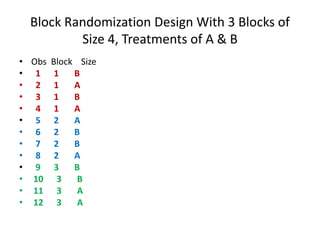
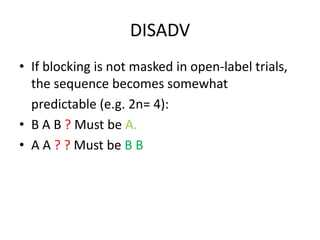
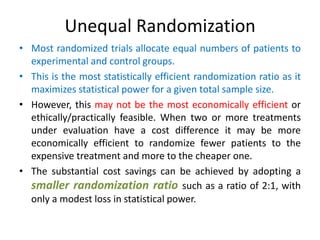
Randomization is a key process in clinical trials that assigns participants to treatment groups in a way that limits bias. It aims to balance groups so they are similar in all ways except for the intervention received. Common randomization methods include coin tossing, random number tables, and computer generation of sequences. Block and stratified randomization can help produce balanced groups with comparable characteristics. Blinding of participants, investigators, and assessors is important to prevent biases from influencing outcomes. Inclusion and exclusion criteria define who can participate in a clinical trial based on factors like age, sex, disease characteristics, and medical history.