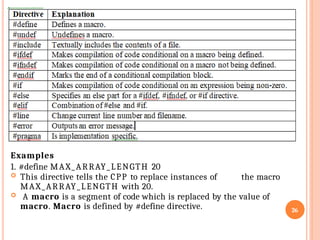
POINTERS Pointers are variables that store the memory address of other variables, acting as references to data locations rather than the data itself, crucial for efficient memory management, dynamic data structures (like linked lists, trees), and low-level operations in languages like C/C++. They use the address-of operator (&) to get a variable's address and the dereference operator (*) to access or change the value at that address, enabling powerful features such as passing data by reference to functions, allowing them to modify original variables.
This video provides a helpful analogy to understand pointers:
Related video thumbnail
08:07
Bro Code
YouTube • 10 Apr 2025
Key Concepts
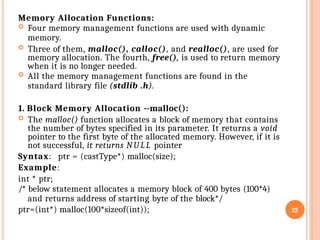
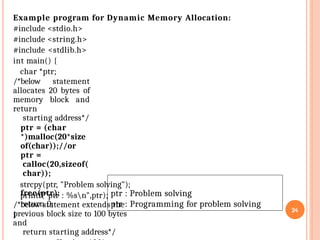
Declaration: data_type *pointer_name; (e.g., int *ptr;).
Storing Address: Use the address-of operator (&) to assign a variable's memory location to a pointer (e.g., ptr = &myVariable;).
Dereferencing: Use the asterisk (*) to access the value stored at the address the pointer holds (e.g., *ptr = 10; changes the value of myVariable).
Watch this video for a step-by-step explanation of declaring and using pointers:
Related video thumbnail
1m
HenrikM Dev
YouTube • 11 Apr 2025
Common Uses
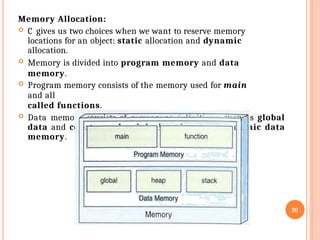
Dynamic Memory Allocation: Managing memory for data structures that grow and shrink at runtime.
Efficient Array Handling: Accessing and manipulating array elements, including strings (character arrays).
Pass-by-Reference: Allowing functions to modify variables outside their scope, improving performance by avoiding large data copies.
Function Pointers: Passing functions as arguments to other functions (callbacks).
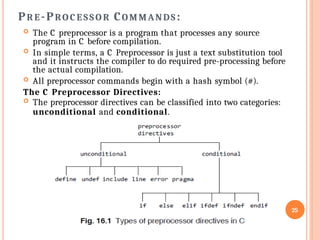
Important Considerations
Memory Safety: Dereferencing an invalid or uninitialized pointer (a "wild pointer" or "dangling pointer") leads to undefined behavior or program crashes (segmentation faults).
Operator Precedence: Parentheses () are often needed with dereferencing to control operation order, e.g., (*ptr)++ vs. *ptr++.
Pointers are easy!
Pointers in C are variables that store the memory address of another variable or data structure. They help in avoiding memory wast...
YouTube
C Pointers
In C, a pointer is a variable that stores the memory address of another variable. Pointers are important because they allow you to...
W3Schools
Pointers - IBM
A pointer type variable holds the address of a data object or a function. A pointer can refer to an object of any one data type; i...

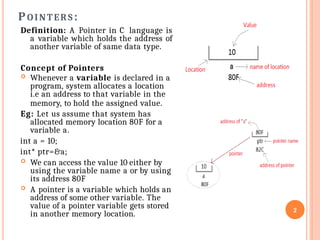



![Pointer to an Array
An array name is a constant pointer to the first element of
the array.
Therefore, in the declaration − double balance[50];
balance is a pointer to &balance[0], which is the address of
the first element of the array balance.
Thus, the following program fragment assigns p as the
address of the first element of balance −
double *p;
double balance[10];
p = balance;
It is legal to use array names as constant pointers, and vice
versa. Therefore, *(balance + 2) is a legitimate way of
accessing the data at balance[2].
Once you store the address of the first element in 'p', you can
access the array elements using *p, *(p+1), *(p+2) and so on.
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppscunit-3pointers-260120081102-d3cbcc10/85/PPSC-Unit-3-POINTERS-pptx-FOR-STUDY-PURP-7-320.jpg)
![#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
/* an array with 3 elements */
double balance[3] = {1000.0, 50000.0, 300.4};
double *p;
int i;
p =
balance;
/* output
each array
element's
value */
for ( i = 0; i < 3; i++ )
printf( "Array values using balance as addressn");
for ( i = 0; i < 3; i++ )
printf("*(balance + %d) : %.2fn", i, *(balance + i)
);
return 0;
}
8
Output:
Array values using
pointer
*(p + 0) : 1000.00
*(p + 1) :50000.00
printf( "Array values using pointern");*(p + 2) : 300.40
Array values using balance as
address
printf("*(p + %d) : %.2fn", i, *(p + i) );*(balance + 0) : 1000.00
*(balance + 1) :
50000.00
*(balance + 2) : 300.40
Example Program:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppscunit-3pointers-260120081102-d3cbcc10/85/PPSC-Unit-3-POINTERS-pptx-FOR-STUDY-PURP-8-320.jpg)

![Pointer Arithmetic
The following Arithmetic operations can be performed on
10
pointer variable vPtr
v[0] v[1] v[2] v[3] v[4]
pointers
Increment/decrement pointer (++ or --)
Add or Subtract an integer to a pointer( + or += , - or -=)
Pointers may be subtracted from each other
For example, consider integer array with 5 elements on machine with 4
byte for int datatype.
– vPtr points to first element v[ 0 ]
• at location 3000 (vPtr = 3000)
– vPtr += 2; sets vPtr to 3008
• vPtr points to v[ 2 ] (incremented by 2), but the machine has
4
byte for int datatype, so it points to address 3008
location
3000 3004 3008 3012
3016](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppscunit-3pointers-260120081102-d3cbcc10/85/PPSC-Unit-3-POINTERS-pptx-FOR-STUDY-PURP-10-320.jpg)
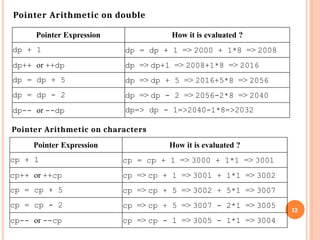


![Pointers and Two-Dimensional Arrays:
Assume that we have a two-dimensional array of integers.
int table[3][4];
When we dereference the array name, we don‟t get one integer, we get an
array of integers. In other words, the dereference of the array name of a two-
dimensional array is a pointer to a one-dimensional array.
Each element in the figure is shown in both index and pointer notation.
Note that table t[0] refers to an array of four integer values. * (table +0)
also refers to an array of four integers.
table [ 0 ] is identical to * ( table + 0 )
To refer to a row, we dereference the array pointer, which gives us a
pointer to a row. Given a pointer to a row, to refer to an individual element,
we dereference the row pointer. This double dereference is given by
*(*(table )
)
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < 4; j++)
printf("%6d", *( *(table + i) + j));
printf( "n" );
} // for i
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppscunit-3pointers-260120081102-d3cbcc10/85/PPSC-Unit-3-POINTERS-pptx-FOR-STUDY-PURP-15-320.jpg)
![Pointers and Strings
We can create a two dimensional array and save multiple
strings in it.
Example: In the below code, we are storing 4 cities name in a
string array city.
char city[4][12] = { "Chennai", "Kolkata", "Mumbai", "New
Delhi" };
Memory representation of the city array is as follows:
16
The problem with this approach is that we are allocating 4x12 = 48
bytes memory to the city array and we are only using 33 bytes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppscunit-3pointers-260120081102-d3cbcc10/85/PPSC-Unit-3-POINTERS-pptx-FOR-STUDY-PURP-16-320.jpg)
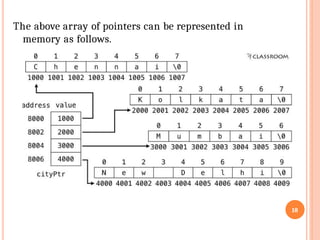
![We can save those unused memory spaces by using pointers as
shown below.
char *cityPtr[4] = { "Chennai", "Kolkata", "Mumbai", "New
Delhi" };
Memory representation of the pointer cityPtr is as follows:
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppscunit-3pointers-260120081102-d3cbcc10/85/PPSC-Unit-3-POINTERS-pptx-FOR-STUDY-PURP-17-320.jpg)
![Array of Pointers
Just like we can declare an array of int, float or char etc, we can
also declare an array of pointers.
Syntax: datatype *array_name[size];
Example: int *arrop[5]
Here arrop is an array of 5 integer pointers. It means that this
array can hold the address of 5 integer variables
Example Program:
#include<stdio.h>
int main() {
int *arrop[3]; //array
of pointers
int a = 10, b = 20, c = 50, i;
arrop[0] = &a;
arrop[1] = &b;
arrop[2] = &c;
for(i = 0; i < 3;
i++)
printf("Address = %dt Value = %dn", arrop[i], *arrop[i]);
return 0;
} 19
Output:
Address =
387130656
Address =
387130660
Address =
387130664
Value =
10
Value =
20
Value =
50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppscunit-3pointers-260120081102-d3cbcc10/85/PPSC-Unit-3-POINTERS-pptx-FOR-STUDY-PURP-19-320.jpg)