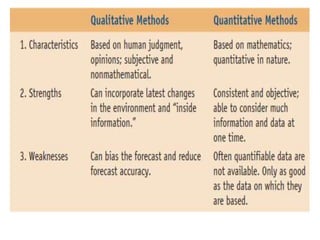
Qualitative forecasting uses expert judgment rather than numerical analysis to estimate future outcomes. It relies on the knowledge and insights of experienced employees and consultants. This approach differs from quantitative forecasting, which analyzes historical data to discern future trends. Qualitative forecasting techniques include the Delphi technique, scenario writing, and subjective approaches.