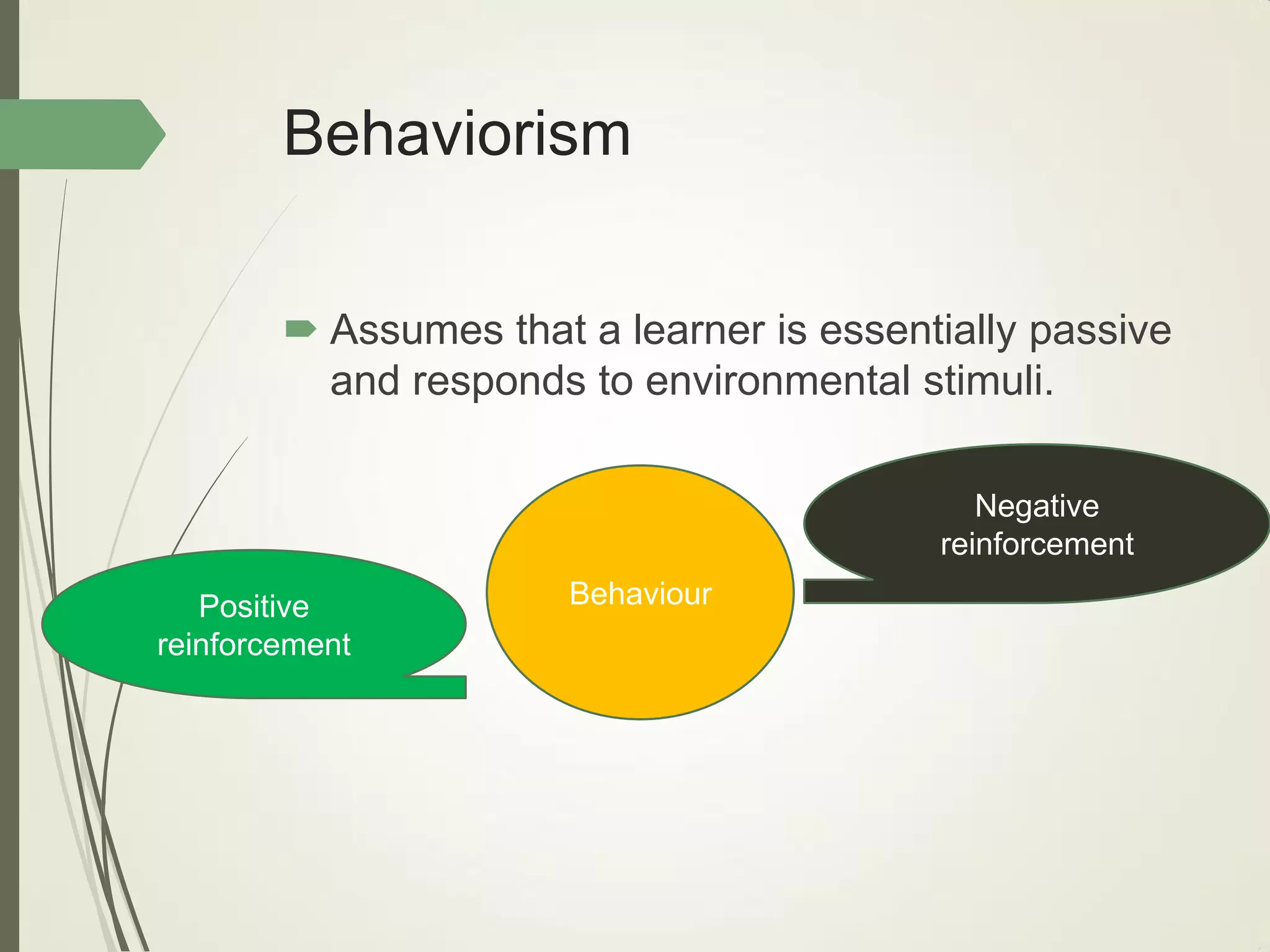
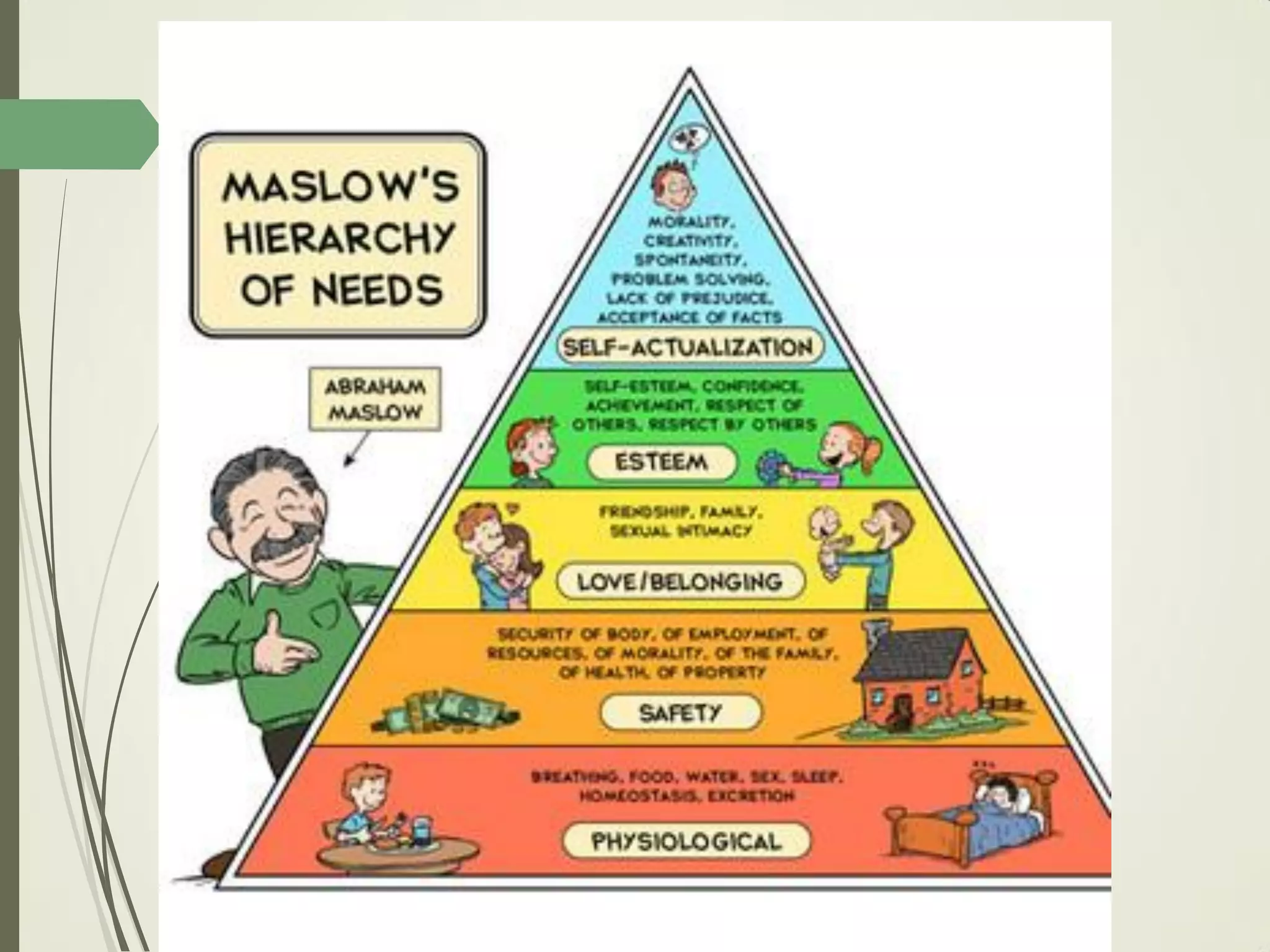
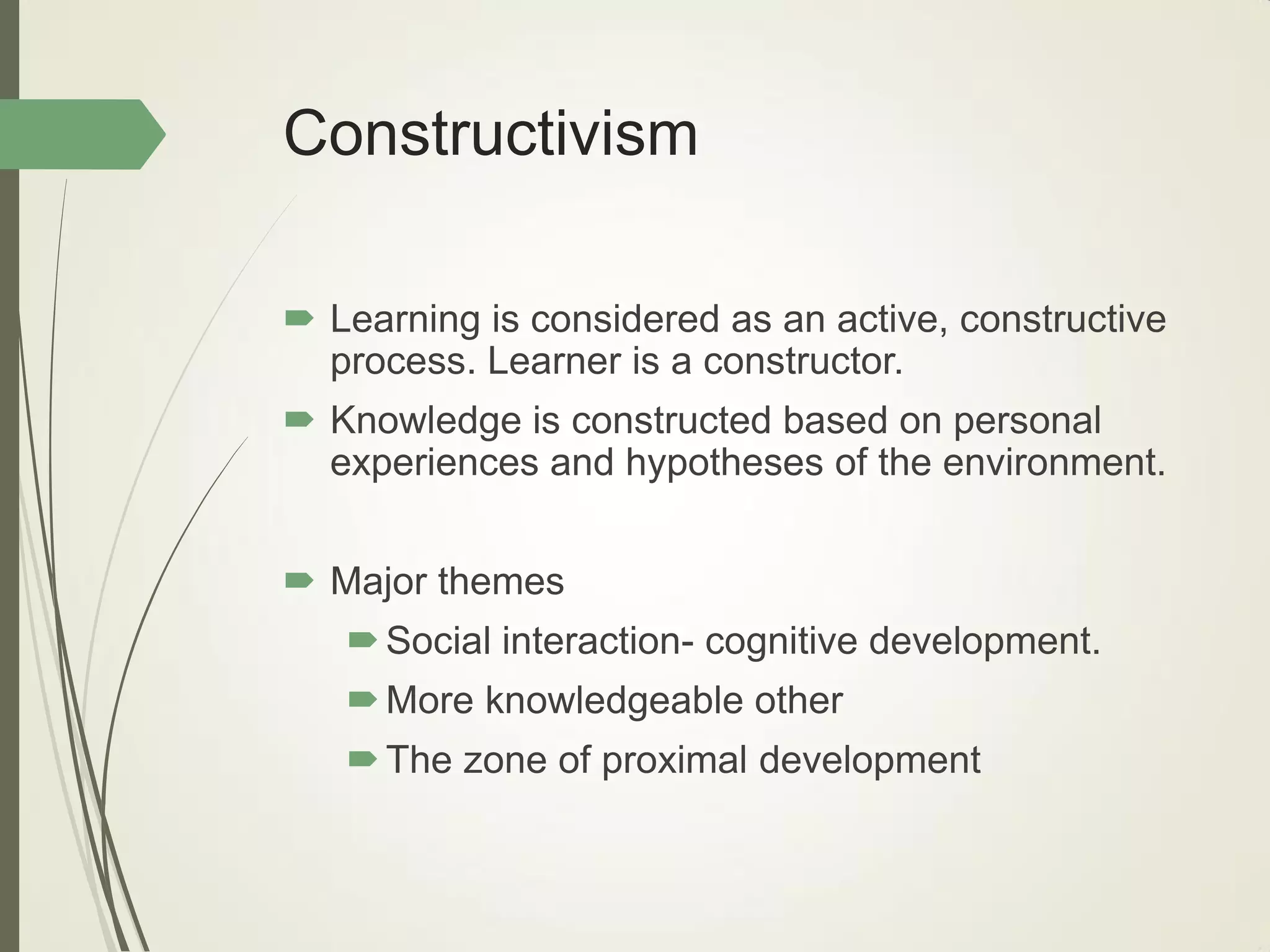
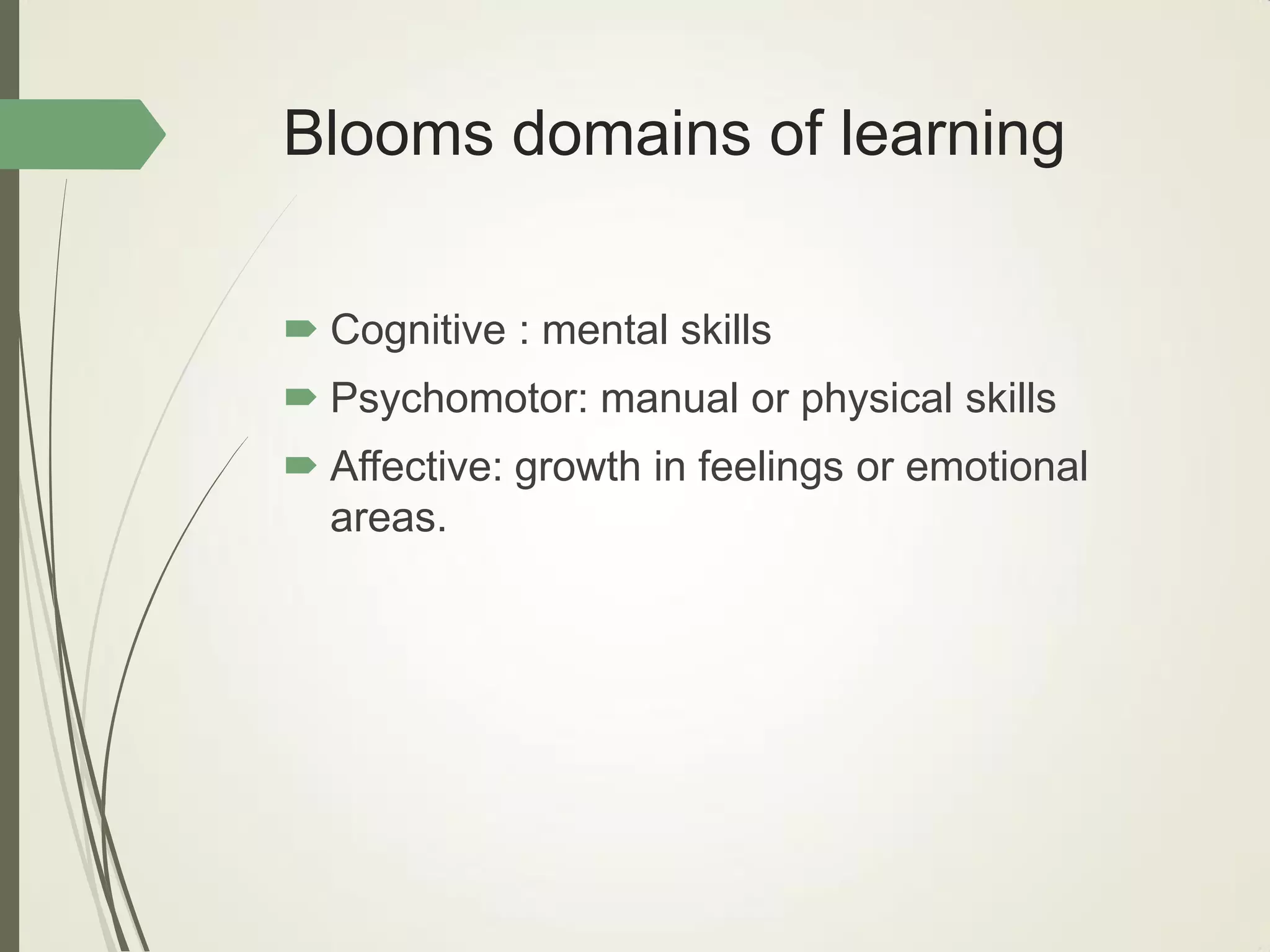
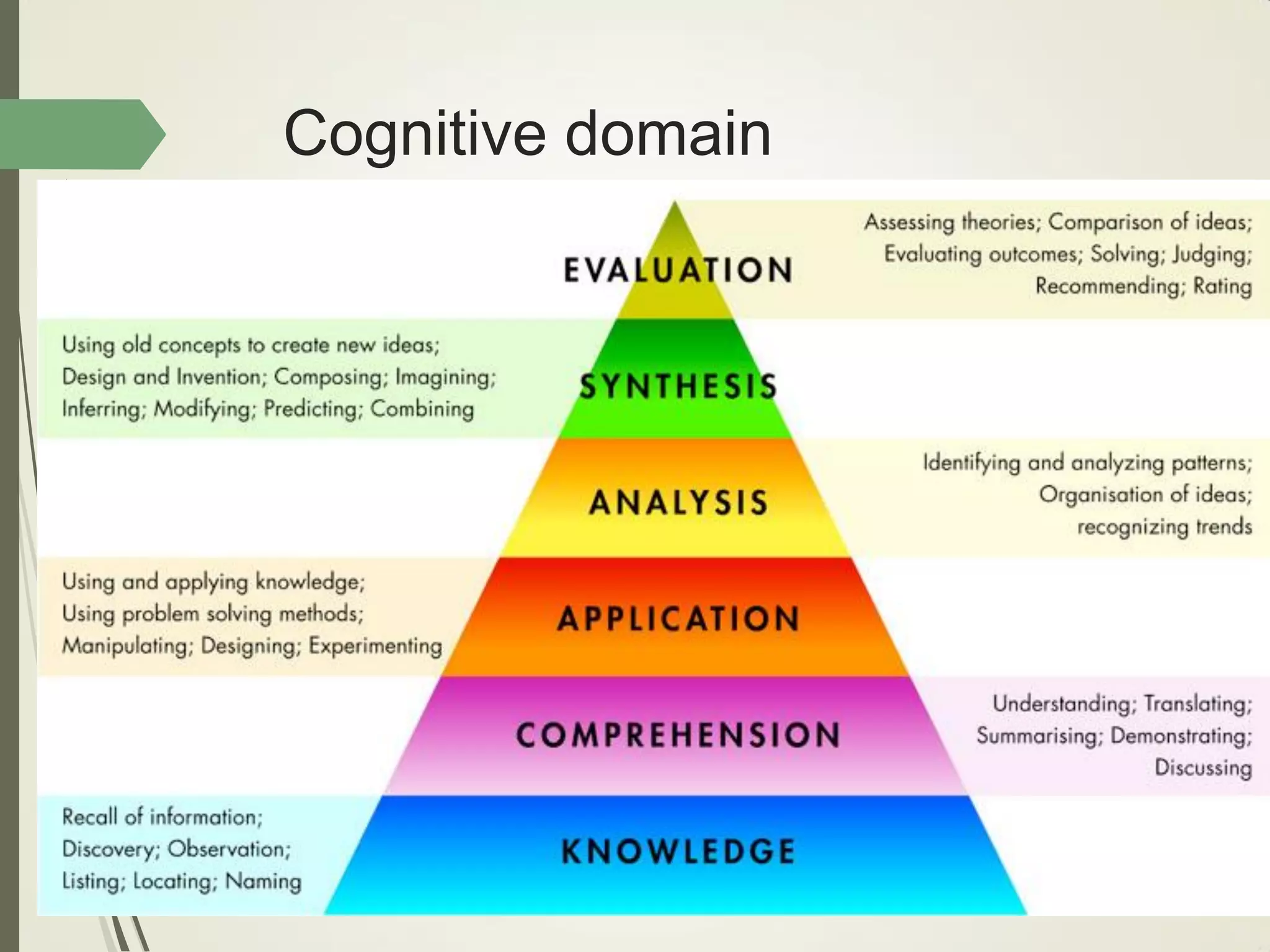
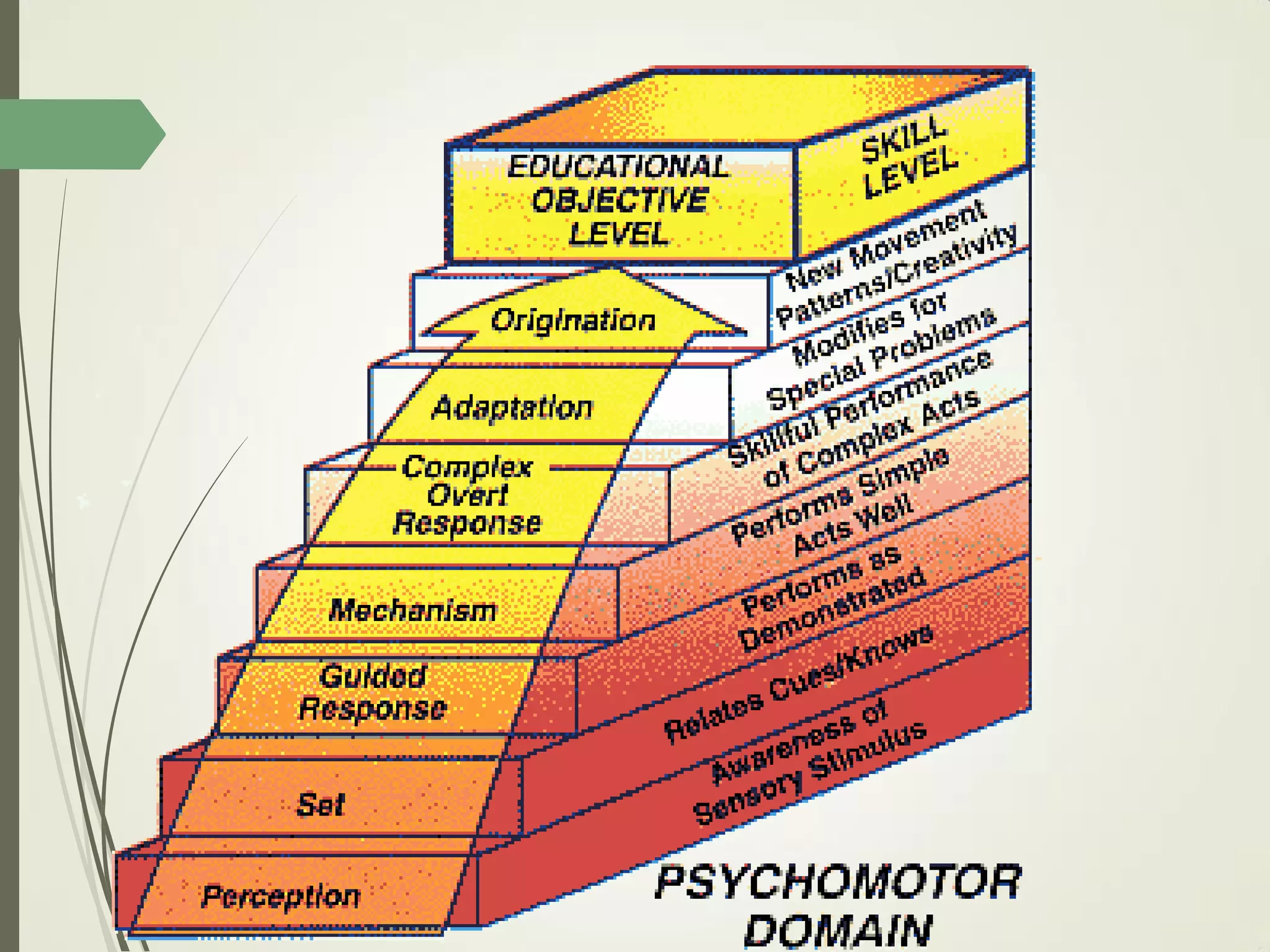
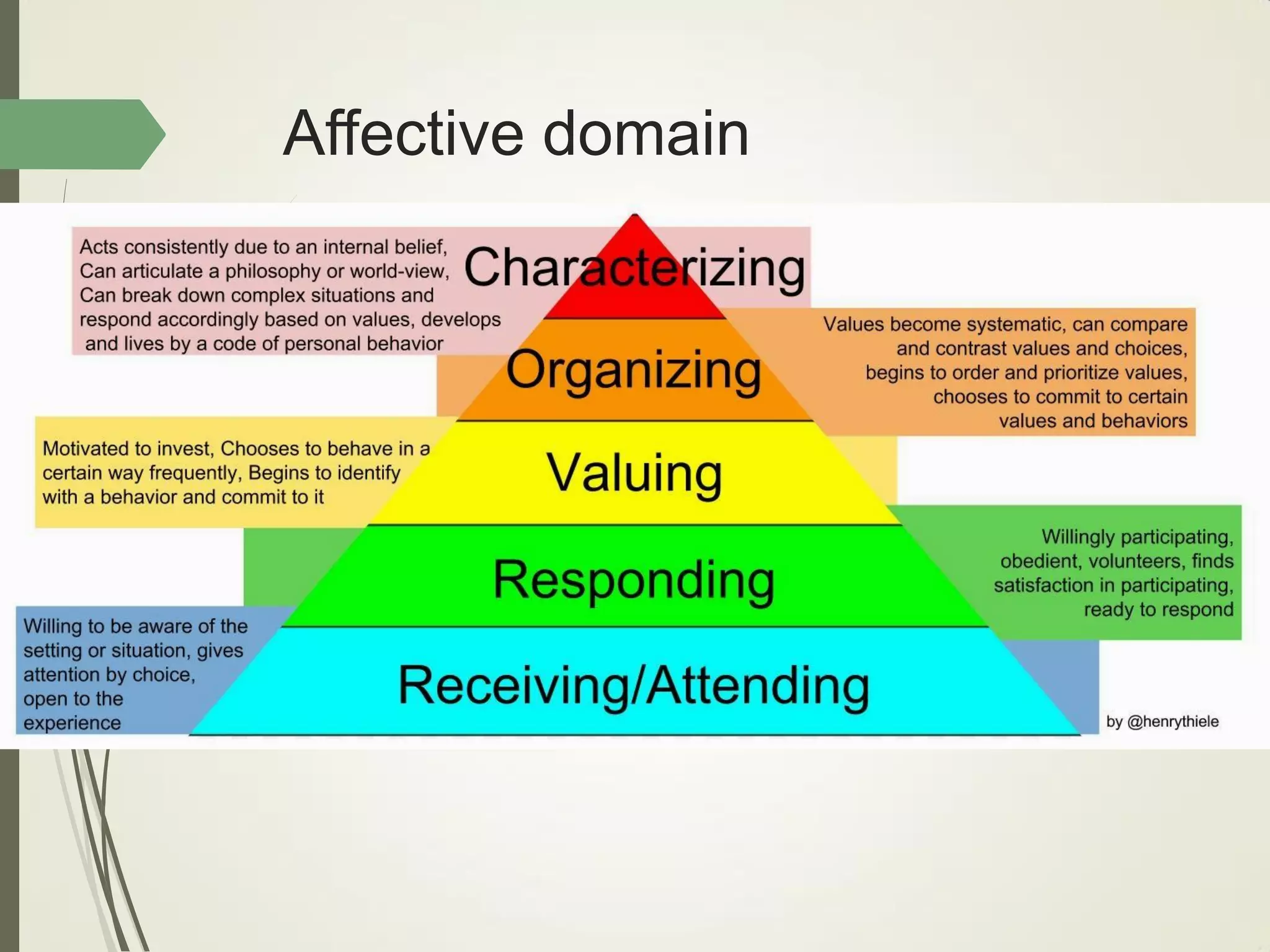
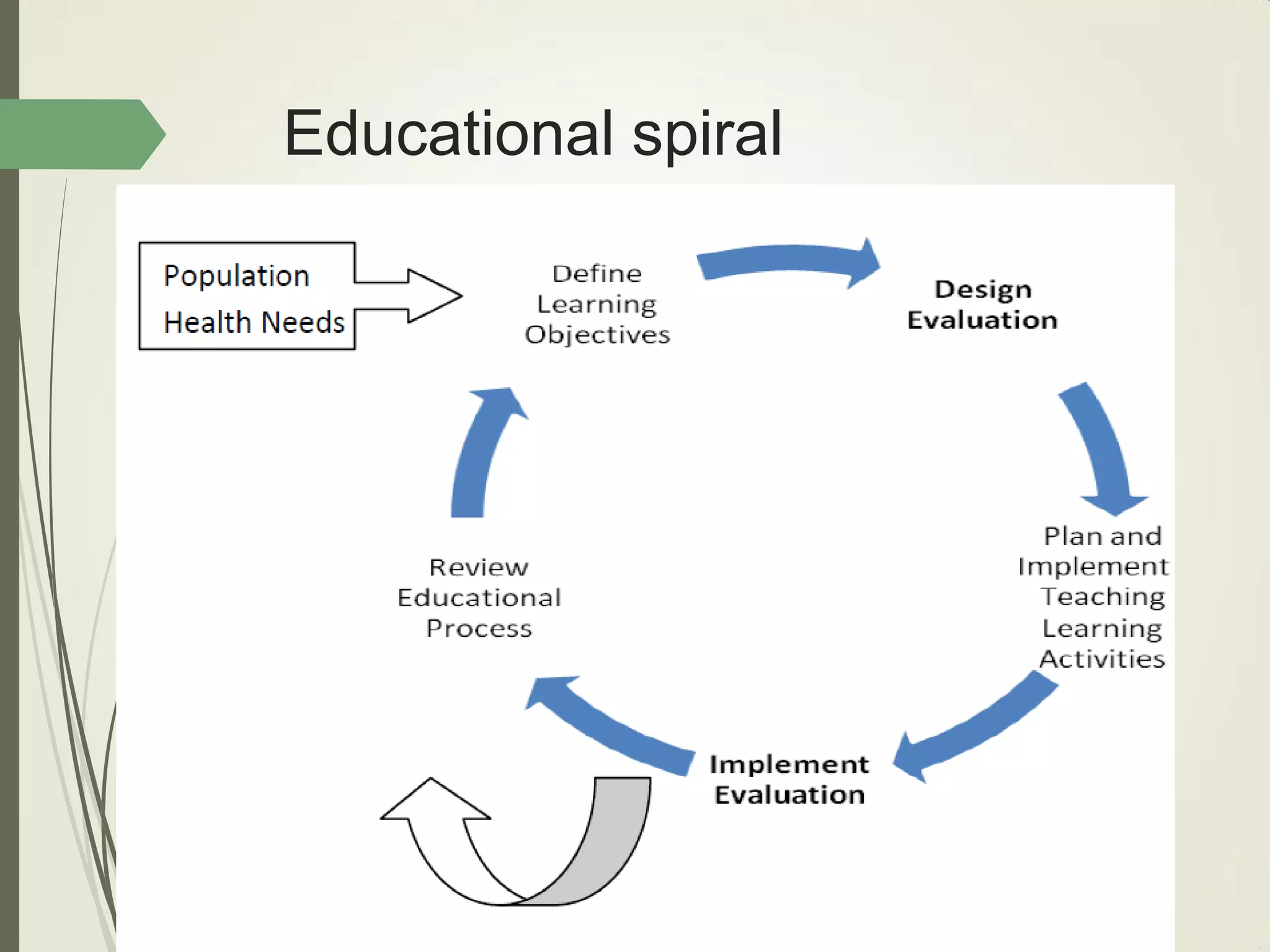
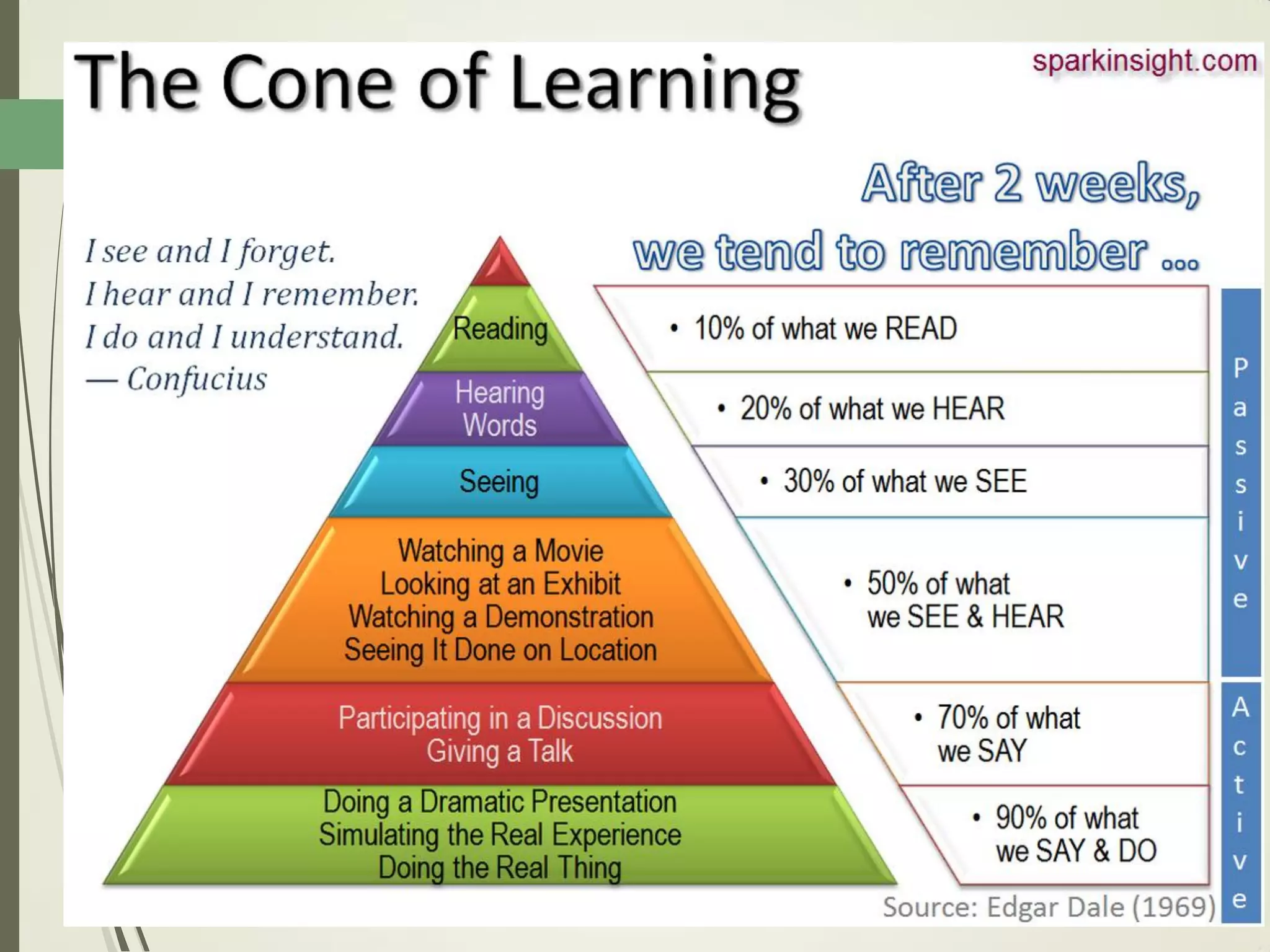
This document outlines principles of learning, including learning theories such as behaviorism, cognitivism, humanism, constructivism, and social learning theory. It discusses Bloom's domains of learning, including cognitive, psychomotor, and affective domains. The educational spiral and components of specific learning objectives are also explained. The overall goal is to understand learning as a process and product, major learning theories, the importance of the educational spiral, how to relate instructional activities to Bloom's domains, and describe qualities and elements of specific learning objectives.