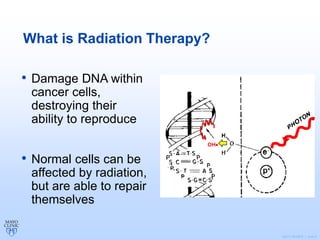
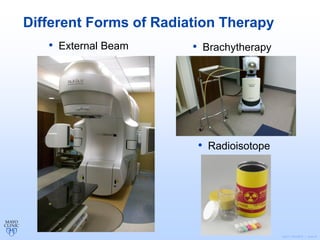
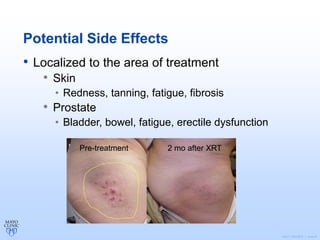
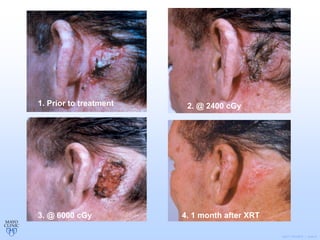
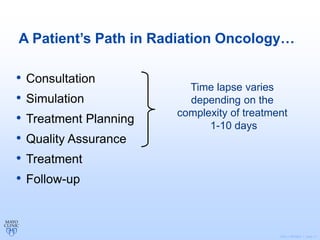
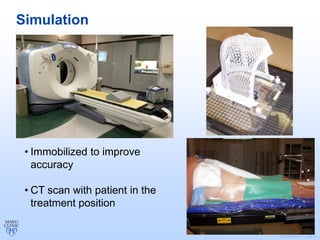
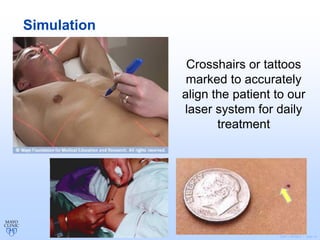
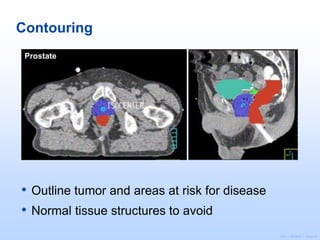
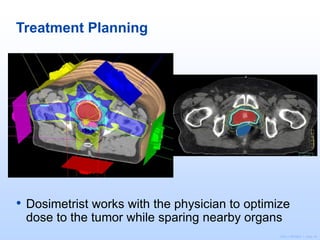
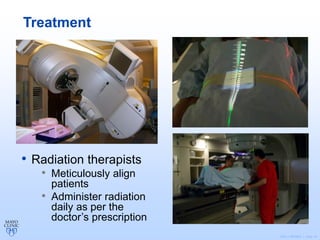
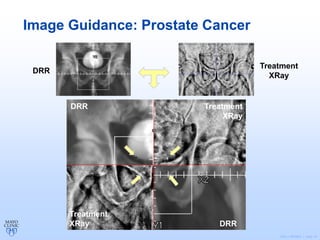
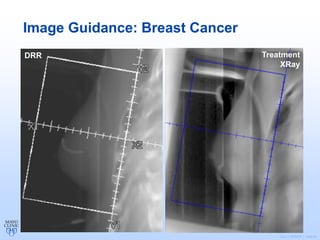
Radiation therapy involves using high-energy beams to damage cancer cells' DNA and destroy their ability to reproduce. It can be used as the primary treatment for some cancers or alongside surgery and chemotherapy. The document outlines the radiation therapy process, including initial consultation, simulation to plan treatment, quality assurance of the plan, daily treatment sessions, and follow-up care. Potential side effects are usually localized to the treatment area and can include skin changes, fatigue, and organ-specific issues depending on the cancer location.