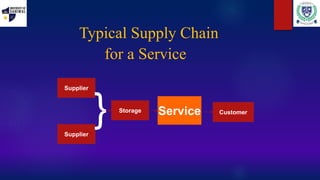
This document discusses supply chain management. It defines supply chain as the management of the flow of goods and services from raw materials to finished products to the end customer. It notes key elements like planning, sourcing, manufacturing, delivering, and returning. It discusses issues like increasing outsourcing, globalization, and e-commerce that create a need for effective supply chain management. Performance is measured based on reliability, flexibility, expenses, and assets. Electronic data interchange and distribution resource planning are also summarized.