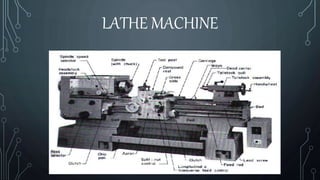
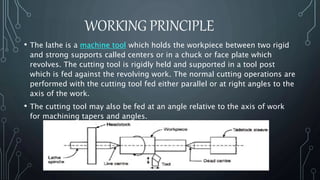
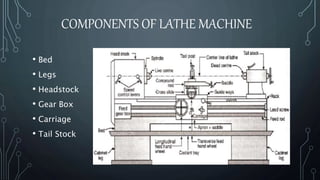
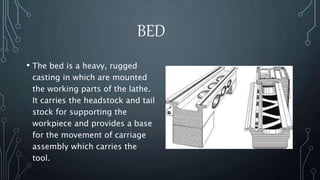
A lathe machine is used to shape materials like metal, wood, glass, and pottery by rotating the workpiece about an axis. It holds the workpiece firmly between centers or in a chuck while a cutting tool is fed into the rotating workpiece. The key components of a lathe include the bed, headstock, gear box, carriage, and tailstock. The headstock houses the spindle that rotates the workpiece while the gear box contains different sized gears to control the spindle speed.