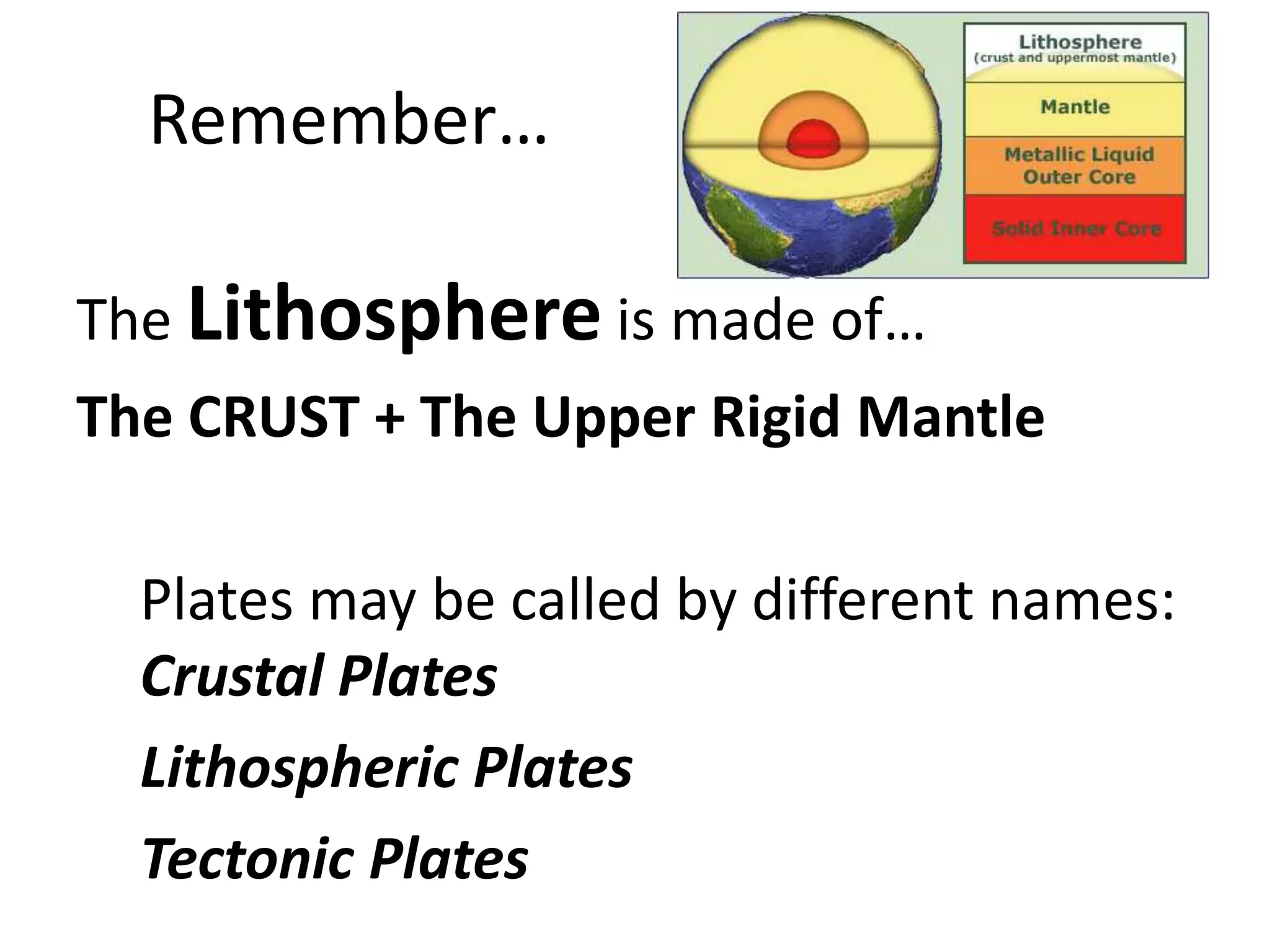
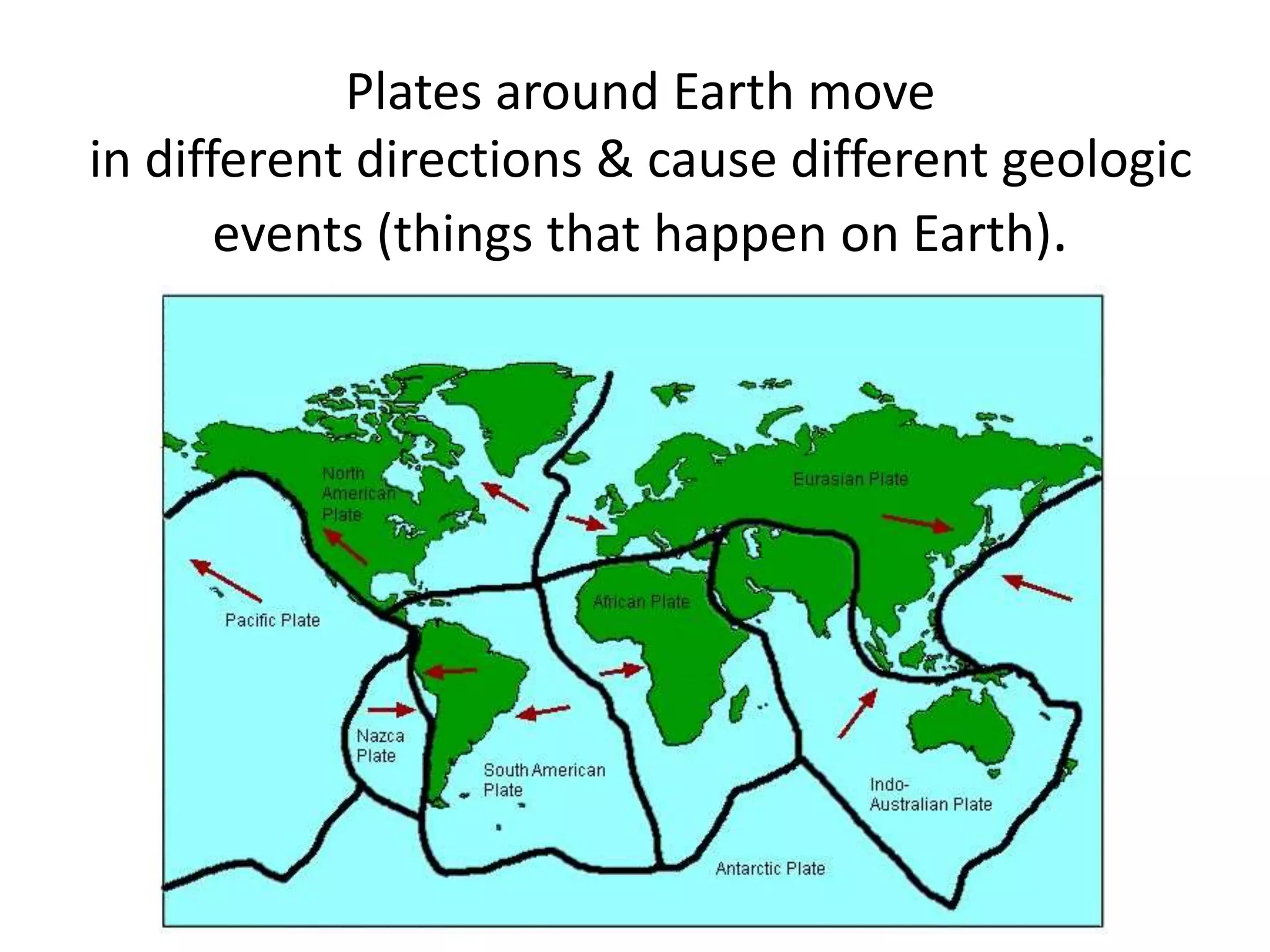
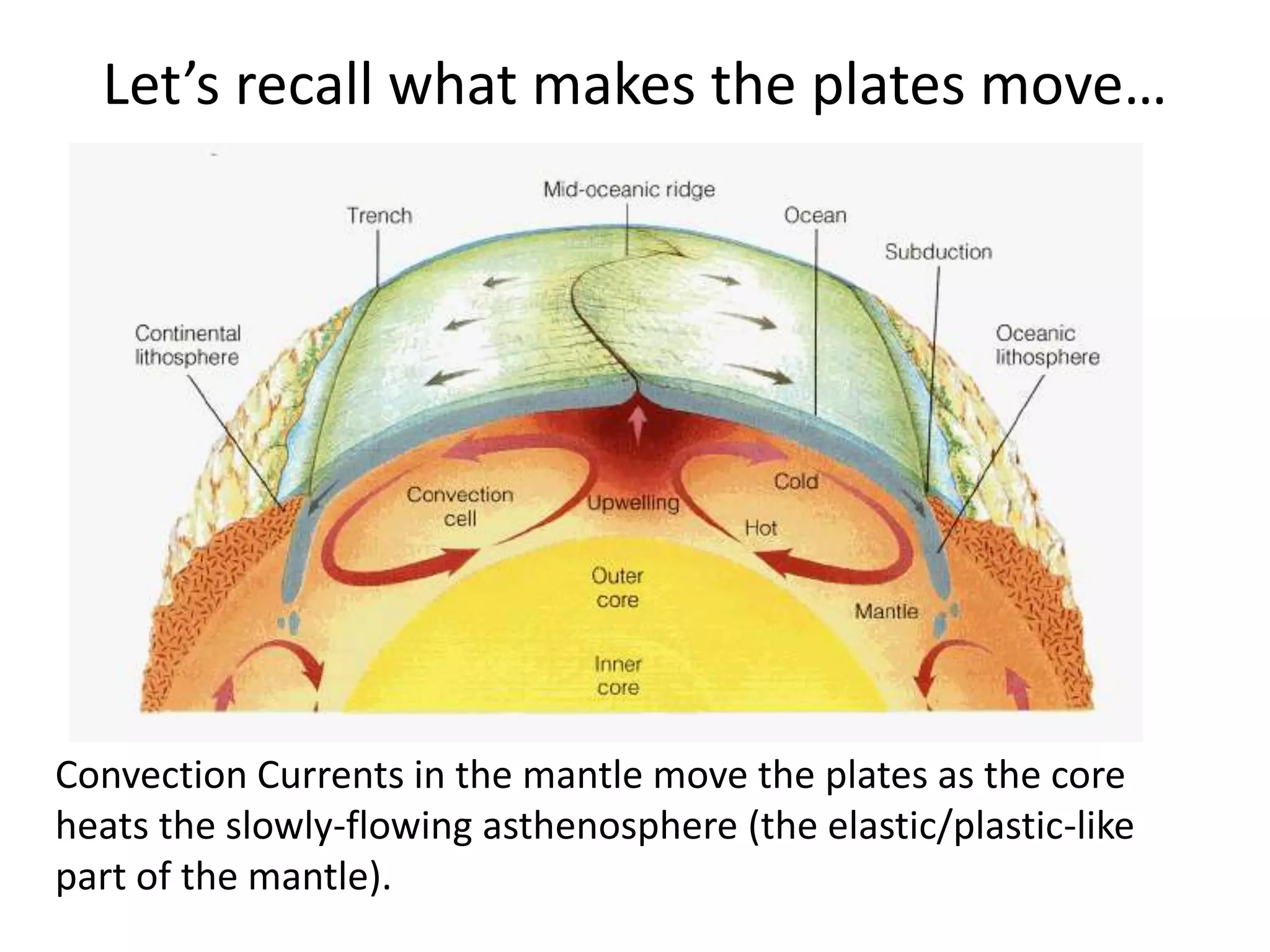
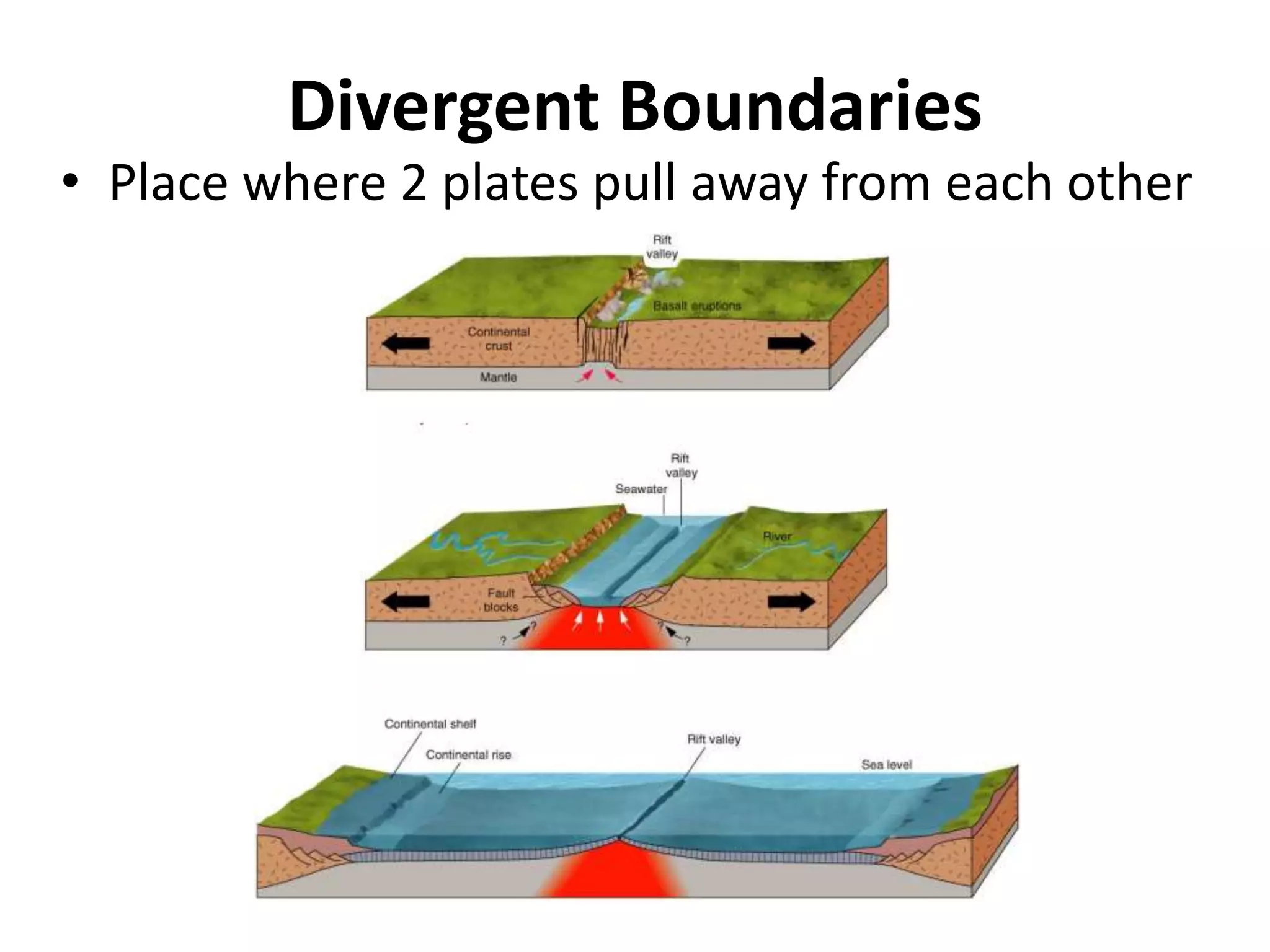
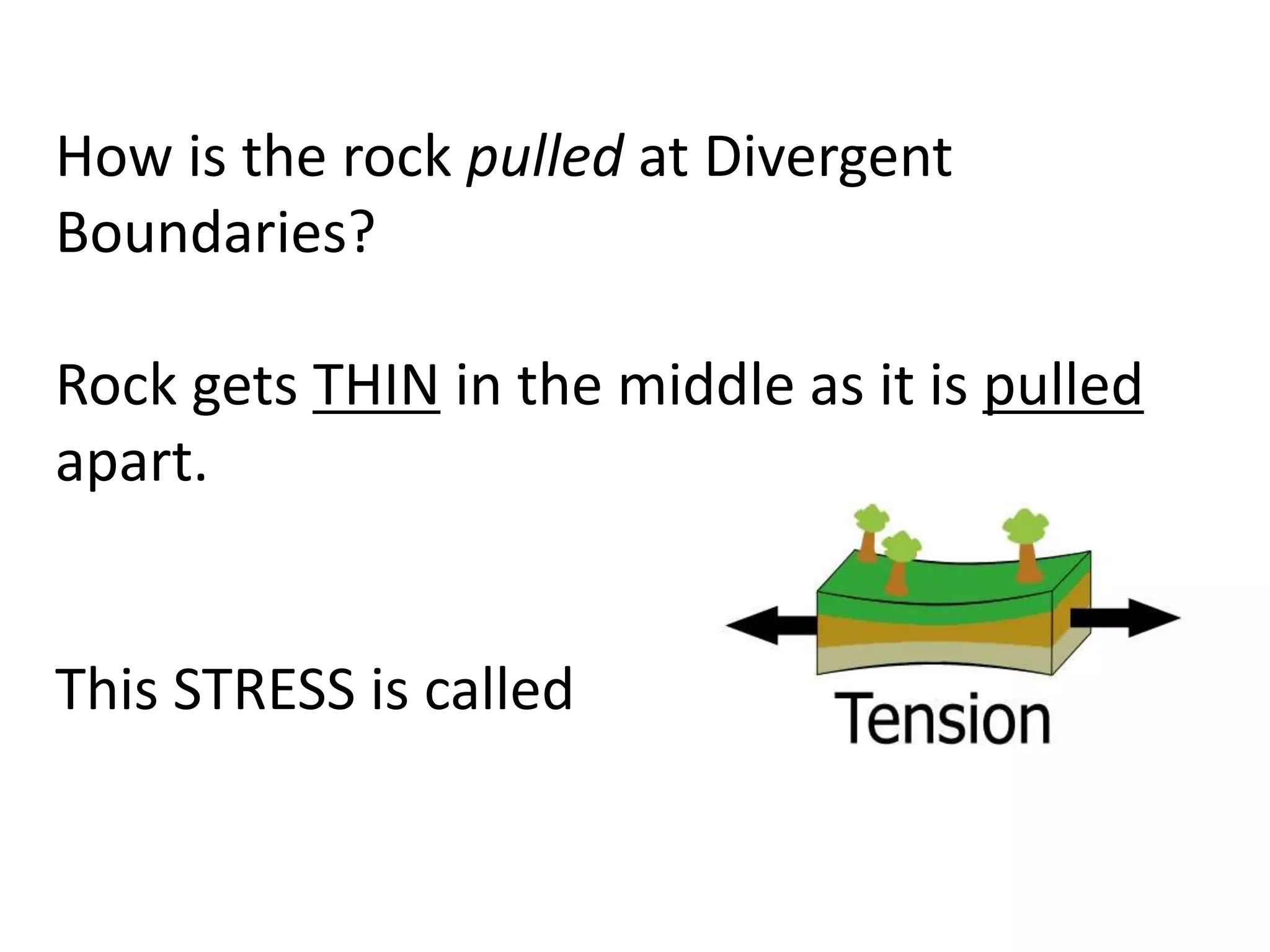
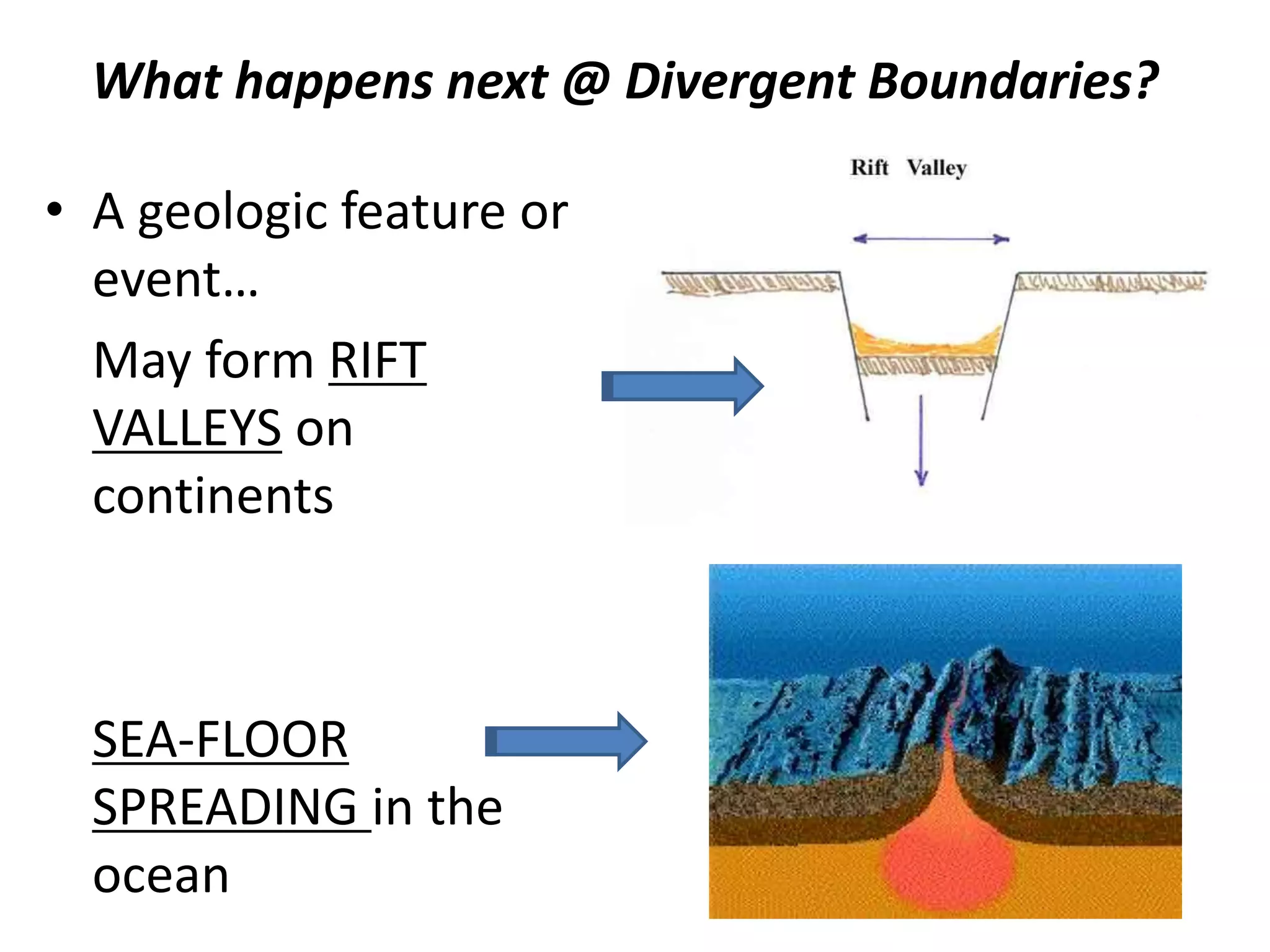
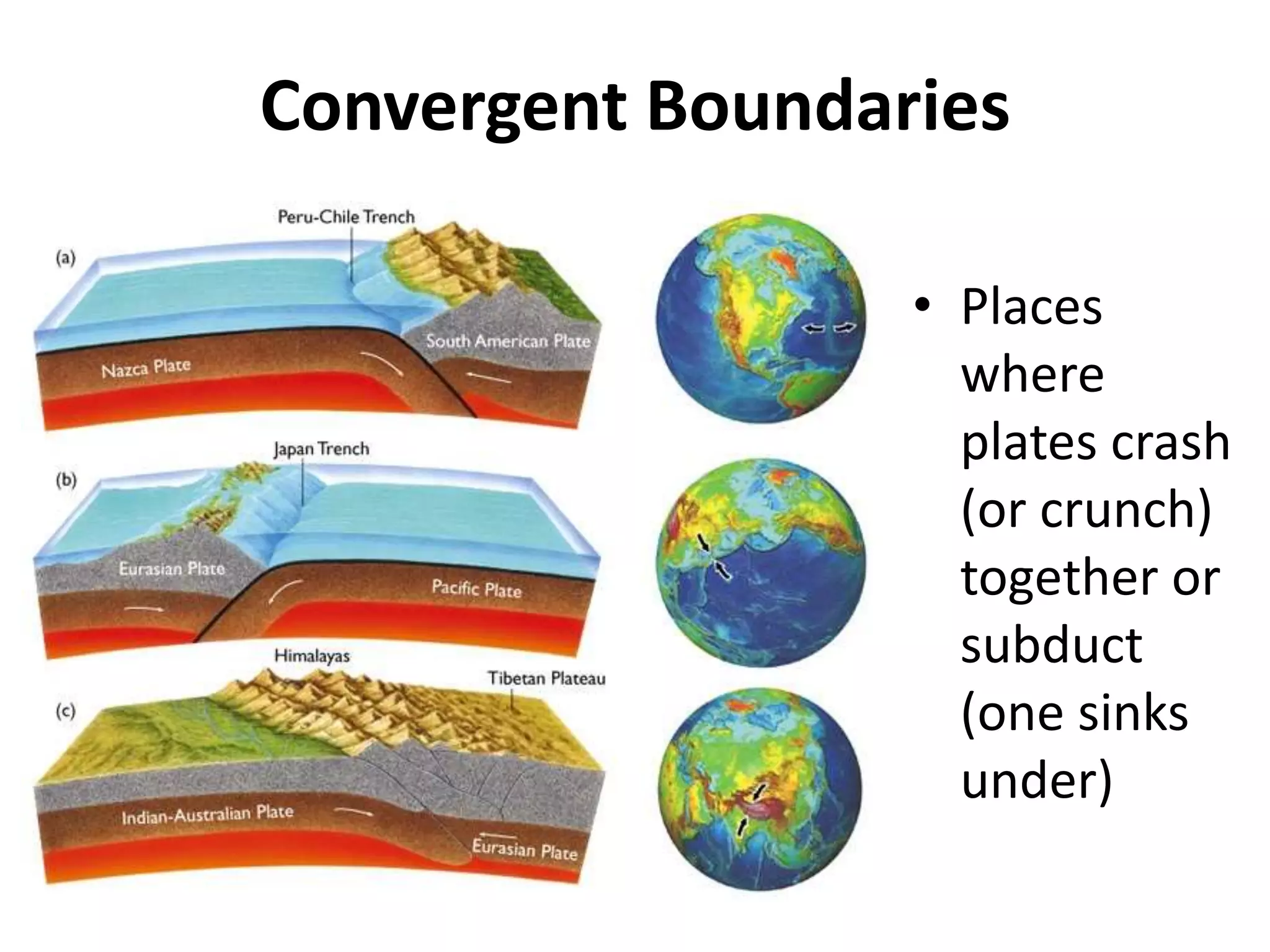
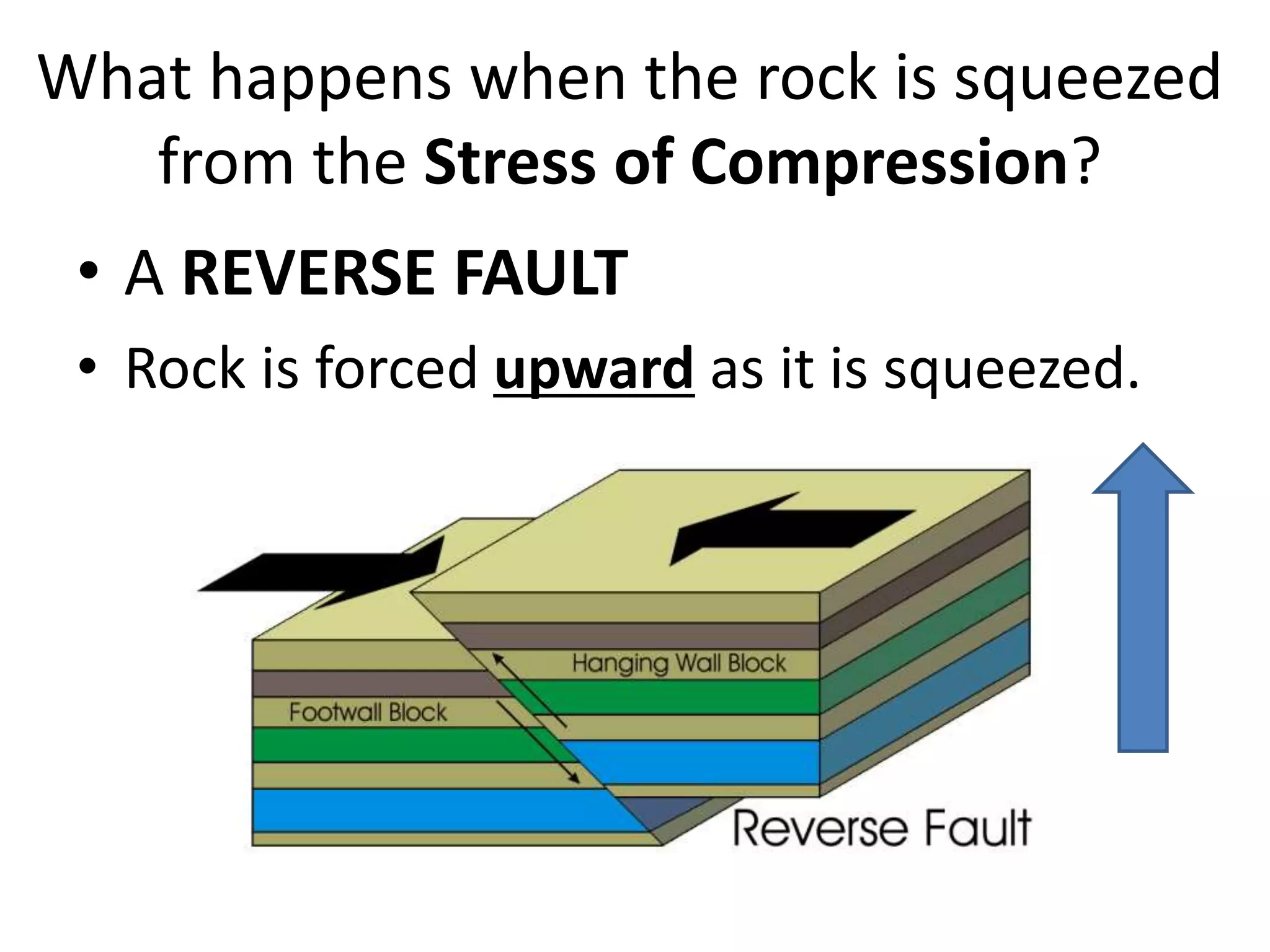
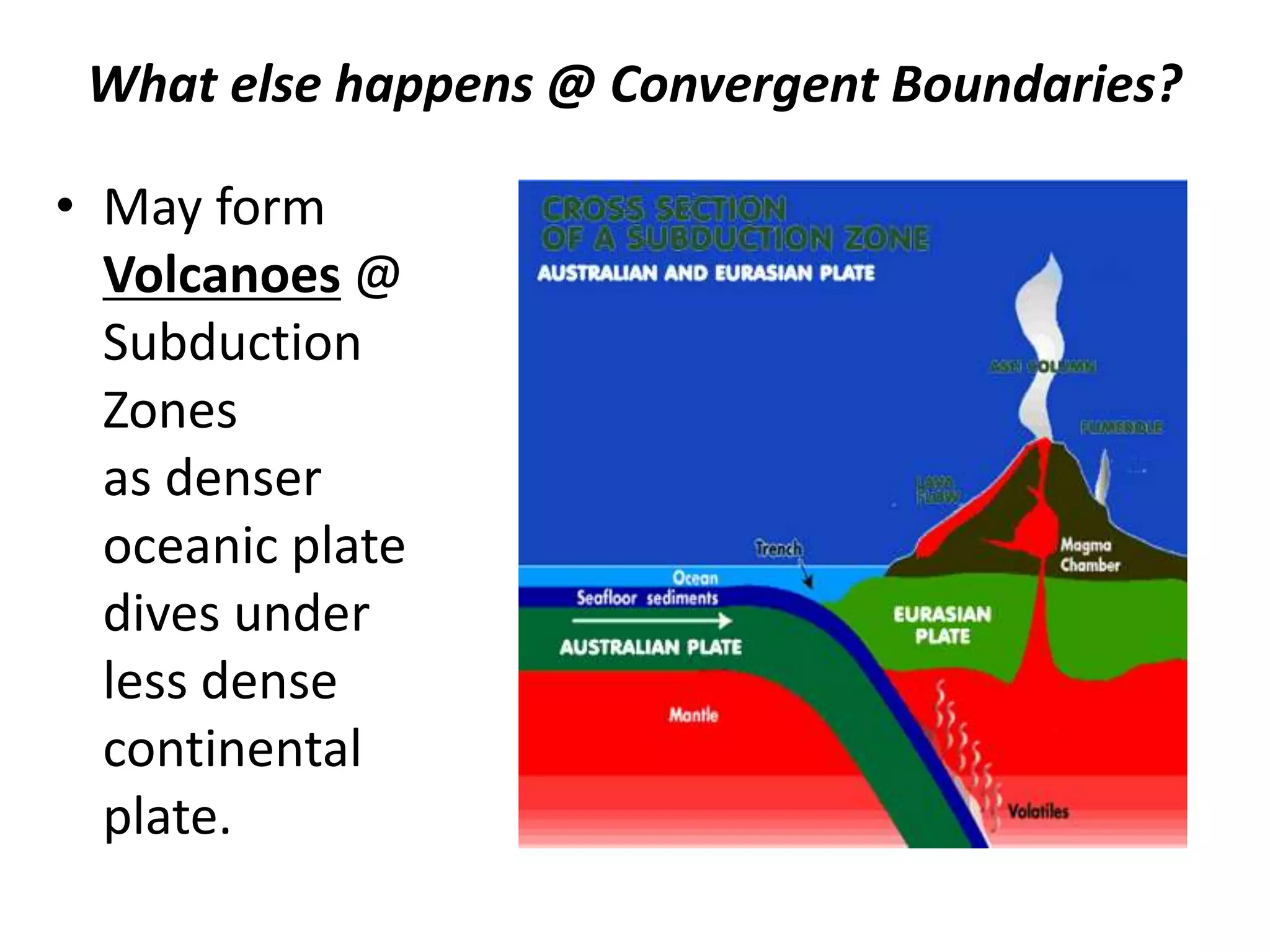
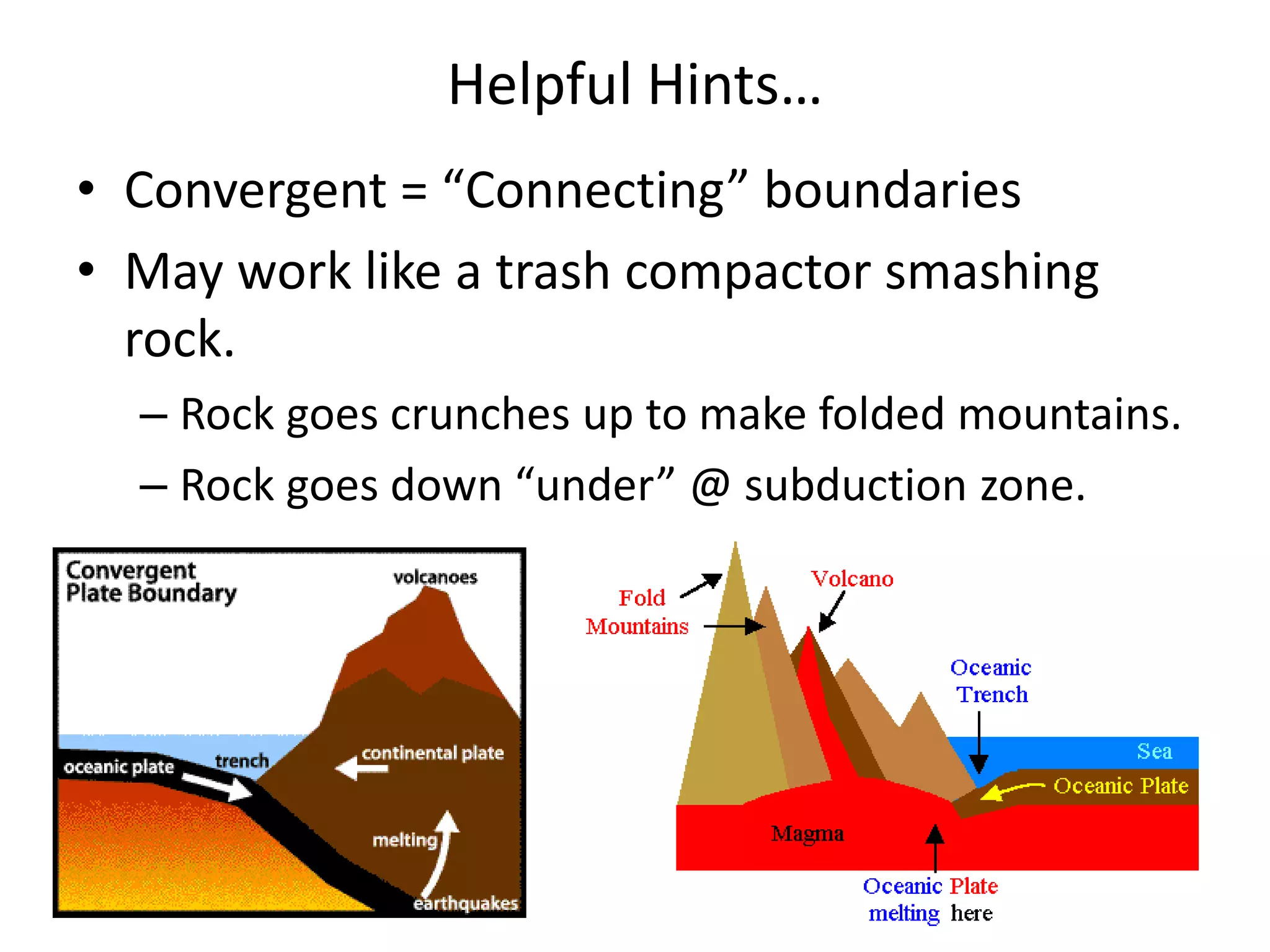
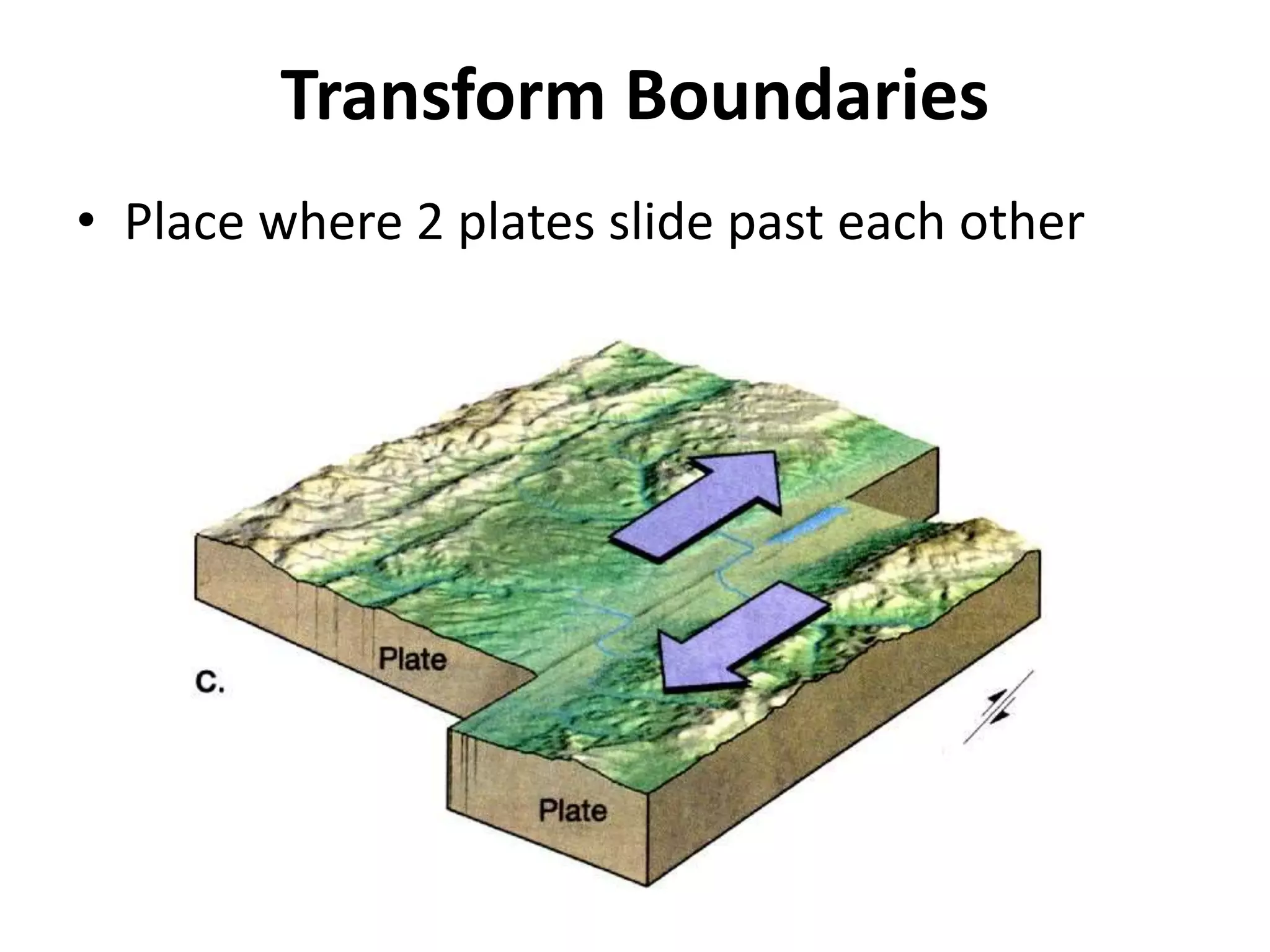
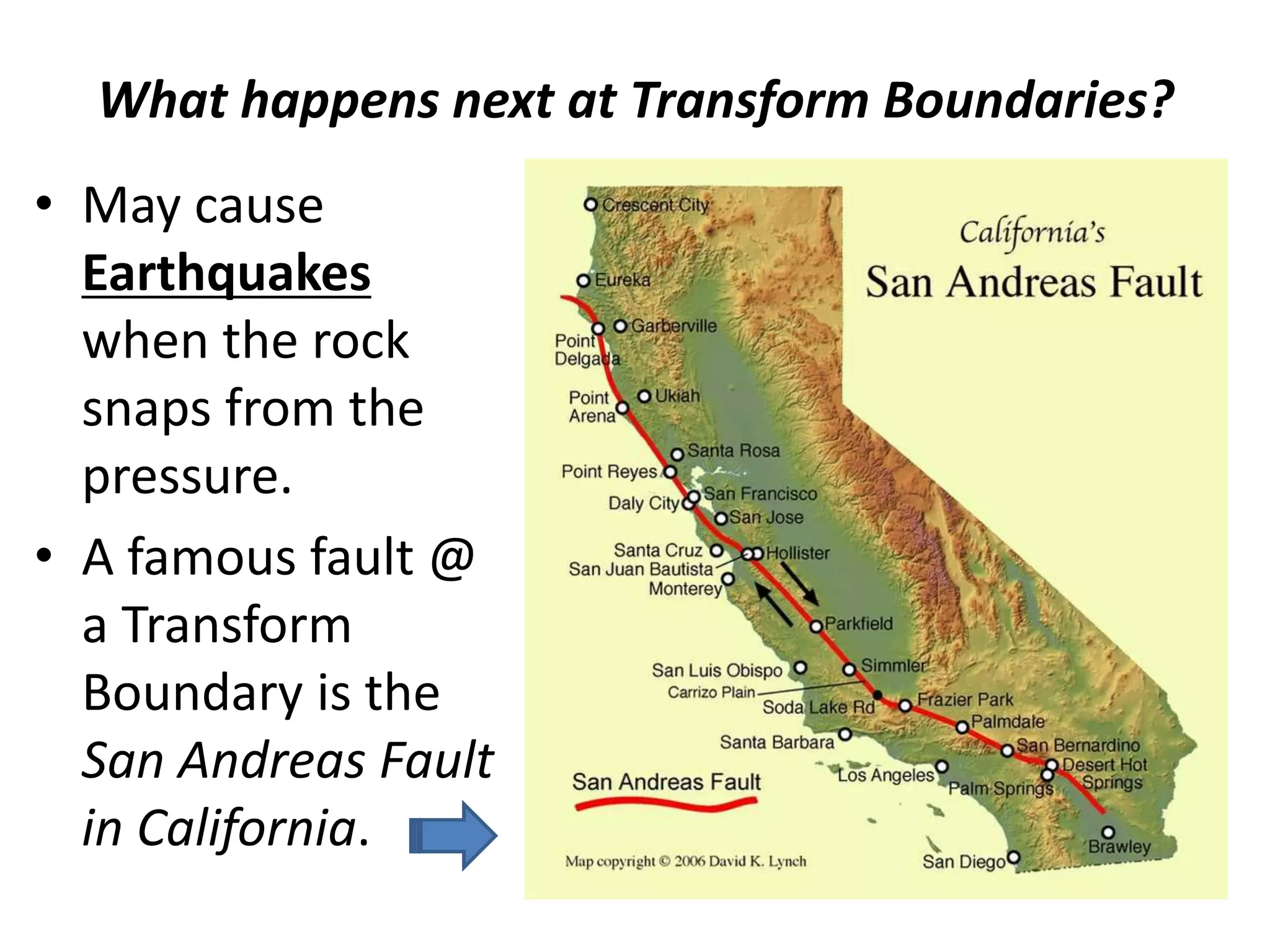
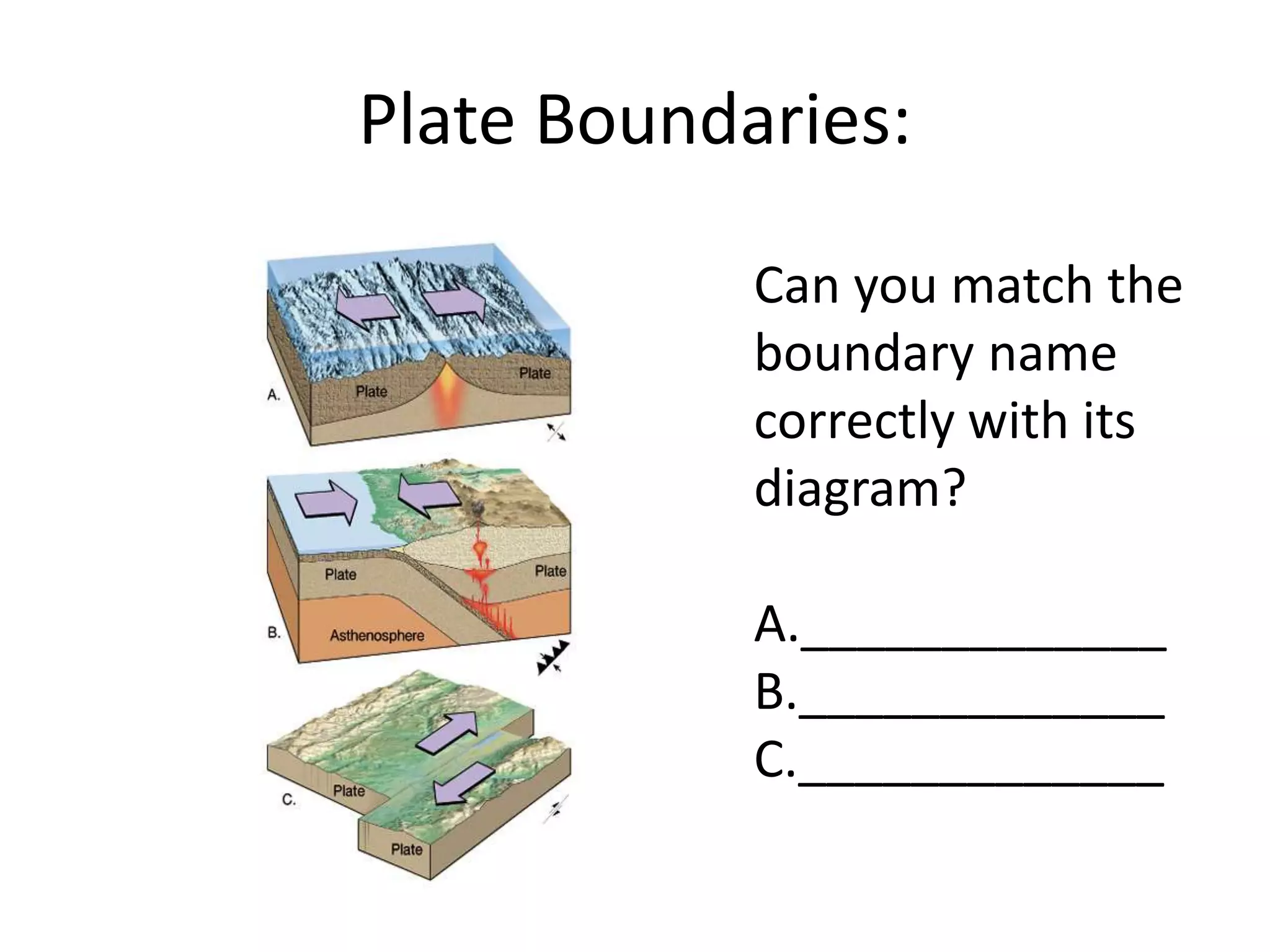
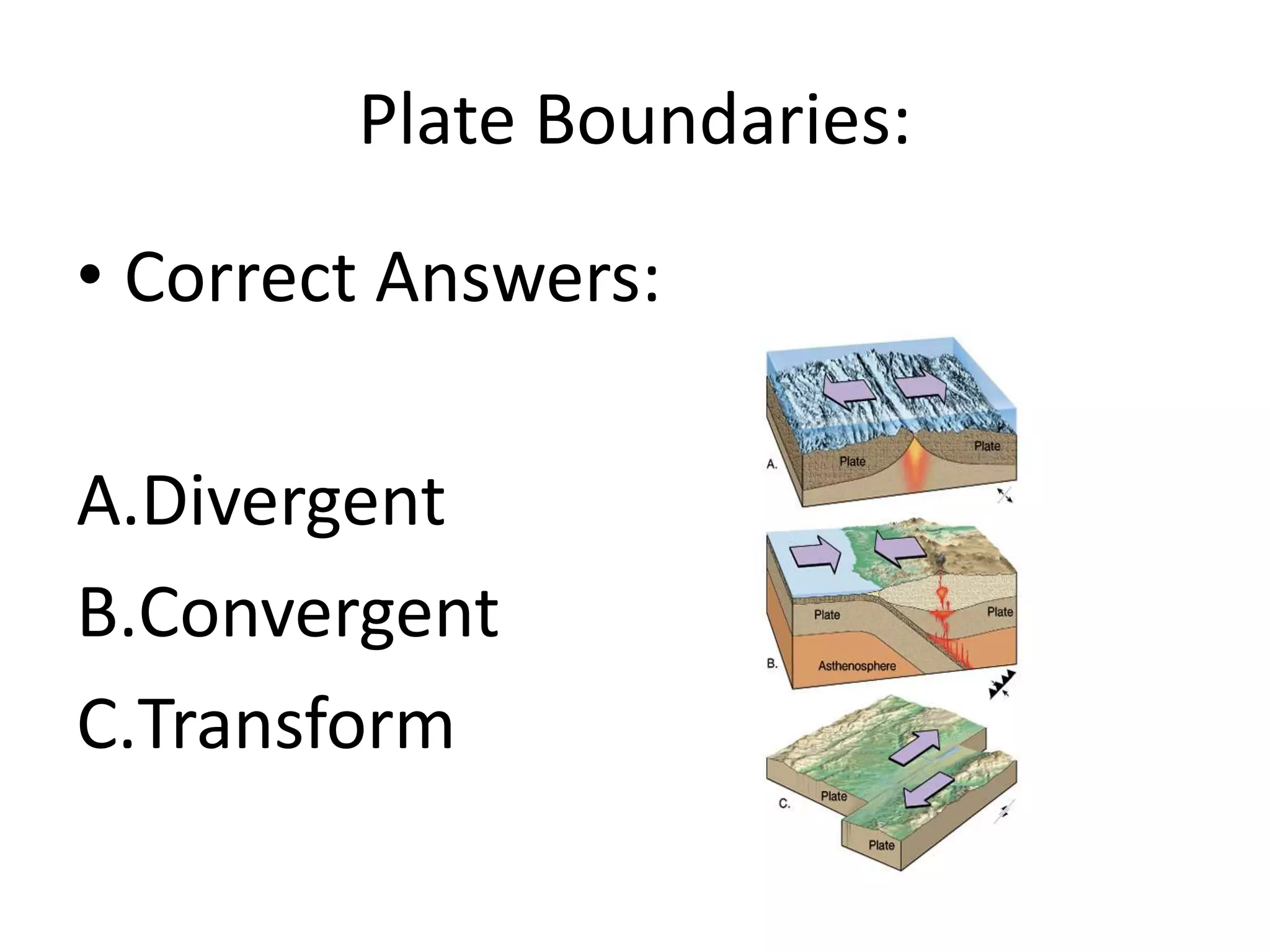
This document discusses plate tectonics and the three types of plate boundaries: divergent boundaries, convergent boundaries, and transform boundaries. It describes how each boundary type results in different stresses on rocks and the formation of different geological features. Divergent boundaries result in tension stresses that cause normal faults and the formation of rift valleys or sea floor spreading. Convergent boundaries result in compression stresses that cause reverse faults and the uplifting of folded mountains or subduction zones and volcanoes. Transform boundaries result in shearing stresses that cause strike-slip faults like the San Andreas Fault in California.