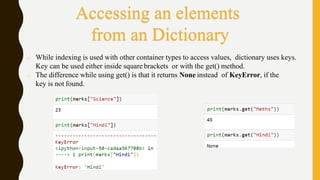
The document discusses different Python data types including lists, tuples, and dictionaries. It provides information on how to create, access, modify, and delete items from each data type. For lists, it covers indexing, slicing, and common list methods. For tuples, it discusses creation, concatenation, slicing, and built-in methods. For dictionaries, it explains how they are created as a collection of unique keys and values, and how to access, add, remove, and delete key-value pairs.


![A list is created by placing all the items (elements) inside a square
bracket [ ], separated by commas.
It can have any number of items and they may be of different types
(integer, float, string etc.).
Example:
list = [1, 2, 3] # list with same data-types list = [1, "Hello", 3.4] #
list with mixed data-types
List Creation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythoncollections-200128062514/85/Python-Collections-3-320.jpg)
![ It can be access in several ways
Use the index operator [] to access an item in a list. Index starts from 0.
So, a list having 5 elements will have index from 0 to 4.
Example:
list = ['p','r','o','b','e']
Output
O
bprint(list[2]) #Positive Indexing b
print(list[-2]) #Negative Indexing
Access Items From List](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythoncollections-200128062514/85/Python-Collections-4-320.jpg)
![ Accessing a range of items in a list by using the slicing operator [ ] using
(colon :).
Slicing can be best visualized by considering the index to be between the
elements.
Example:
list = ['p','r','o','b','e']
print(list[0:4]) #Positive
print(list[-2:-1]) # Negative
Output
['p', 'r', 'o', 'b']
['b']
4
Slice List](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythoncollections-200128062514/85/Python-Collections-5-320.jpg)


![Tuple1 = ( ) //empty tuple
Tuple2 = ('zooming', 'For ’) //tuple with
strings l i s t 1 = [1, 2, 4, 5, 6]
Tuple
3
= tuple ( l i s t 1 ) //tuple with the use of l i s t
Tuple
4
= (‘zooming’,) * 3 //tuple with repetition
Tuple
5
= (5, 'Welcome', 7, ‘zooming’) //tuple with
mixed datatypes
Creation of Tuples](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythoncollections-200128062514/85/Python-Collections-8-320.jpg)

![# with Numbers
Tuple1 = tuple(‘ZOOMING')
# From First element
print(Tuple1[1:])
# Reversing the Tuple
print(Tuple1[::-1])
# Printing elements of a
Range
print(Tuple1[2:5])
( ‘ O ’ , ’ O ’ , ’ M ’ , ’ I ’ , ’ N ’ , ’
G ’ )
( ‘ G’ , ’ N’ , ’ I ’ , ’ M’ , ’ O’ , ’
O’ , ’ Z’ ) ( ‘ O ’ , ’ M ’ , ’ I ’ )
Slicing of Tuples](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythoncollections-200128062514/85/Python-Collections-10-320.jpg)