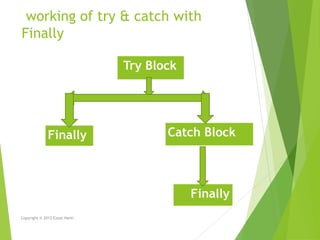
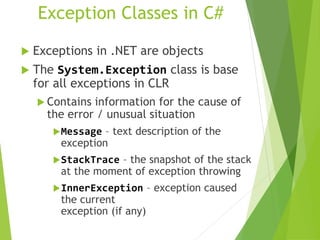
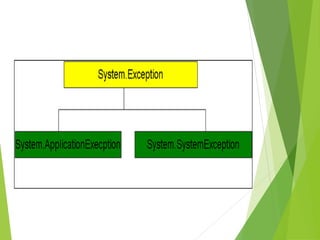
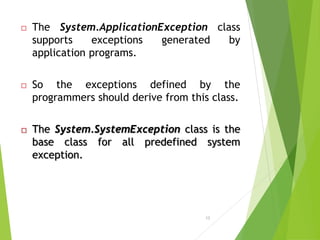
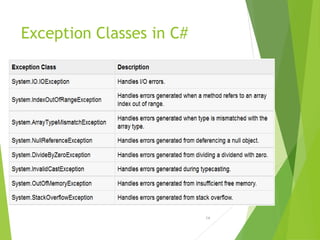
This document discusses exception handling in C#. It defines an exception as a problem that arises during program execution, such as dividing by zero. It describes how try, catch, and finally keywords allow programmers to transfer control when exceptions occur. The try block identifies code that could cause exceptions. Catch blocks handle specific exception types. Finally blocks contain code that always executes regardless of exceptions. Common exception classes derive from System.Exception. The example shows a method catching and handling a DivideByZeroException using try, catch, and finally.









![1. finally
2. {
3. Console.WriteLine("Result: {0} ", result);
4. }
5. }
6. static void Main(string[] args)
7. {
8. division(10,0);
9. Console.ReadLine();
10. } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160412165828/85/Presentation1-16-320.jpg)

