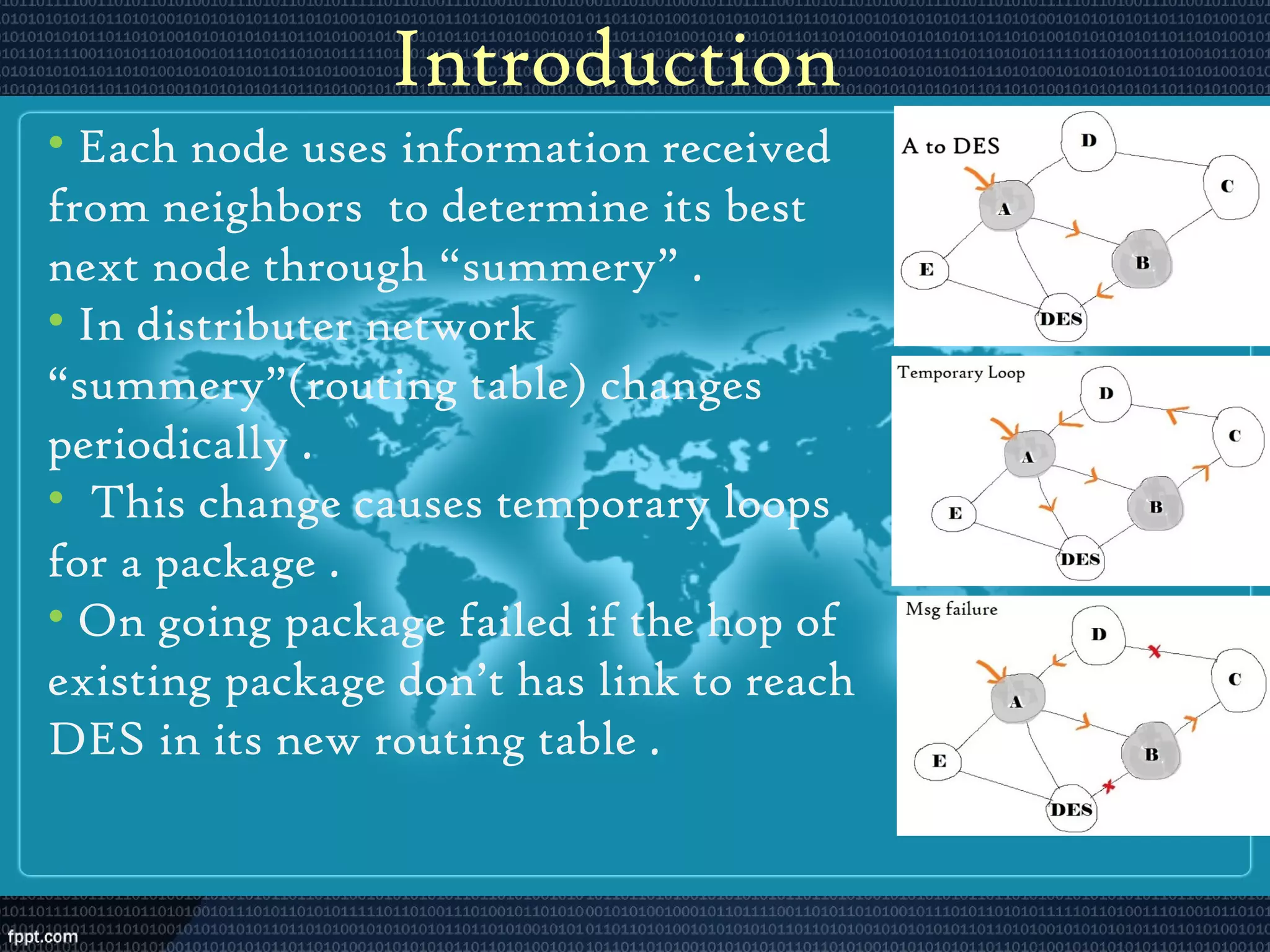
The document discusses a literature review on a responsive distributed routing algorithm that enhances computer network routing by addressing temporary loops and improving recovery time during network link failures. It introduces a new dynamic algorithm that utilizes summarized information instead of global topology to manage routing, allowing for efficient hop count detection and processing of multiple freeze acknowledgments. The findings suggest that while the algorithm reduces recovery times, it still requires significant time and memory to handle the summarized routing tables, and proposes the use of global routing topology to mitigate potential issues.