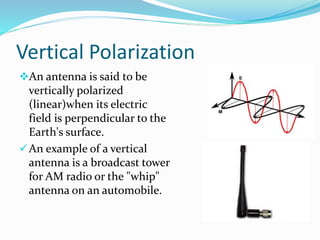
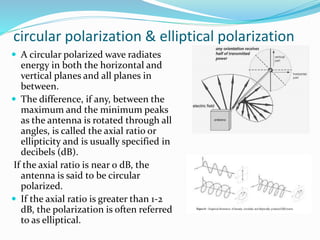
Polarization describes the orientation of an antenna's electric field. There are several types of polarization: vertical, horizontal, and circular polarization radiate linearly, while elliptical polarization is a mix of linear and circular. Different polarization types are used for different applications - vertical polarization radiates well in all directions for mobile devices, horizontal is commonly used for television to avoid interference, and circular polarization is ideal for satellite communications since it maintains signal integrity despite environmental anomalies.