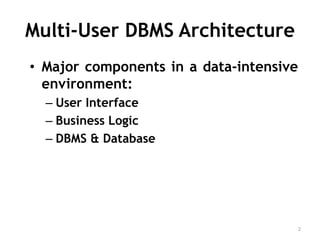
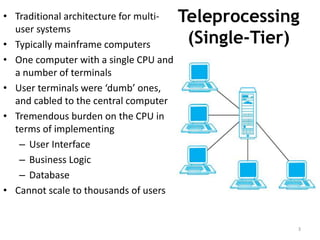
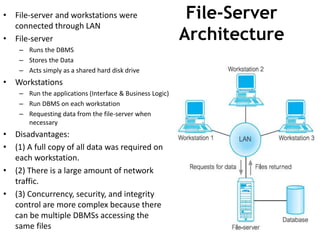
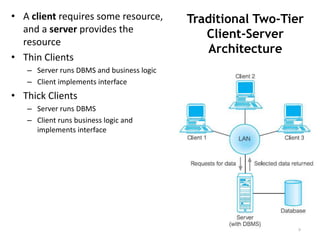
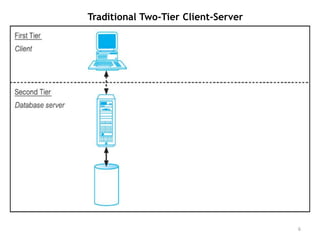
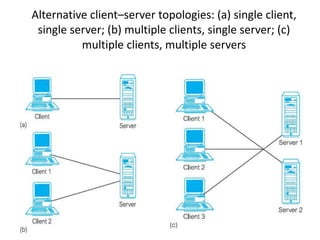
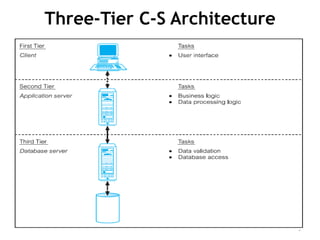
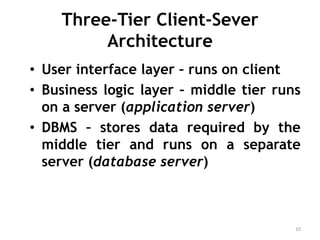
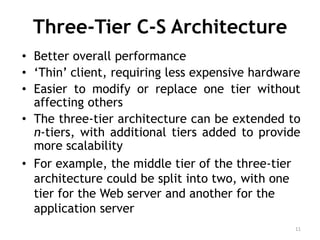
The document discusses different architectures for multi-user database management systems (DBMS). It describes teleprocessing/single-tier, file-server, and traditional two-tier client-server architectures. The traditional two-tier architecture had disadvantages like being resource-intensive for clients. The three-tier client-server architecture was then proposed in 1995 to address these issues by separating the user interface, business logic, and data storage layers across client and multiple server machines. This three-tier approach improved performance, used less expensive clients, and made each layer more modular and scalable.