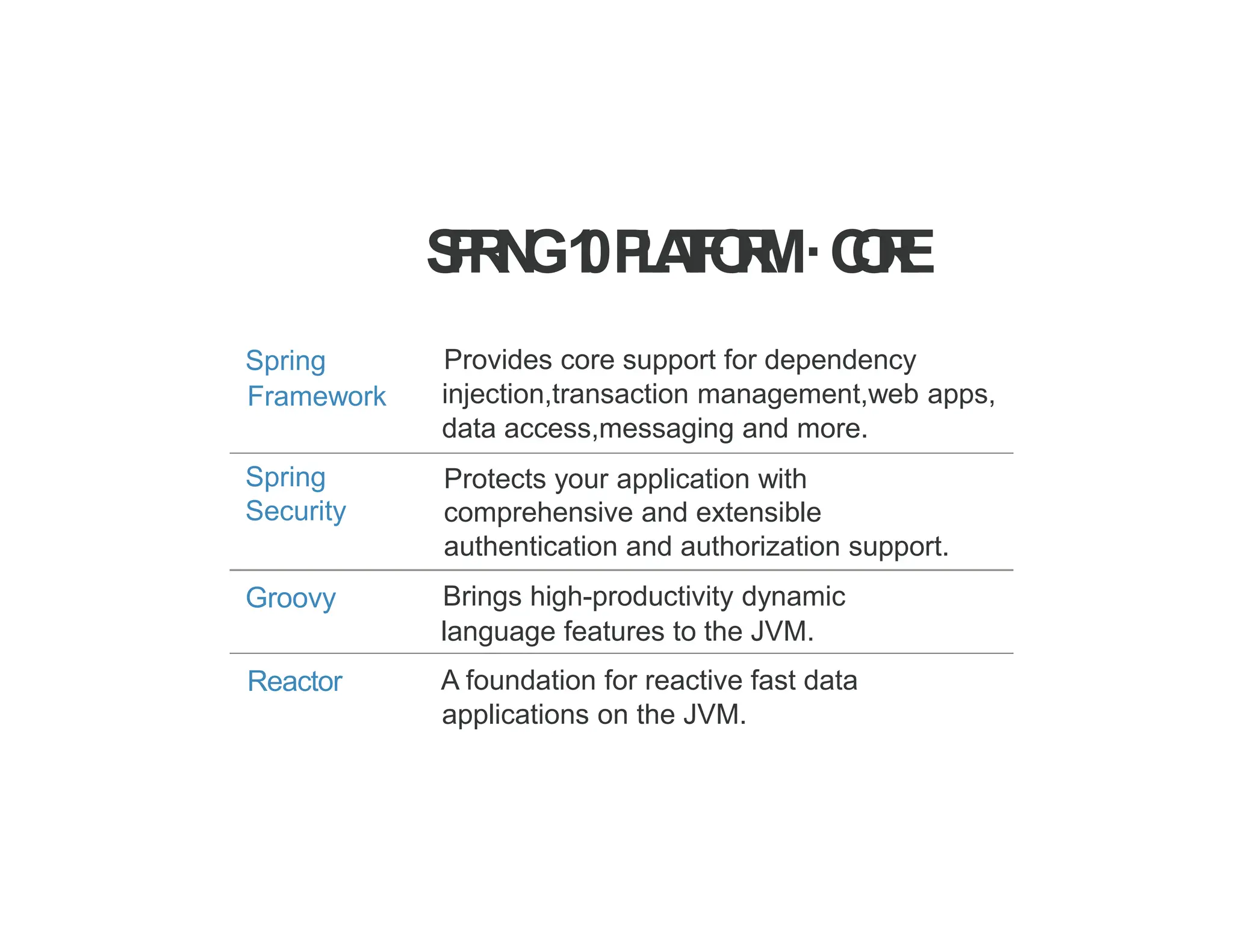
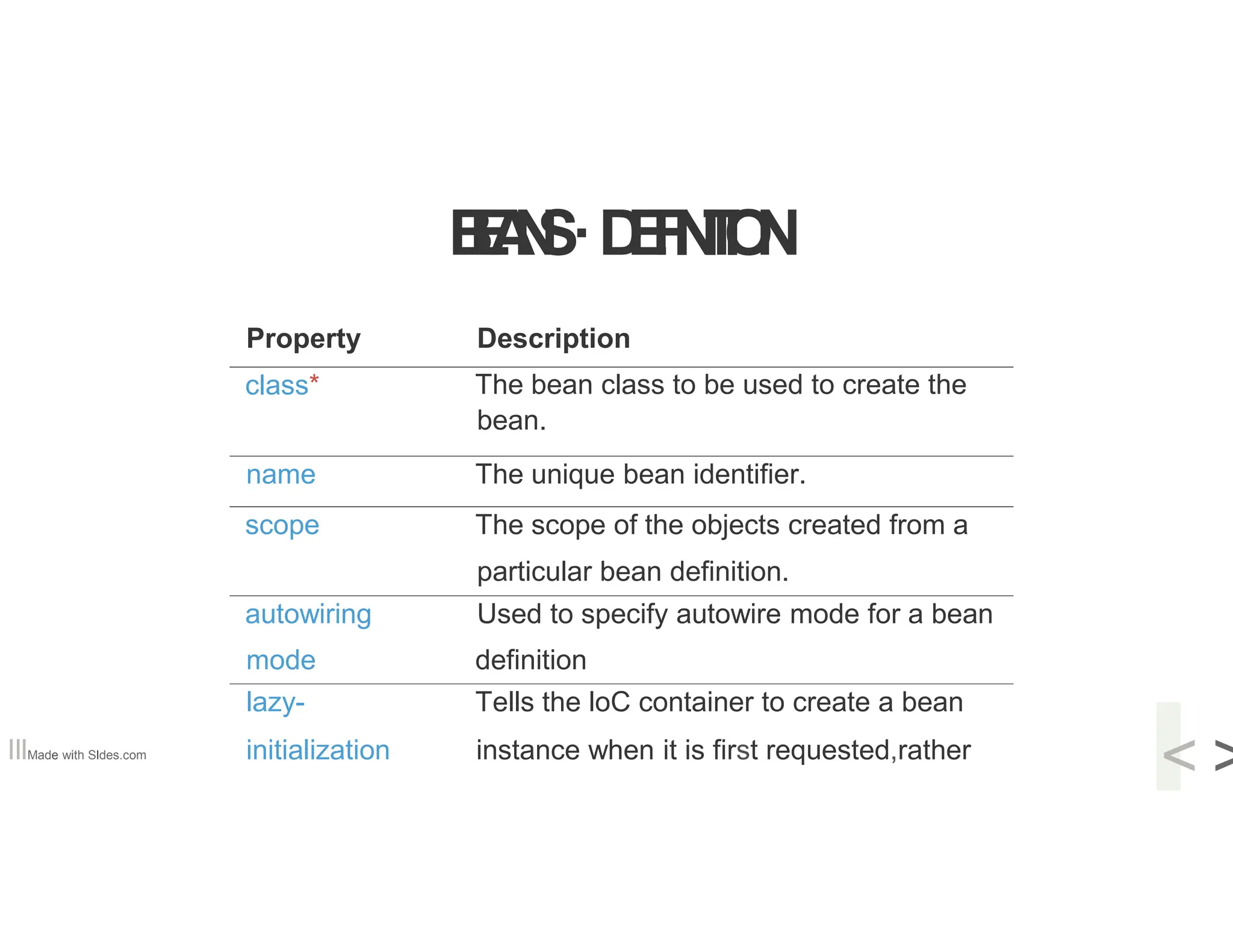
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the Spring framework, highlighting its importance for enterprise Java application development and features like dependency injection and inversion of control. It details the framework's modular architecture, components, and various modules such as data access and web MVC, as well as practical setup instructions for development environments. Additionally, it introduces the concepts of beans, their definitions, and lifecycle management within the Spring container.