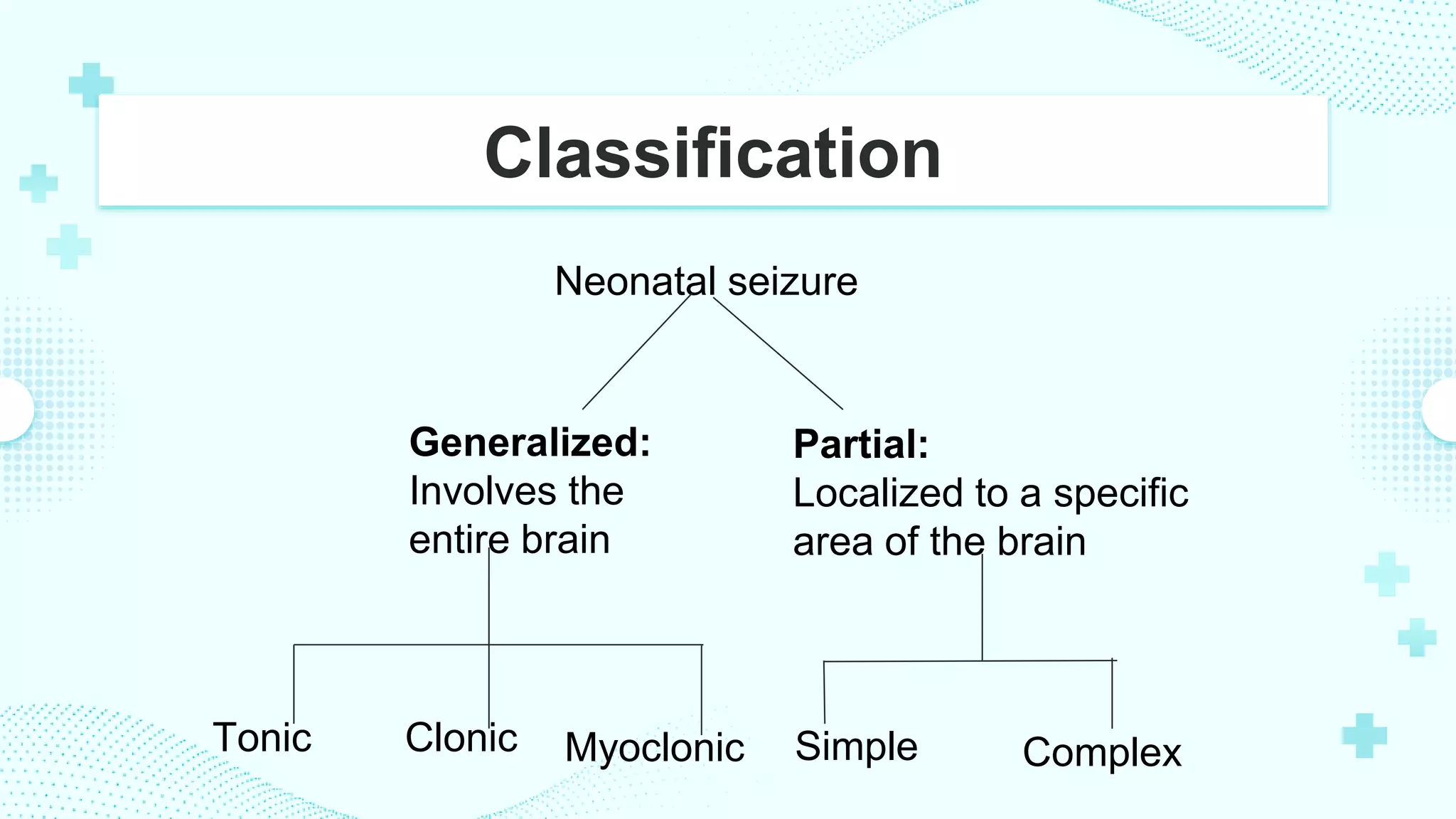
Neonatal seizures occur within the first 28 days of life and can be caused by factors like infection, brain injury, or genetic disorders. The incidence is estimated to be between 1-5 per 1,000 live births. Risk factors include prematurity, birth trauma, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, and congenital brain malformations. Seizures are classified as either generalized, involving the entire brain, or partial, localized to a specific area. Management includes medical treatment with anti-seizure medications as well as surgical options if medications are ineffective. Nursing care focuses on monitoring for signs of seizures, maintaining safety, and educating family.