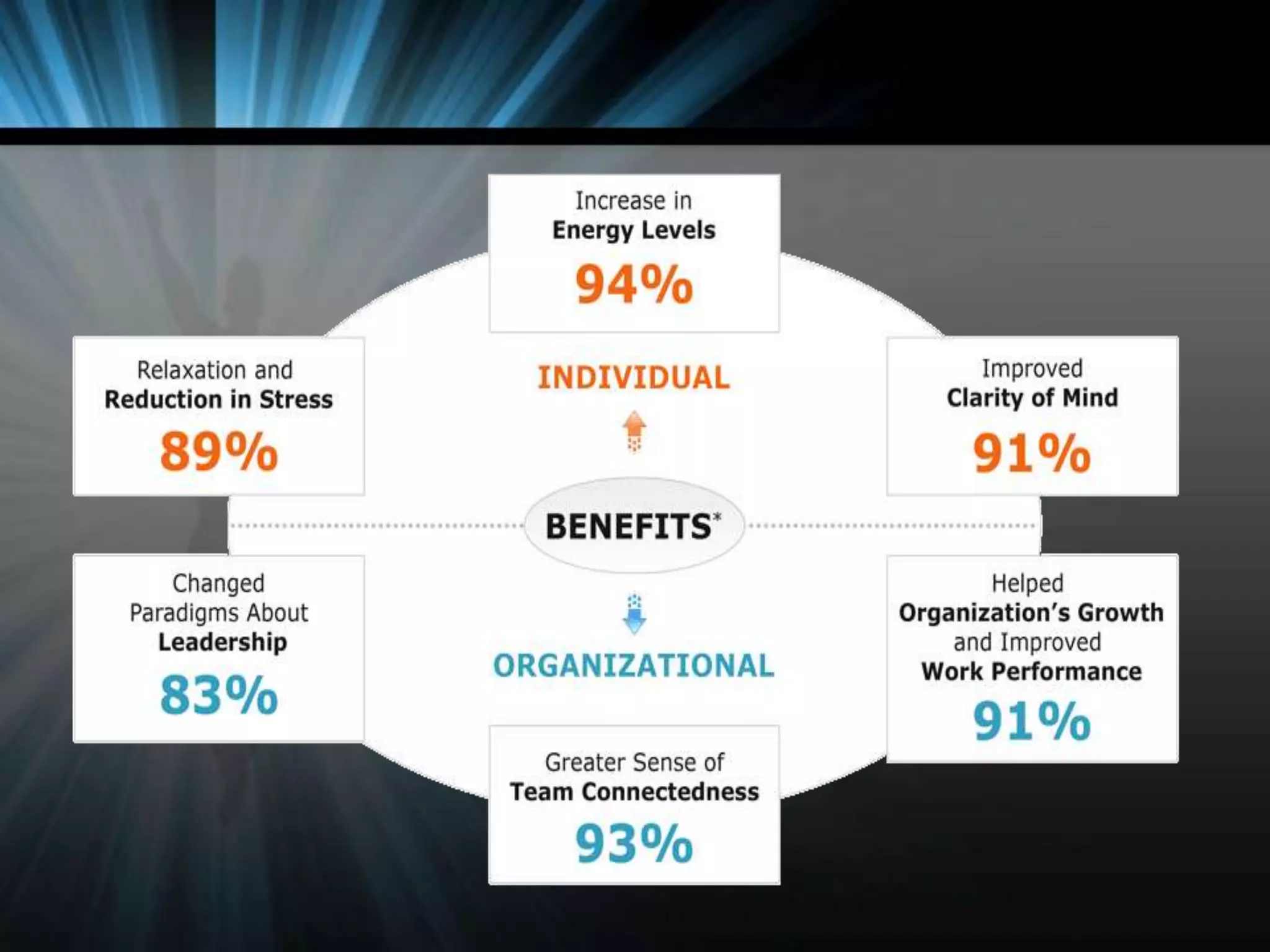
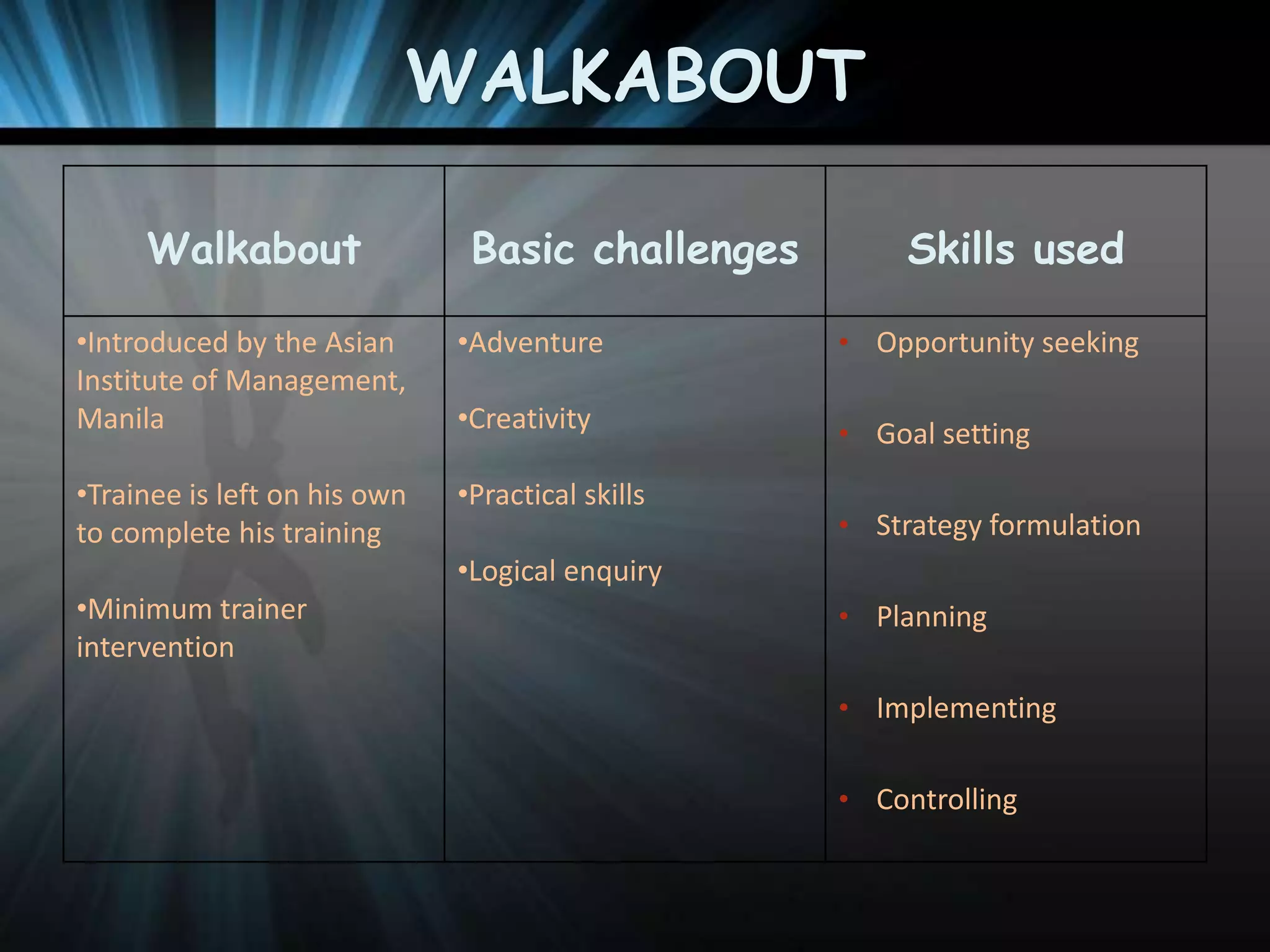
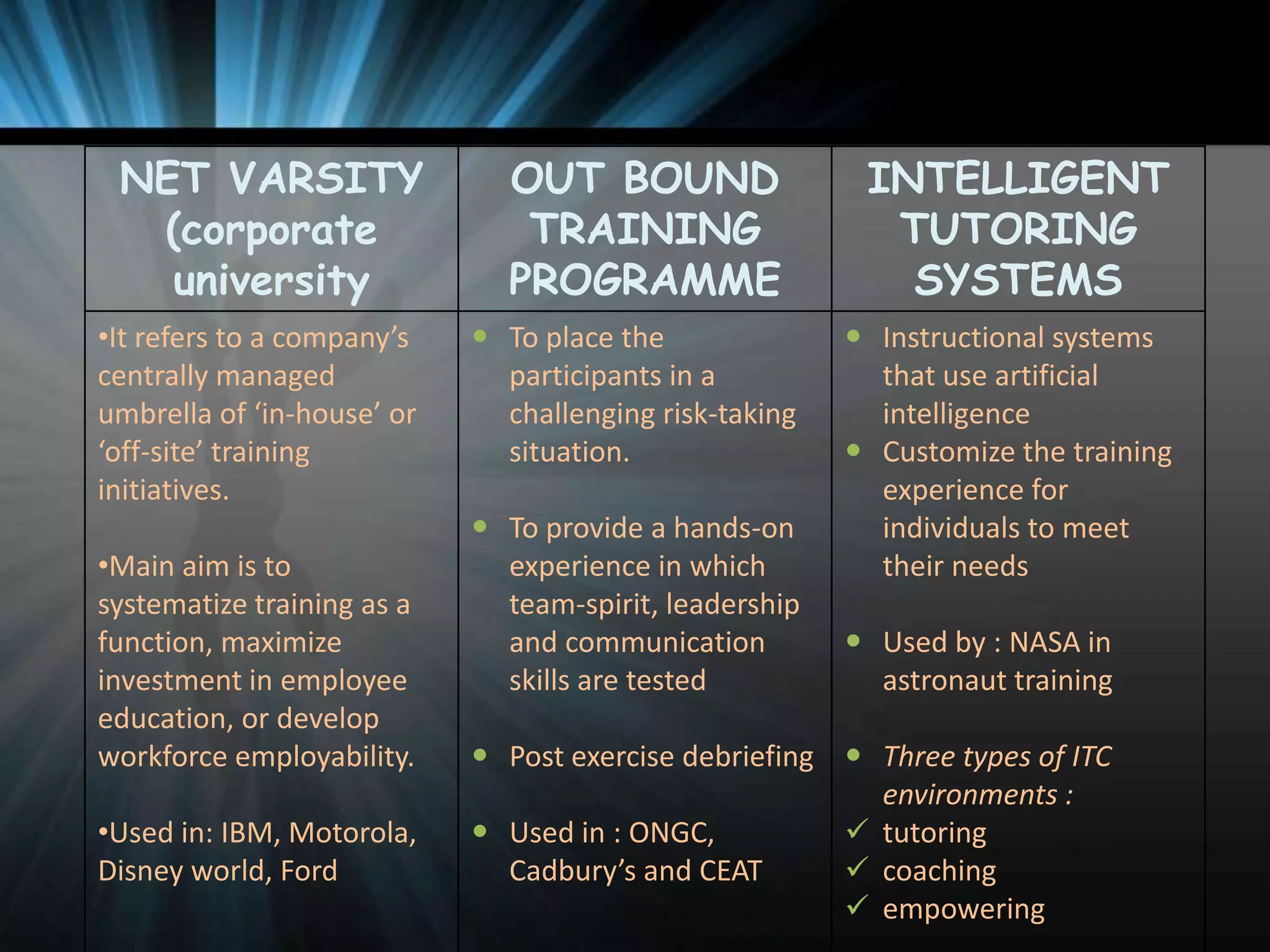
The document discusses the latest trends in training and development. It outlines that organizations are increasingly using technology for training delivery to reduce costs and reach remote employees. There is also a greater demand for training around virtual work arrangements. Organizations are placing more emphasis on speed of design, focused content, and multiple delivery methods. Capturing intellectual capital and promoting a learning organization is also a growing trend. The latest methods used by organizations include computer-based training, e-learning, learning portals, distance learning, and blended learning. Emerging technologies being used include virtual reality, groupware, and intelligent tutoring systems.