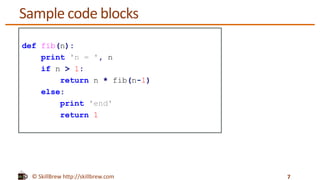
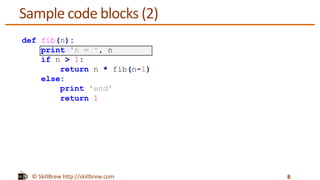
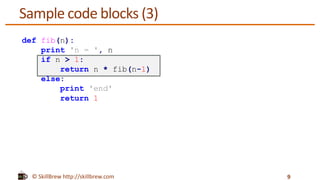
This document discusses Python statements, code blocks, and indentation. It notes that statements in Python are typically written on individual lines, but can span multiple lines using line continuation characters or parentheses. Code blocks, like if/else statements and functions, are defined by indentation rather than brackets - any indented code will be executed as part of the code block. Indentation is significant in Python and code blocks must be indented consistently using spaces.