The document discusses priority queues and quicksort. It defines a priority queue as a data structure that maintains a set of elements with associated keys. Heaps can be used to implement priority queues. There are two types: max-priority queues and min-priority queues. Priority queues have applications in job scheduling and event-driven simulation. Quicksort works by partitioning an array around a pivot element and recursively sorting the sub-arrays.





![Priority Queue HEAP-MAXIMUM(A) return A[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/priority-queueppt2006/85/Algorithm-priority-queue-6-320.jpg)
![Priority Queue HEAP-EXTRACT-MAX(A) if heap-size[A] < 1 then error “heap underflow” max A[1] A[1] A[heap-size[A]] heap-size[A] heap-size[A]-1 MAX-HEAPIFY(A,1) return max](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/priority-queueppt2006/85/Algorithm-priority-queue-7-320.jpg)
![Priority Queue HEAP-INCREASE-KEY(A, i, key) if key < A[i] then error “new key is smaller than current key” A[i] key while i > 1 and A[PARENT(i)] < A[i] do exchange A[i] A[PARENT(i)] i PARENT(i)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/priority-queueppt2006/85/Algorithm-priority-queue-8-320.jpg)
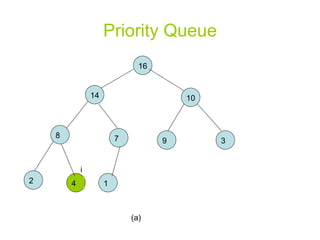
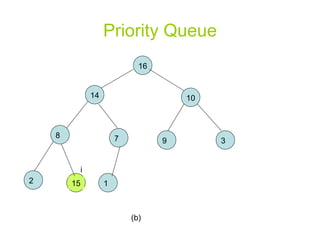
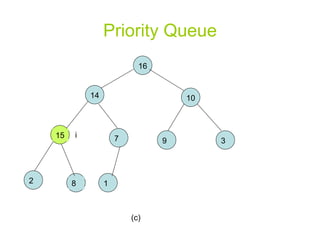
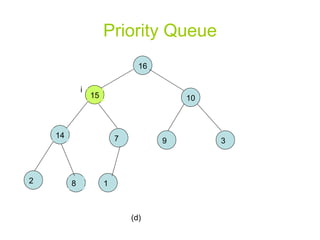
![Priority Queue MAX-HEAP-INSERT(A, key) heap-size[A] heap-size[A]+1 A[heap-size[A]] - ∞ HEAP-INCREASE-KEY (A, heap-size[A], key)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/priority-queueppt2006/85/Algorithm-priority-queue-13-320.jpg)
![Quick Sort Divide: Partition the array into two sub-arrays A[p . . q-1] and A[q+1 . . r] such that each element of A[p . . q-1] is less than or equal to A[q], which in turn less than or equal to each element of A[q+1 . . r]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/priority-queueppt2006/85/Algorithm-priority-queue-14-320.jpg)
![Quick Sort Conquer: Sort the two sub-arrays A[p . . q-1] and A[q+1 . . r] by recursive calls to quick sort.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/priority-queueppt2006/85/Algorithm-priority-queue-15-320.jpg)


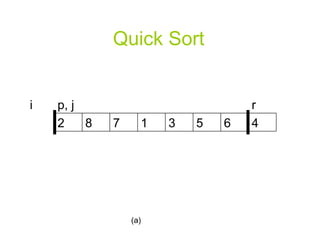
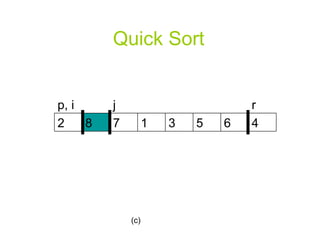
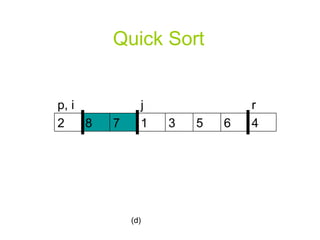
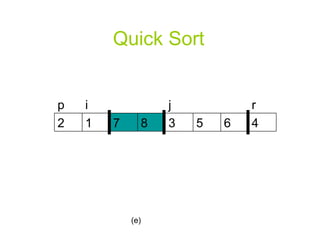
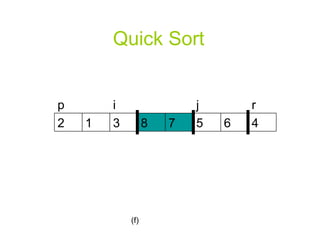
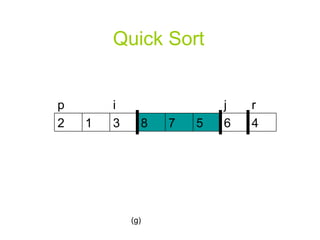
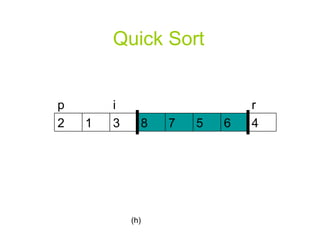
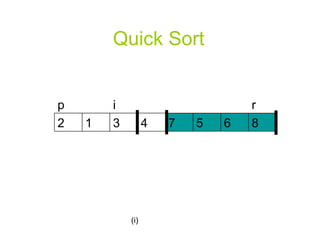
![Quick Sort PARTITION(A, p, r) x A[r] i p-1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/priority-queueppt2006/85/Algorithm-priority-queue-18-320.jpg)
![Quick Sort for j p to r-1 do if A[j] <= x then i i+1 exchange A[i] A[j] exchange A[i+1] A[r] return i+1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/priority-queueppt2006/85/Algorithm-priority-queue-19-320.jpg)