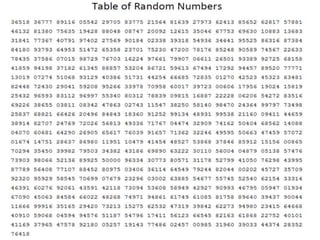
This document discusses simple random sampling, which is a type of probability sampling technique where each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. It provides examples to illustrate simple random sampling, such as selecting sugar from a bag or using a lottery system or random number table to randomly pick sample members. The key aspects of simple random sampling are that selection is random and does not depend on the characteristics of the population members, giving each member an equal chance of selection.