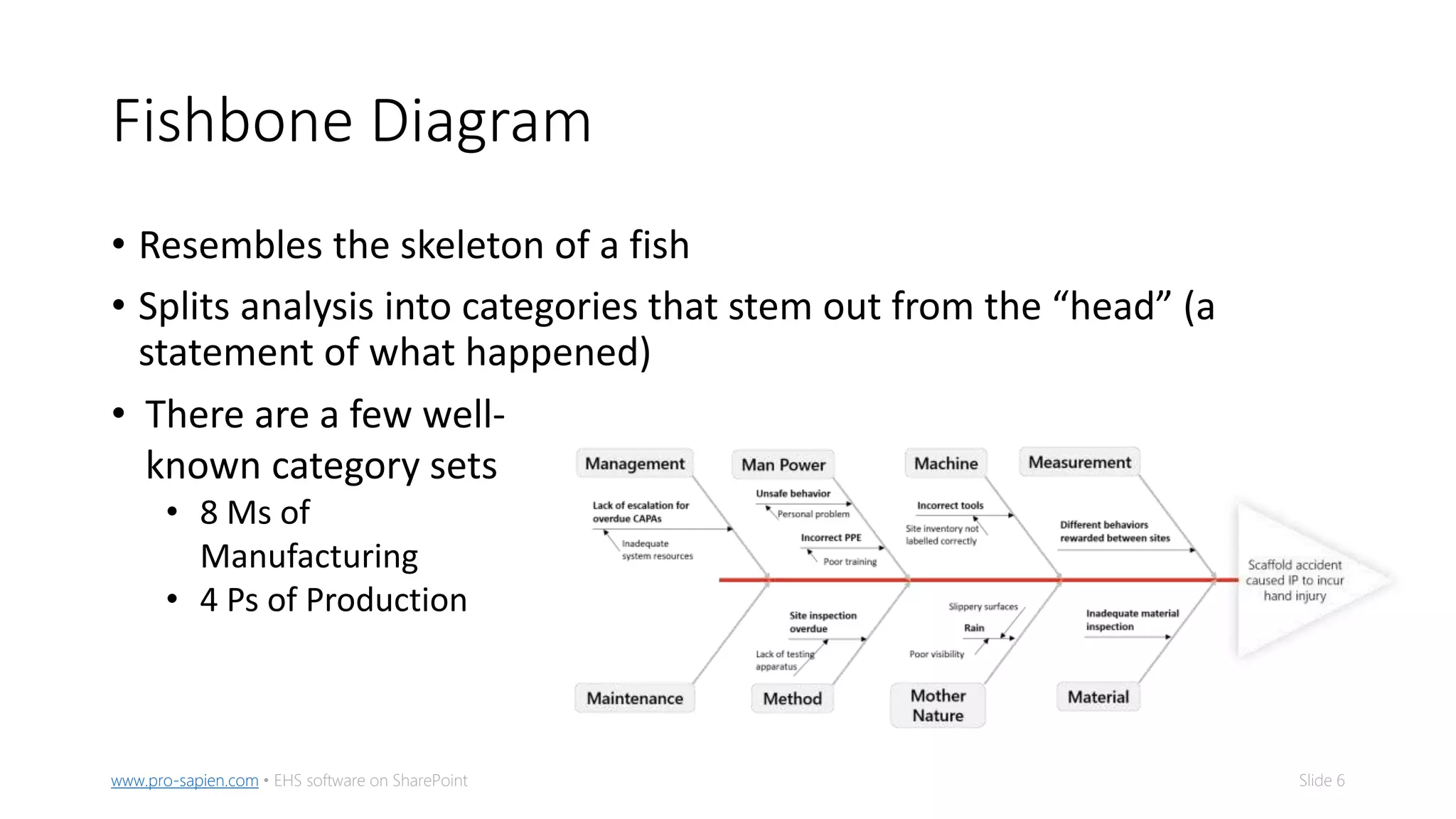
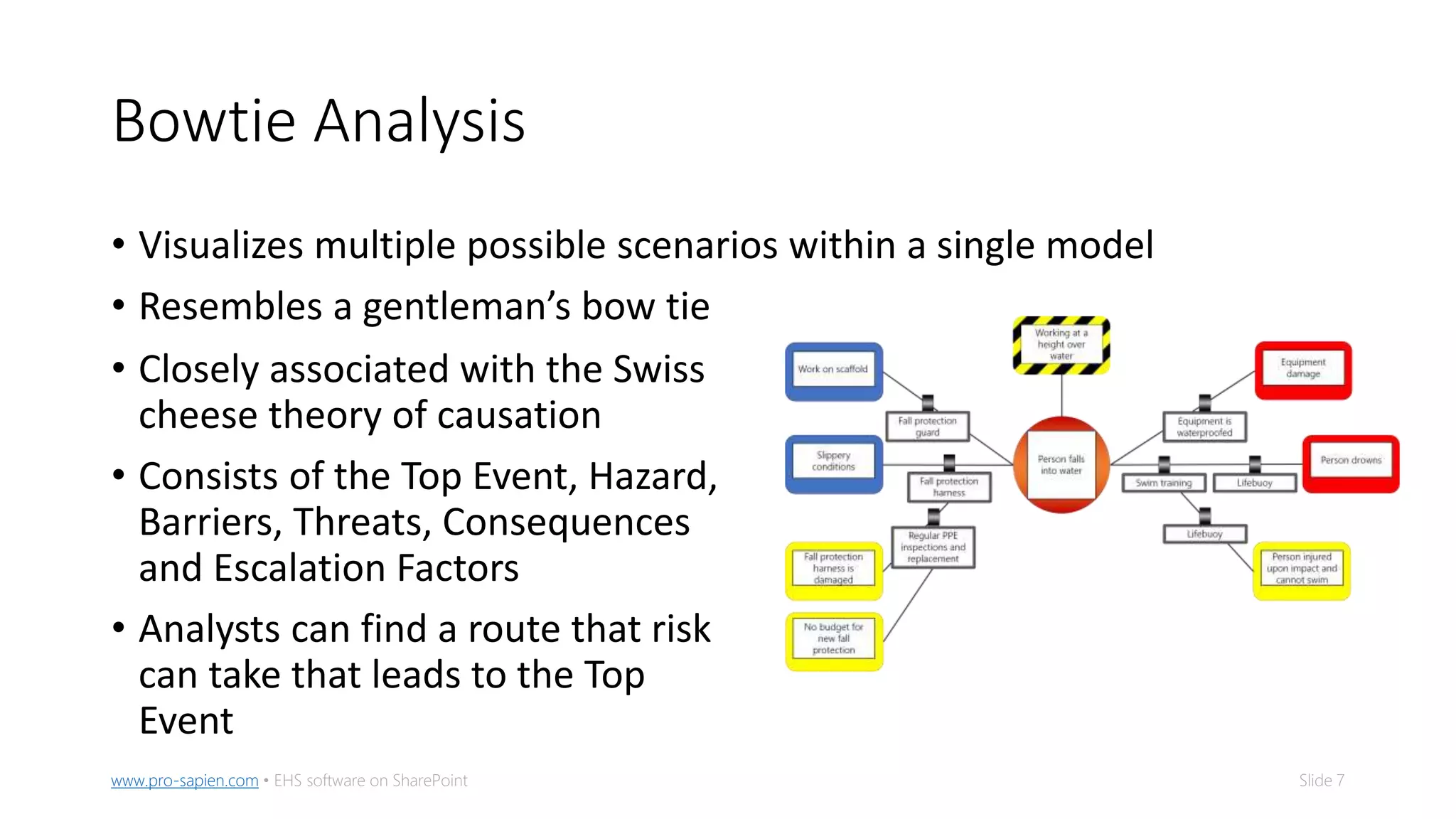
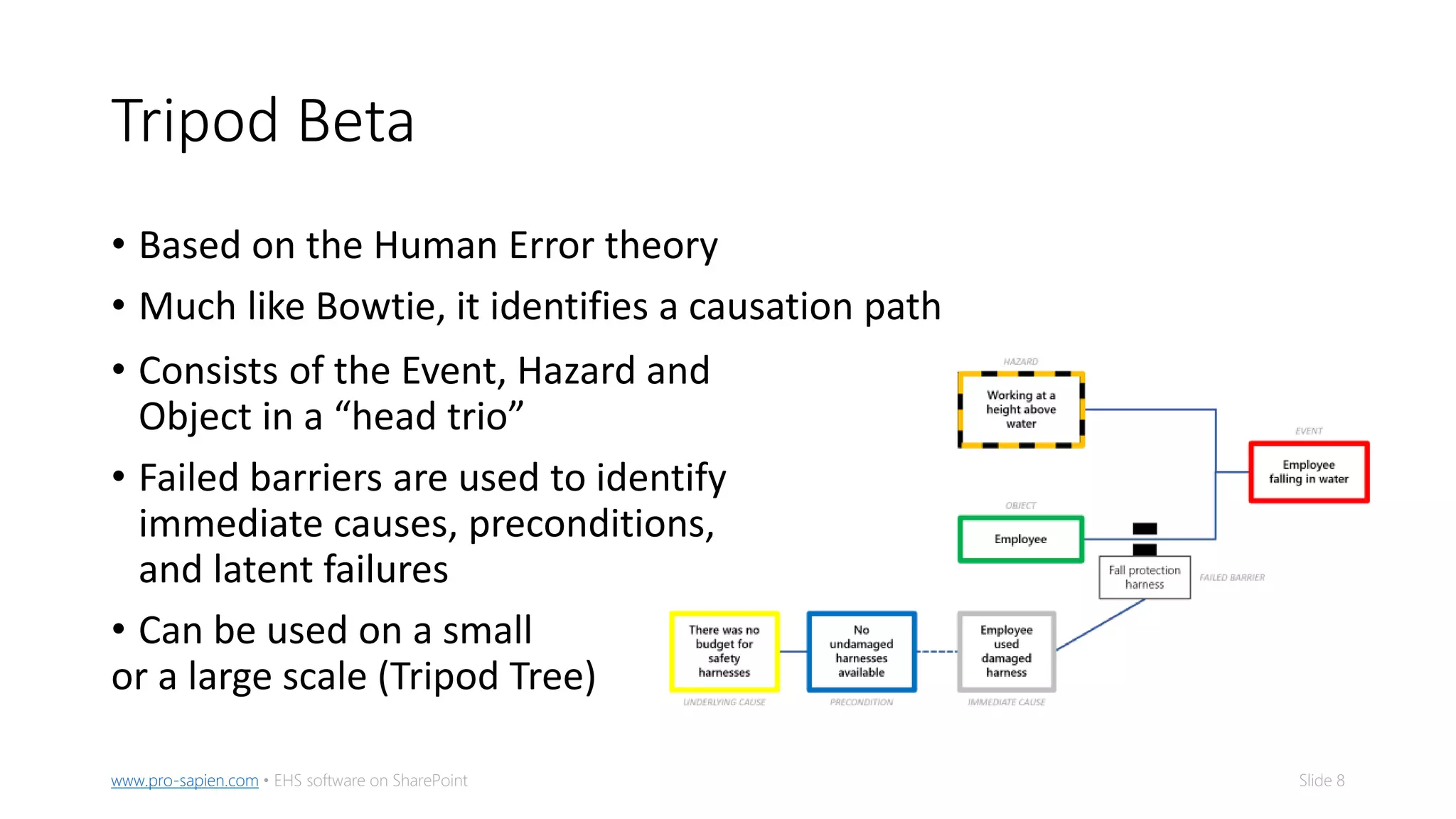
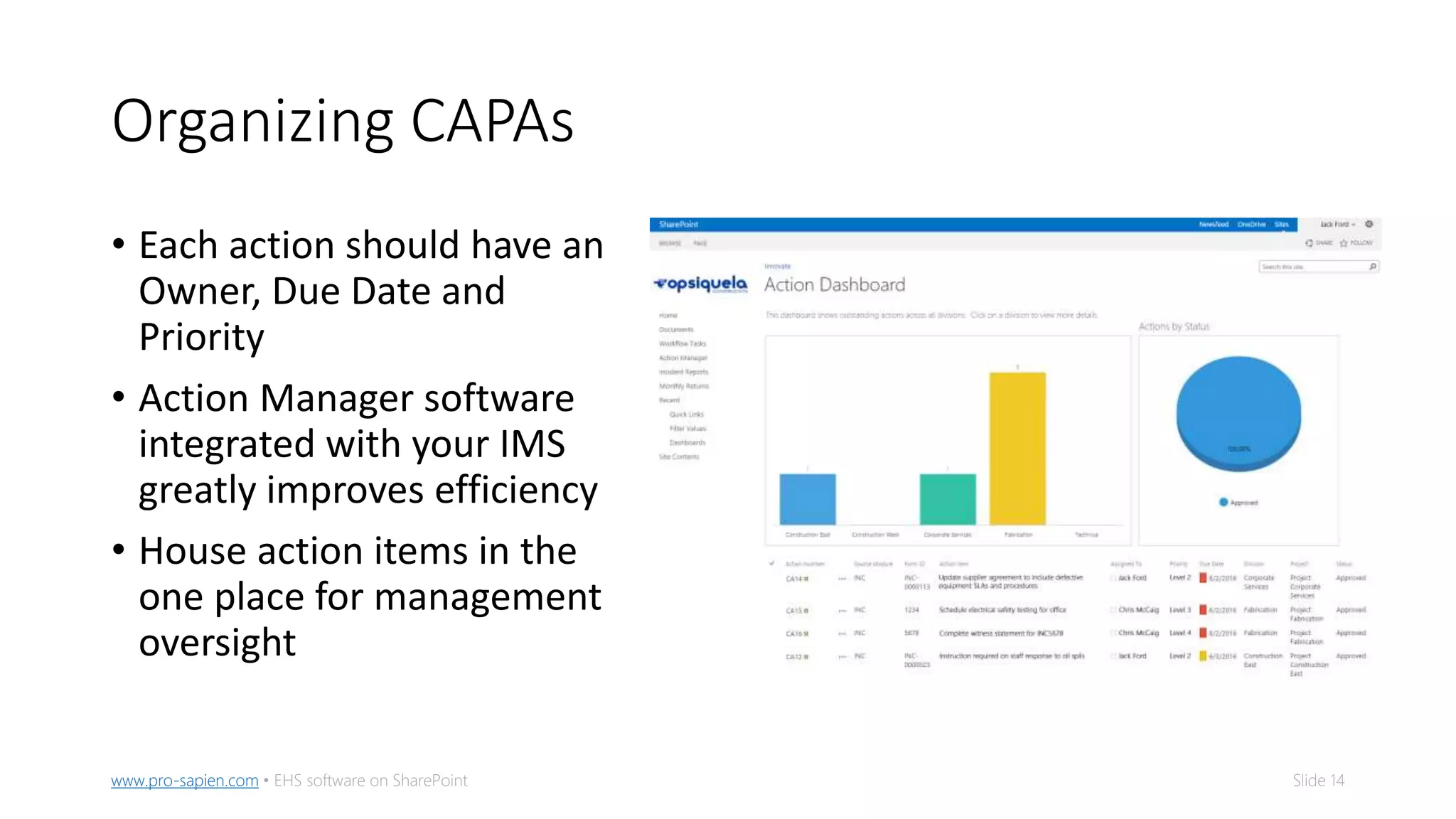
The document outlines five methods for conducting root cause analysis (RCA) in incident investigations, including 5-whys, fishbone diagram, bowtie analysis, tripod beta, and fault tree analysis. It emphasizes the importance of identifying root causes to prevent recurrence, implementing corrective and preventive actions (CAPAs), and tracking their effectiveness. The document provides guidance on prioritization, organization, and automation of CAPAs to enhance incident management and improve safety outcomes.