This document discusses socket programming concepts in Java including server-client communication using sockets, the InetAddress class and its methods like getLocalHost(), getByName(), and getAllByName(), and the Socket and ServerSocket classes. It provides code examples to demonstrate how to use these classes and methods to establish connections between a client and server and exchange data over the network.




![getLocalHost()
import java.net.*;
class obtainIP
{
public static void main(String args []) throws UnknownHostException
{
InetAddress adr;
adr=InetAddress.getLocalHost();
System.out.println("nInfo about Machine: " + adr);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptofsocket-121030031042-phpapp02/85/Ppt-of-socket-7-320.jpg)
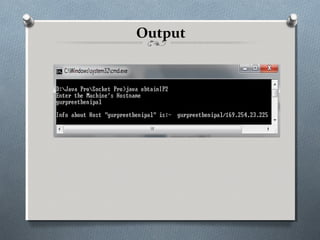
![getByName(String hostName)
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class obtainIP2
{ public static void main(String args []) throws IOException
{ InetAddress adr;
String host;
DataInputStream input=new DataInputStream(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the Machine's Hostname");
host=input.readLine();
try {
adr=InetAddress.getByName(host);
System.out.println("nInfo about Host "" + host + "" is:- " + adr);
}
catch( UnknownHostException e) {
System.out.println("No such host exist"); }
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptofsocket-121030031042-phpapp02/85/Ppt-of-socket-8-320.jpg)
![getAllByName(String hostName)
import java.io.*; try {
import java.net.*; adr=InetAddress.getAllByName(host);
class obtainIP3 for(int i=0;i<adr.length;i++)
{ {
public static void main(String args [ ]) j++;
throws IOException System.out.println(j +"t" + adr[i]);
{ }
InetAddress adr[]; int j=0; }
String host;
DataInputStream input=new catch( UnknownHostException e)
DataInputStream(System.in); {
System.out.println("No such host exist");
System.out.println("Enter host "); }
host=input.readLine(); }
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptofsocket-121030031042-phpapp02/85/Ppt-of-socket-10-320.jpg)
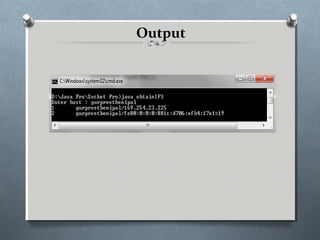
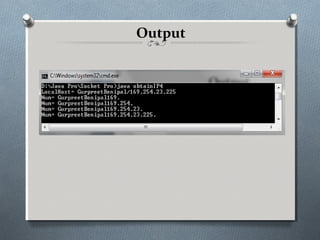
![getAddress() & getHostName()
import java.net.*;
class obtainIP4
{ public static void main(String args []) throws UnknownHostException
{
String msg;
byte num[];
InetAddress adr;
adr=InetAddress.getLocalHost();
num=adr.getAddress();
msg=adr.getHostName();
System.out.println("LocalHost= " + adr);
for(int i=0;i<num.length;i++)
{
msg +=(num[i] & 255) + ".";
System.out.println("Num= " + msg);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptofsocket-121030031042-phpapp02/85/Ppt-of-socket-12-320.jpg)