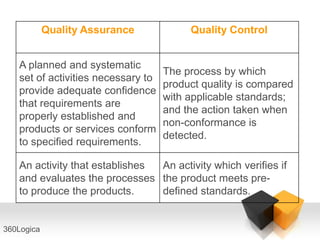
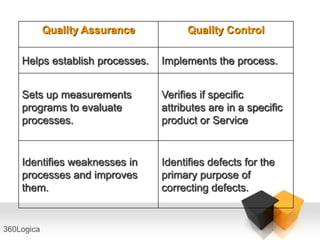
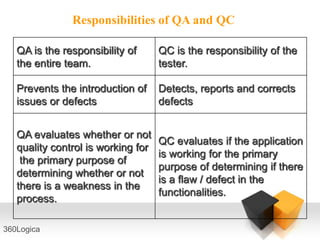
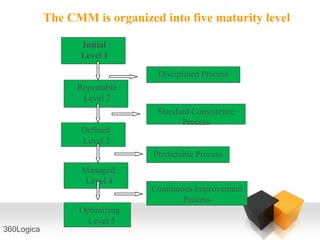
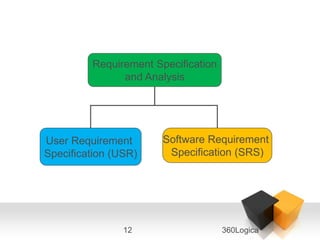
The document outlines key quality principles in testing, emphasizing that quality is crucial for long-term organizational performance and productivity. It details the costs associated with quality, including prevention, appraisal, and failure costs, alongside the responsibilities of quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) in software development. Additionally, it describes the software development life cycle (SDLC) phases and various life cycle models, including the capability maturity model (CMM) developed by the Software Engineering Institute (SEI).