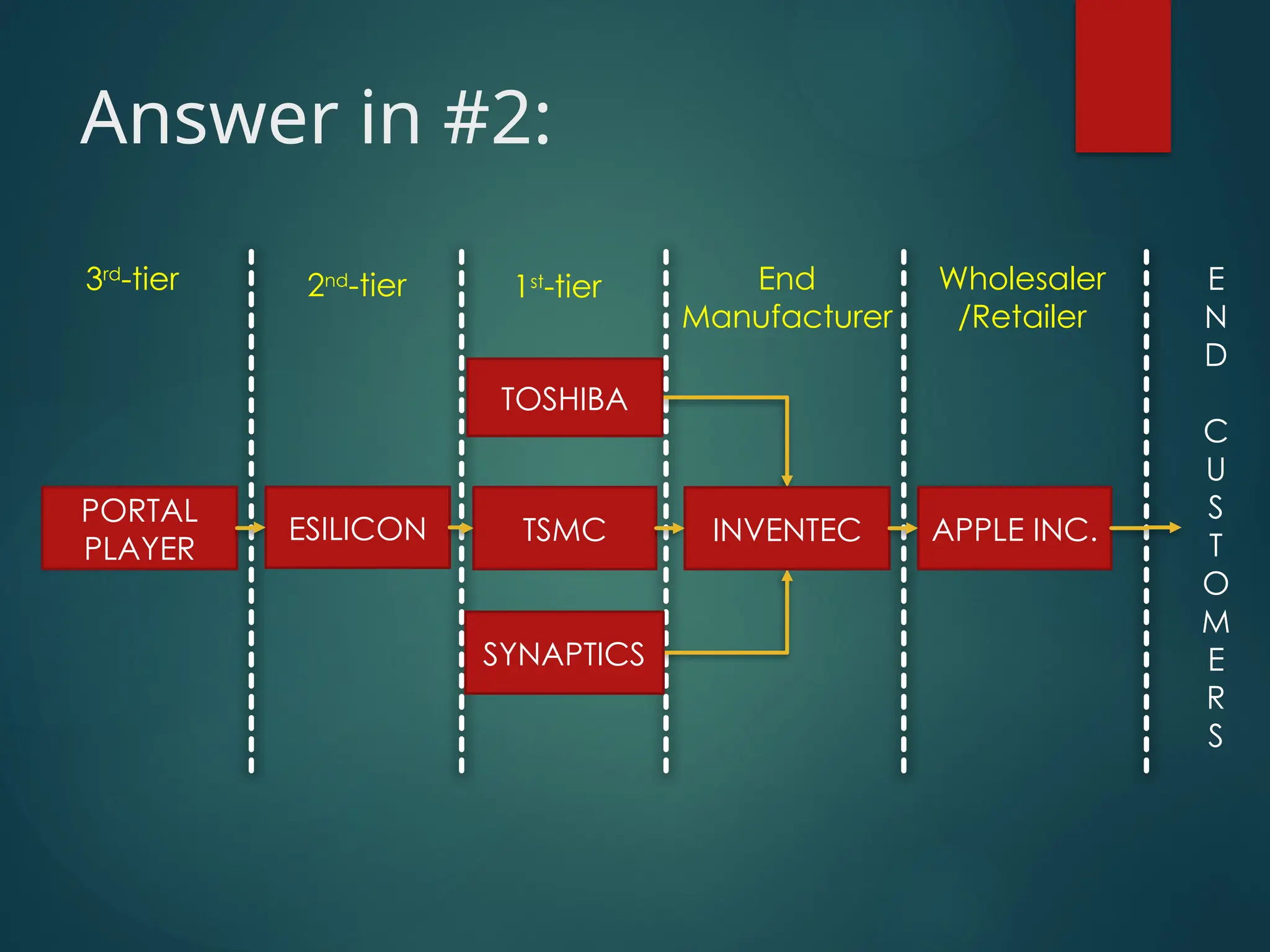
The document provides an introduction to supply chain management, outlining its definition as the design and management of processes across organizational boundaries to meet customer needs. It highlights the shift from vertically integrated firms to a collaborative approach involving multiple specialized suppliers and customers, emphasizing the importance of information flow and integration in maximizing supply chain profitability. Additionally, an example of Apple's iPod illustrates the interconnectedness of various suppliers and manufacturers within a supply chain.