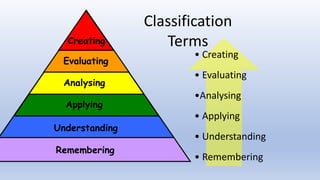
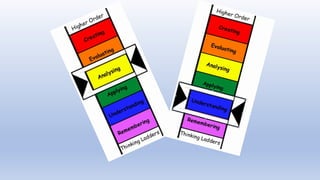
This document provides information about Bloom's Taxonomy, which was created by American psychologist Benjamin Bloom to promote higher-order thinking in education. Bloom's Taxonomy classifies different levels of thinking from lower to higher order, including Remembering, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, Evaluating, and Creating. The taxonomy is used in education to encourage skills like critical thinking, problem solving, and debate. It can be applied across subjects and helps teachers plan questions and assessments at different cognitive levels. Both curriculum and home activities can utilize Bloom's Taxonomy to support student learning.