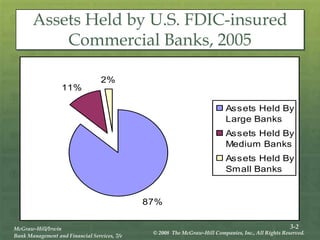
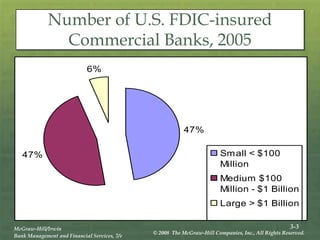
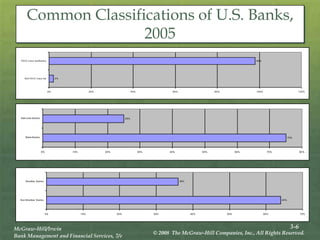
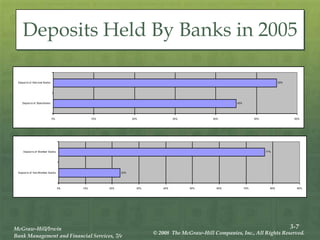
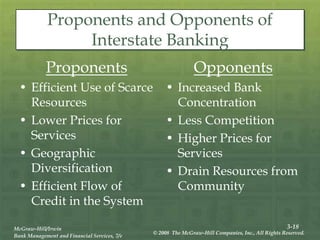
The document provides an overview of the structure and organization of banks in the U.S. and international banking systems, detailing categories such as community banks, money center banks, unit banks, and branch banks. It highlights trends in bank classifications, branching growth, and the establishment of bank holding companies, along with their advantages and challenges. Furthermore, it discusses regulatory frameworks affecting banking, including the Riegle-Neal Act and the concept of financial holding companies, as well as the efficiency of banking operations and goals in corporate governance.