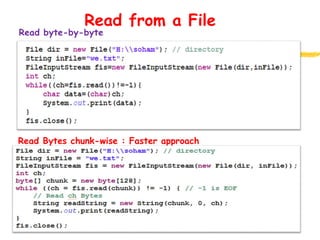
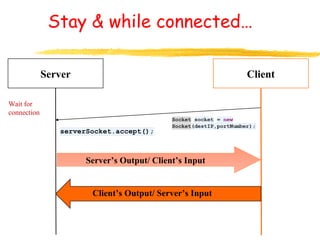
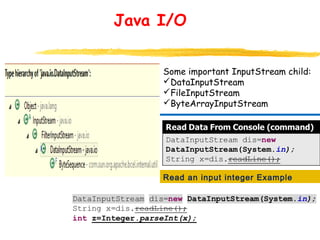
This document discusses network programming in Java. It shows how to get the local host address and address of google.com. It defines a server as a program that listens on a TCP port for connections and a client as a program that initiates connections. It demonstrates how to create a server socket to listen on a port and how a client socket can connect to an IP address and port. It also discusses Java I/O streams for input and output and how to handle files in Java including checking if a directory exists, creating it if not, opening output streams to write to files, and approaches for reading from files.

![public static void main(String[] args) throws
UnknownHostException {
InetAddress localAddress = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
System.out.println(localAddress.getHostAddress());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws
UnknownHostException {
InetAddress googleAddress =
InetAddress.getByName("www.google.com");
System.out.println(googleAddress.getHostAddress());
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networkprogramming1-141013060139-conversion-gate01/85/Network-programming1-2-320.jpg)


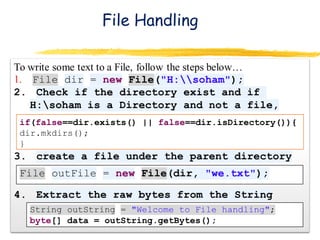

![Write to a File : Second approach
DataOutputStream provides a wrapper over an OutputStream to
write primitive data types, not just byte[]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networkprogramming1-141013060139-conversion-gate01/85/Network-programming1-9-320.jpg)