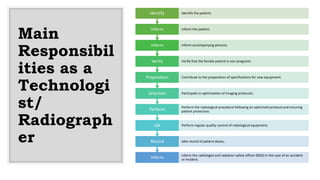
This document outlines safe practices in imaging departments to reduce radiation exposure. It recommends reducing fluoroscopy procedure time and increasing distance from the x-ray source to reduce individual radiation dose. It also stresses the importance of using protective shields like lead aprons and monitoring devices, ensuring equipment is properly maintained, and updating practices according to regulatory requirements. Radiation exposure can be minimized by collimating beams, avoiding unnecessary exposure, using safety devices, and standing away from patients during exams. Proper storage and testing of protective equipment is also advised.