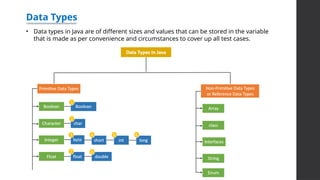
The document is a summer internship report by Syed Ali Azhar from Government Engineering College, Aurangabad, focusing on Core Java concepts. It covers Java fundamentals, including its history, advantages, and disadvantages, as well as key programming principles like OOP concepts, data types, and control statements. The report concludes that Java is a widely used, platform-independent programming language ideal for various applications including mobile and web development.



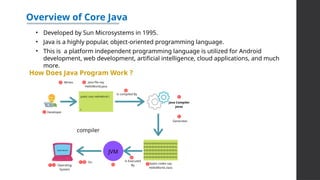



![Hello World Program in Java
class HelloWorld
{
public static void main(String []args)
{
System.out.println(“Hello World!!! ”);
}
};
• Compiling the program :
To compile the program, we must run the Java compiler (javac), with the name
of the source file on “command prompt” like as follows
javac HelloWorld.java
If everything is OK, the “javac” compiler creates a file called
“Test.class”
• Running the program :
java HelloWorld](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syedaliazhar94-250127075413-4549e3c2/85/Power-Point-Presentation-on-Core-Java-For-the-Beginers-9-320.jpg)