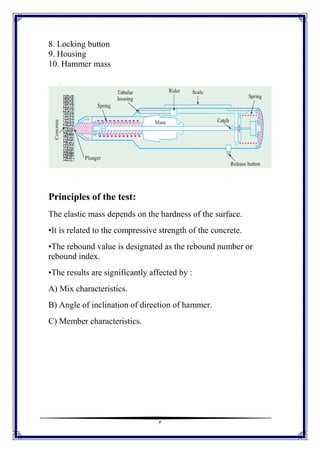
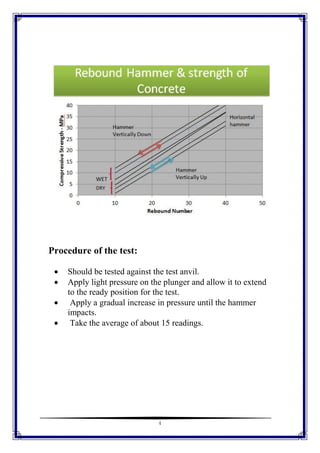
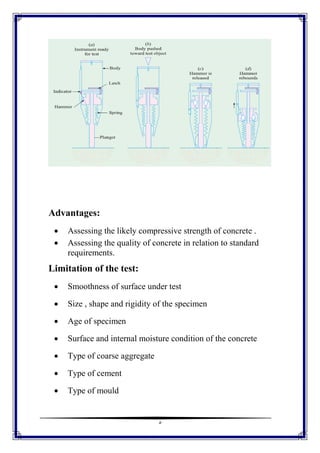
This document discusses the Schmidt Hammer as a nondestructive testing method for structural engineering. It provides an introduction to rebound hammers and how they are used to determine the strength and durability of concrete or rock. The components of the hammer are described including the impact spring, rider, window, housing, and hammer mass. The principles of the test are that the elastic mass depends on the surface hardness, which is related to compressive strength. The results can be affected by mix characteristics, angle of inclination, and member characteristics. The procedure involves testing against an anvil and taking the average of about 15 readings. Advantages are assessing likely compressive strength and quality, while limitations include surface smoothness and moisture conditions.