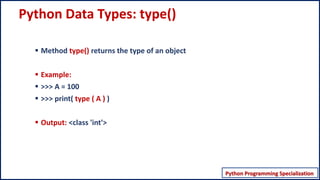
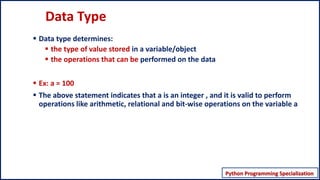
This document discusses Python data types. It begins by explaining that data types determine the type of value stored in a variable, the operations that can be performed on the data, and provides an example. It then outlines some key properties of Python data types - that Python is dynamically typed, type can change during execution, data types are classes and variables are instances, and Python is strongly but not weakly typed. The document proceeds to explain how to get the data type using type() and categorizes main Python data types into scalars, sequences, mappings and sets.



![Python Programming Specialization
Python Programming – Data Structures
Python Data Types: Property1
▪ Python is a dynamically typed language
▪ Advance Declaration of variables is not required in Python
▪ Depending on the value assigned to the variables, their type is decided
▪ Examples:
▪ >>> a = 10 # int
▪ >>> b = 10.3 # float
▪ >>> c = “Python” # string
▪ >>> d = [10, 20, 30, 40] # list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypesproperties-201127055746/85/Python-Data-types-properties-7-320.jpg)