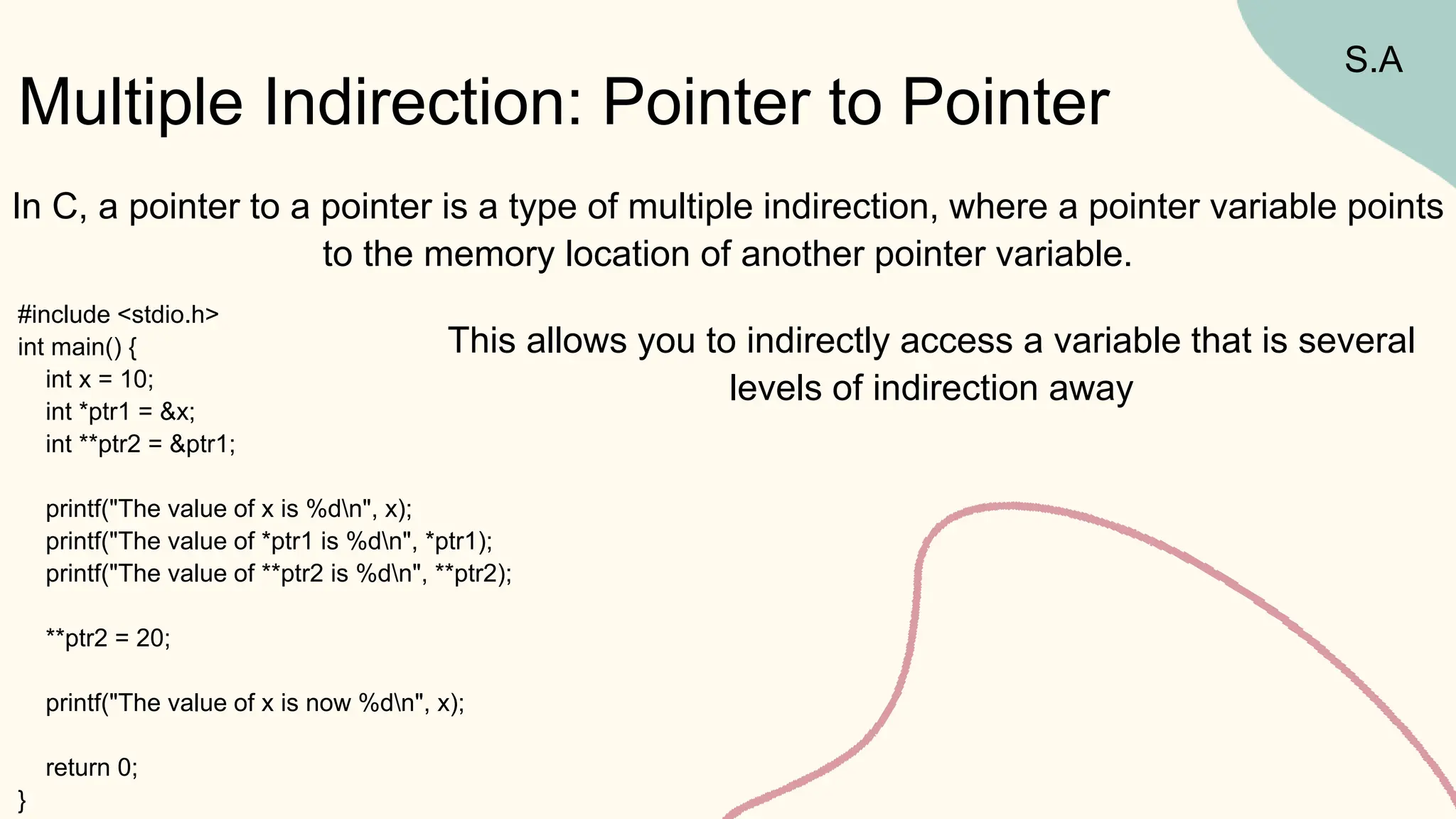
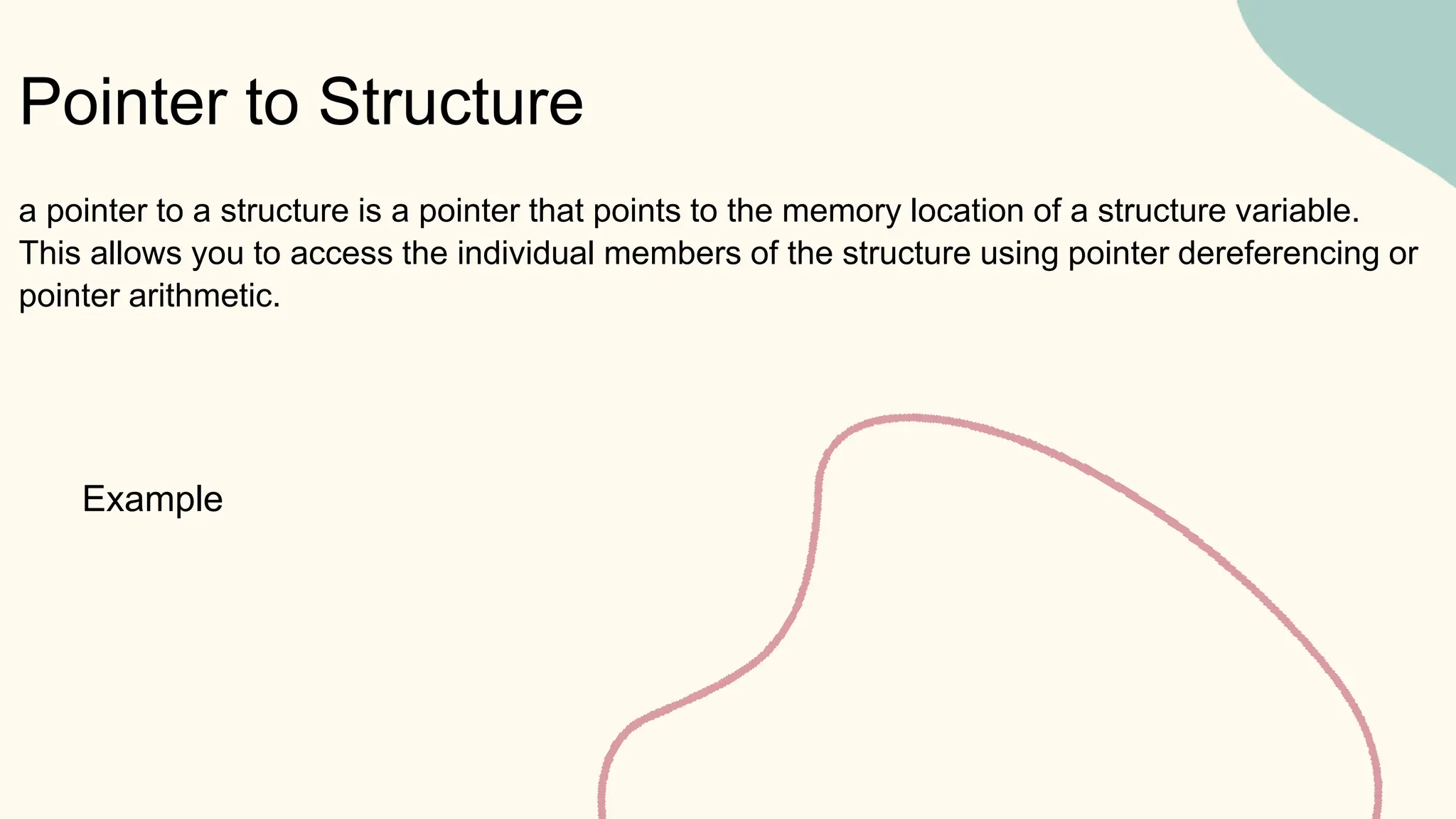
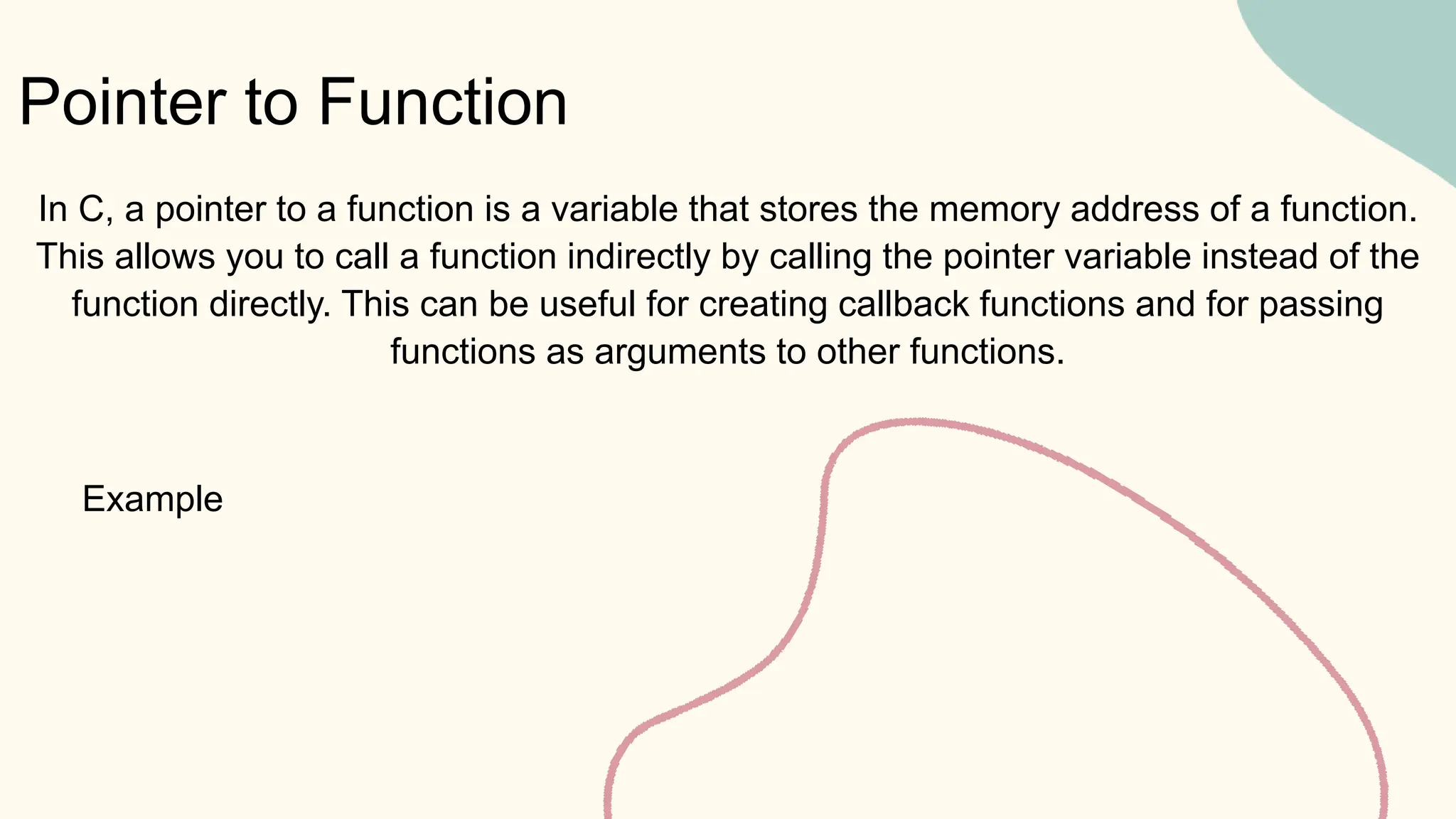
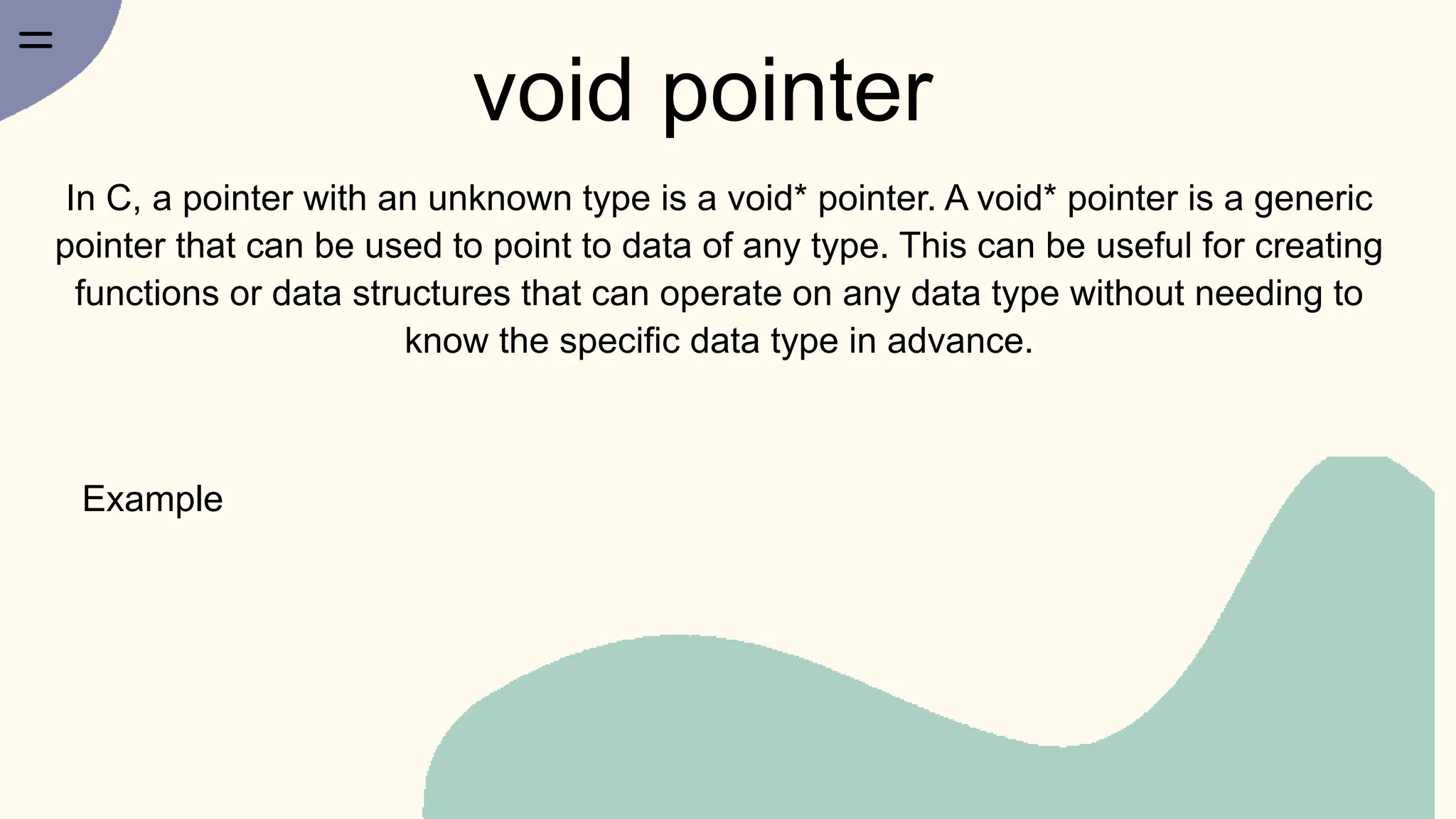
Ahmed Badr Sayed is a mechatronics engineer at Ain Shams University who specializes in embedded systems and embedded Linux. His presentation covers pointers in C, including: (1) declaring and initializing pointers and why they are needed; (2) the difference between passing by value vs. reference; (3) pointer operations like incrementing and subtracting; (4) passing arrays to functions; (5) multiple indirection using pointer to pointer; (6) pointers to structures and functions. He also discusses void pointers, dangling pointers, wild pointers, and NULL pointers. The presentation provides an overview of pointers for programmers to better understand and work with them.







![S.A
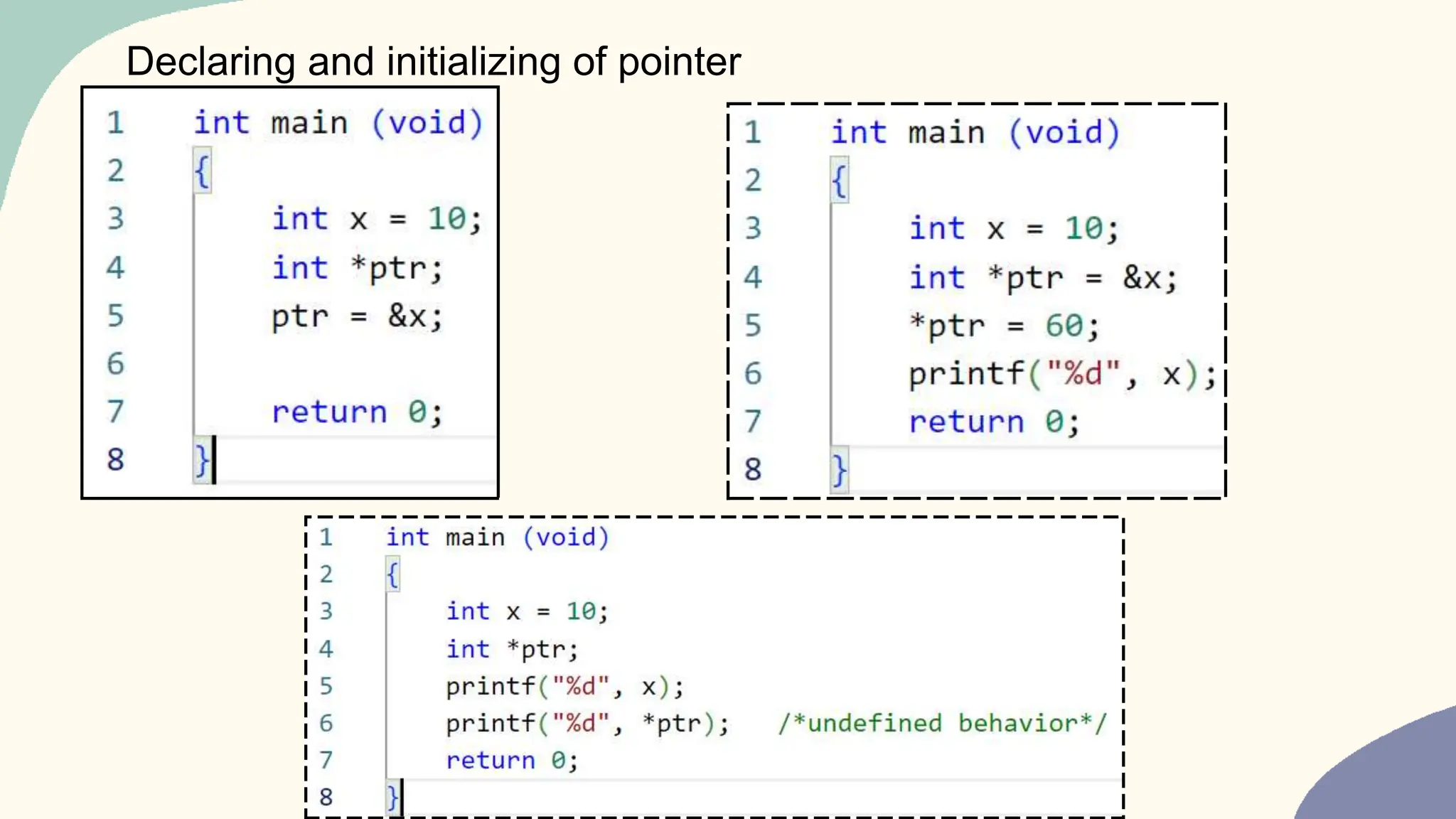
Passing array to function
Remember that name of the array is the address of its first element.
Then arr is the same as &arr[0].
i.e. if we have an array:
int arr[10];
Which means if you passed the array name arr to function called func for example, then
you are passing address to int. So, the function func prototype should be declared as:
void func ( int *ptr);
Now, inside the function func, *ptr means that you are accessing the first element of the
array, *(ptr+1) means that you are accessing the second element of the array, and so on
…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers2024-240209052023-a265487b/75/Pointers_in_c_2024-01-10_embedded-_c-pptx-11-2048.jpg)
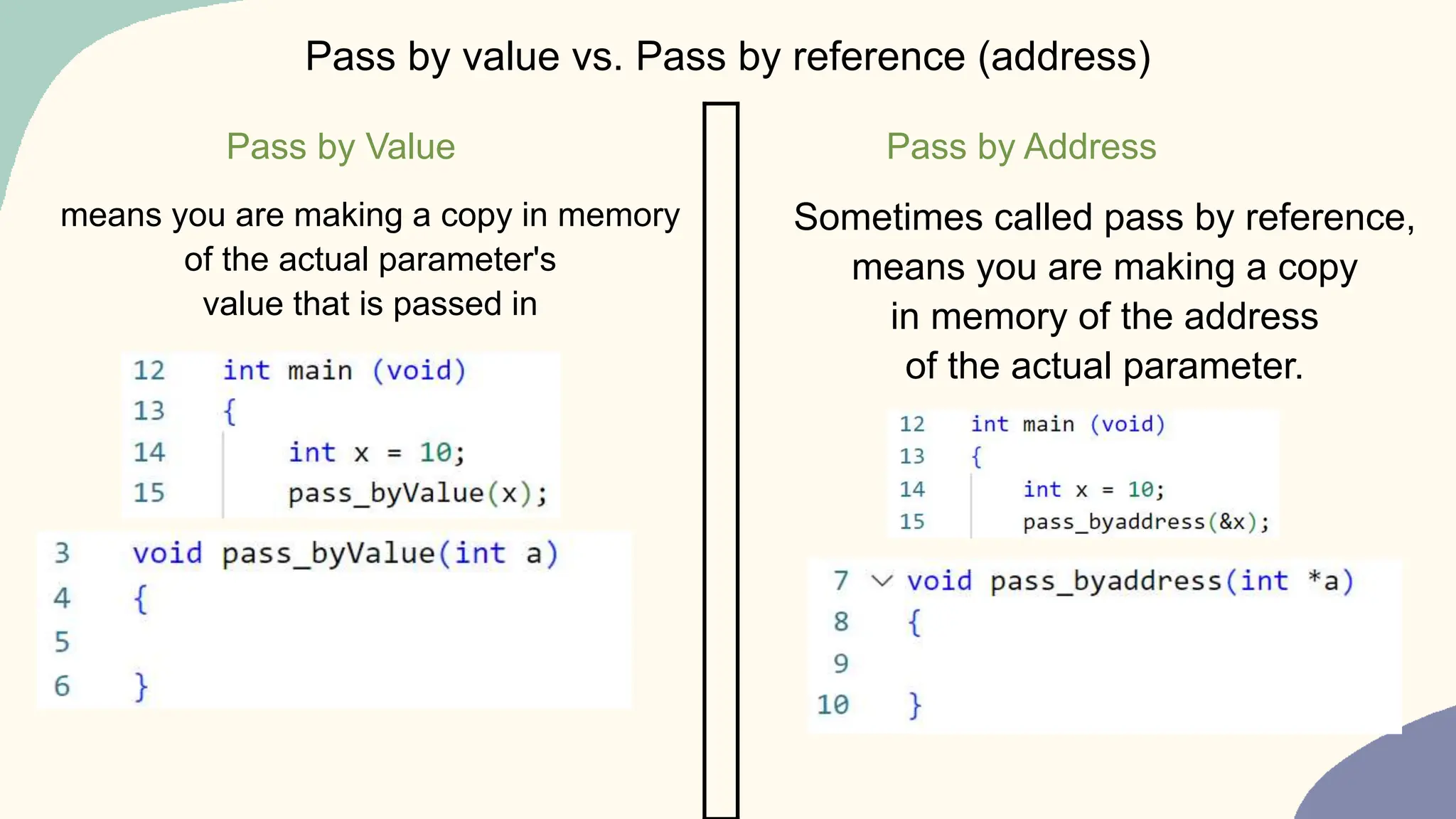
![Subscriptor vs Dereference operators
Example
if we have a pointer int *ptr;
Then ptr[0] is the same as *ptr
Also, ptr[1] is the same as *(ptr+1)
Also, ptr[10] is the same as *(ptr+10).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers2024-240209052023-a265487b/75/Pointers_in_c_2024-01-10_embedded-_c-pptx-12-2048.jpg)