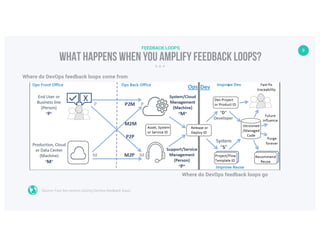
The document discusses the concept of feedback loops, particularly in the context of traffic regulation and behavioral changes. It highlights the Garden Grove experiment where dynamic speed displays led to a significant reduction in speeding by providing real-time feedback to drivers. The document emphasizes the importance of using emotional and relevant data to influence behavior and improve outcomes.