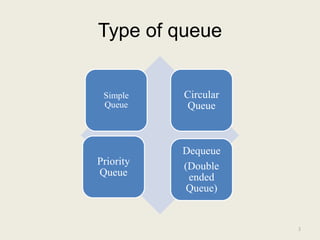
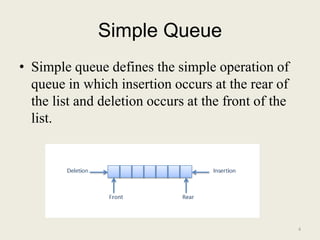
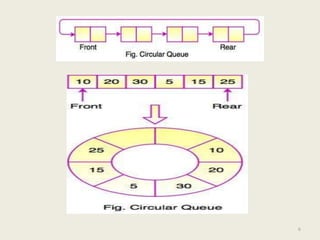
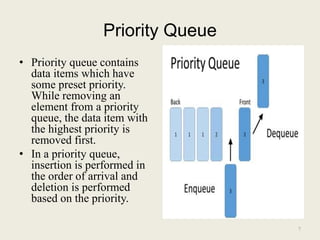
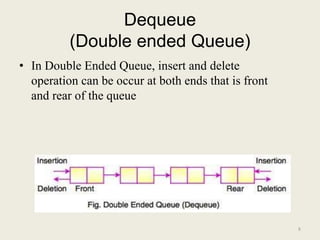
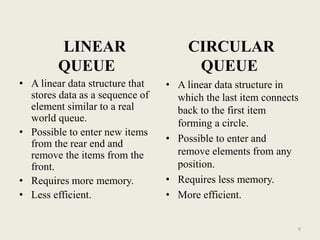
The document discusses different types of queues, including simple, circular, priority, and double-ended queues. It describes the basic queue operations of enqueue and dequeue, where new elements are added to the rear of the queue and existing elements are removed from the front. Circular queues are more memory efficient than linear queues by connecting the last queue element back to the first, forming a circle. Priority queues remove elements based on priority rather than order of insertion. Double-ended queues allow insertion and removal from both ends. Common applications of queues include CPU and disk scheduling, synchronization between asynchronous processes, and call center phone systems.




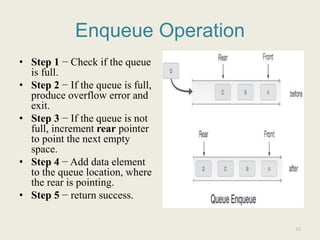
![Algorithm Of Enqueue
procedure enqueue(data)
if queue is full
return overflow
12
rear ← rear + 1
queue[rear] ← data
return true
end procedure
int enqueue (int data)
if(isfull())
return 0;
rear = rear + 1;
queue[rear] = data;
return 1;
end procedure
Example of
Enqueue
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queueppt-191018053228/85/Queue-ppt-12-320.jpg)
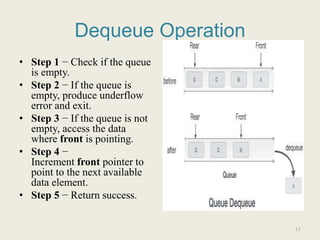
![Algorithm for
dequeue operation
procedure dequeue
if queue is empty
return underflow
end if
data = queue[front]
front ← front + 1
return true
end procedure
int dequeue()
{
if(isempty())
return 0;
int data = queue[front]; front =
front + 1;
return data;
}
Example of
Dequeue Operation
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queueppt-191018053228/85/Queue-ppt-14-320.jpg)

