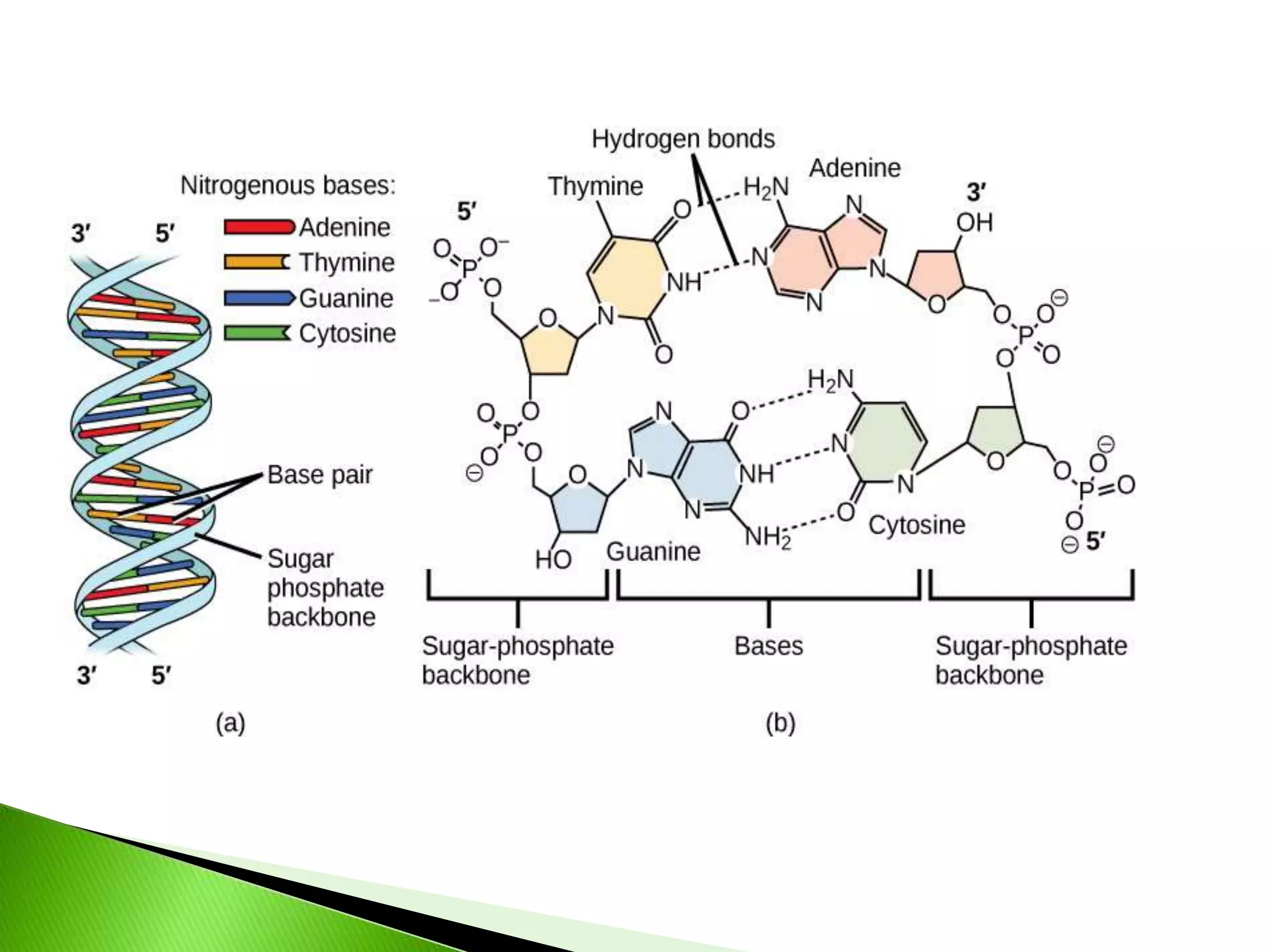
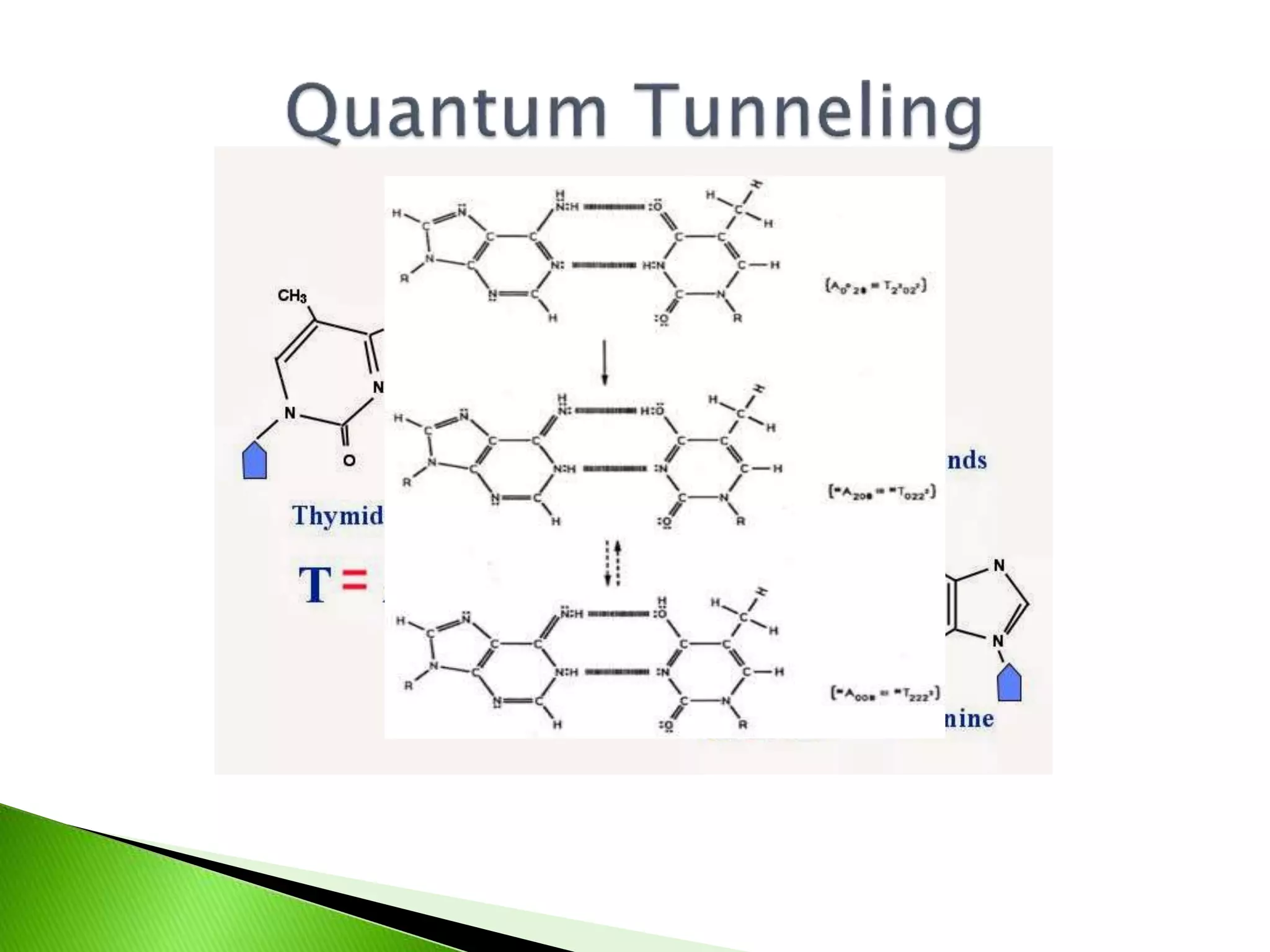
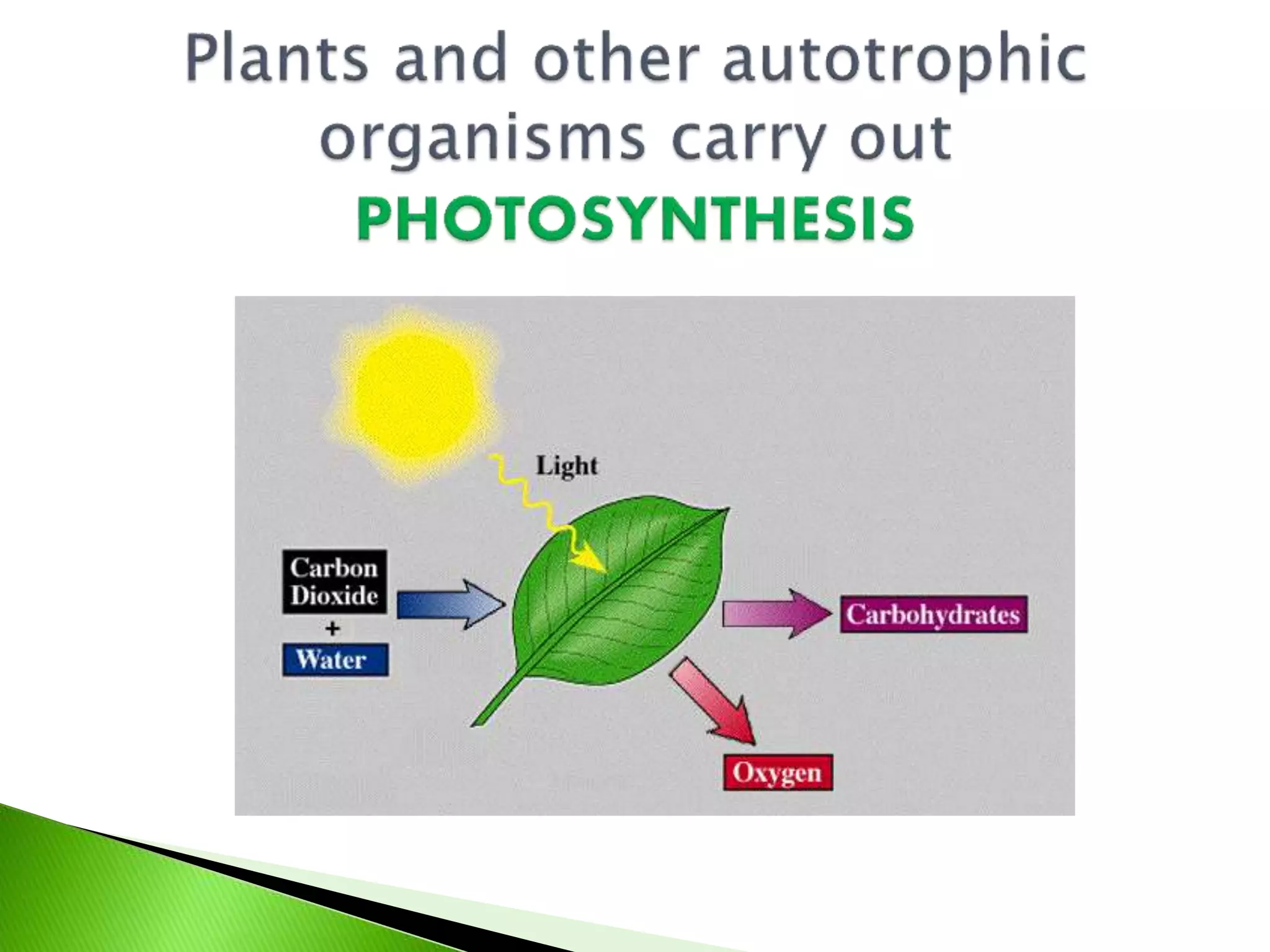
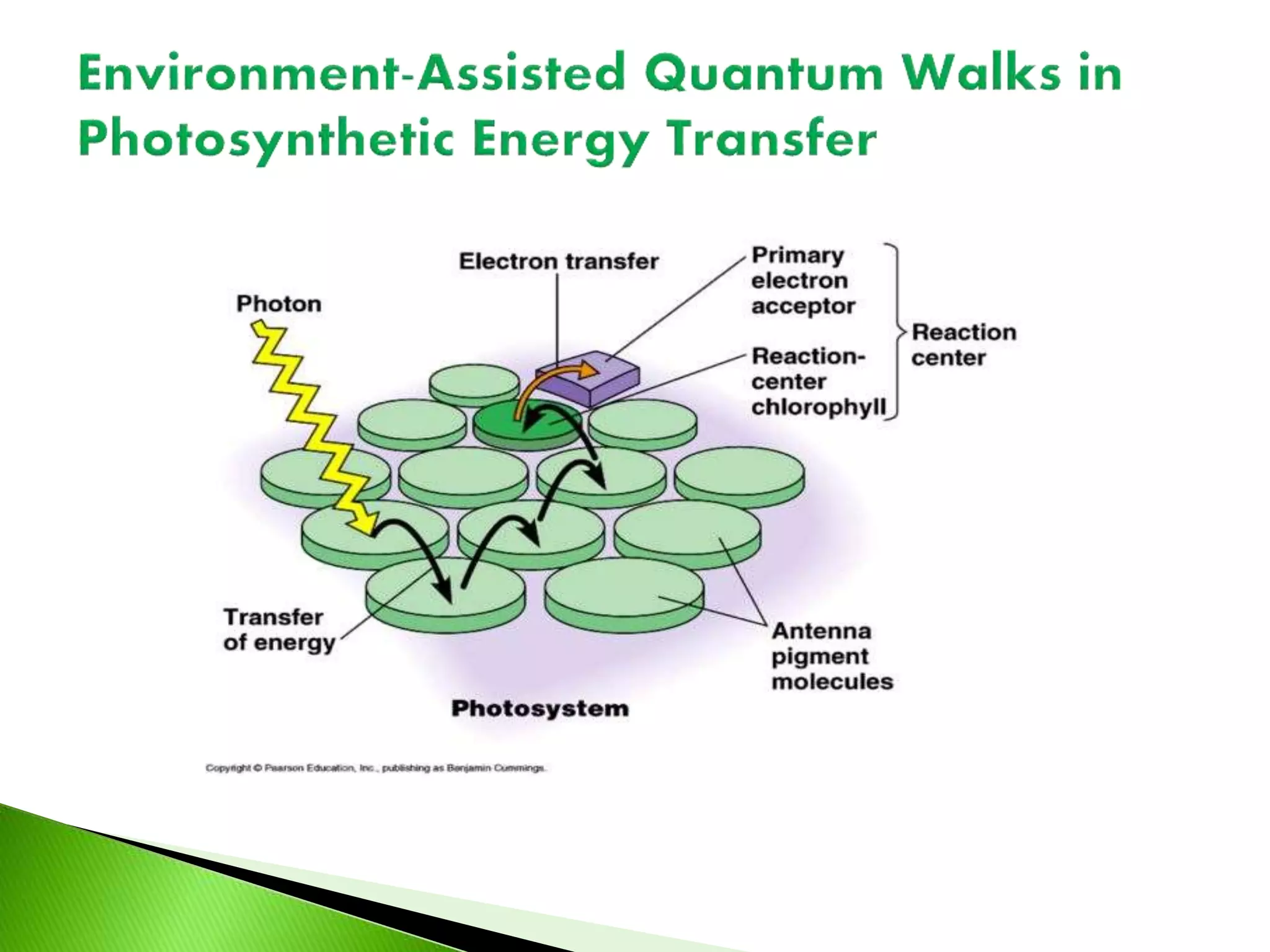
This presentation discusses the emerging field of quantum biology. Quantum biology refers to applying quantum mechanics principles to biological systems and processes. Many biological processes involve energy conversions that occur through quantum mechanical means. It has been an area of science since the early 1900s when quantum physics was developed, founded by scientists like Erwin Schrodinger. Some examples covered include how European robins use cryptochrome in their retinas to sense the Earth's magnetic field for migration via quantum effects. The dual wave-particle nature of light is also discussed as a fundamental example of quantum properties. Several references on the topic are provided.