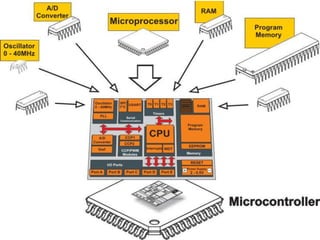
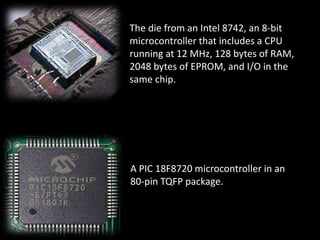
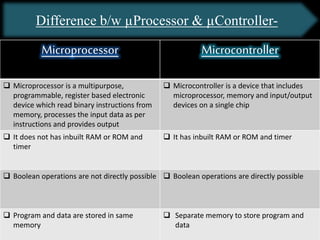
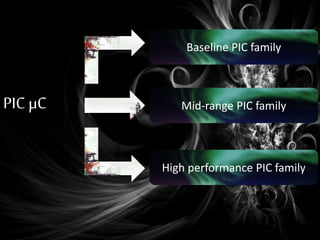
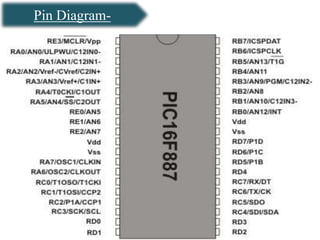
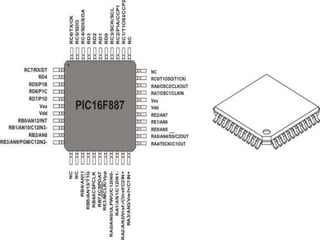
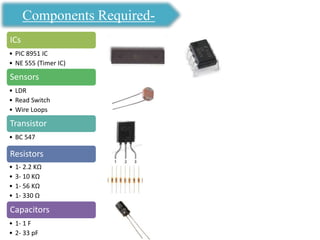
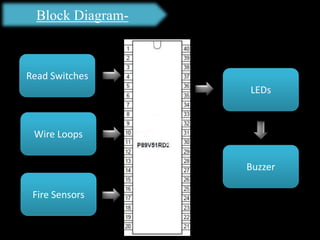
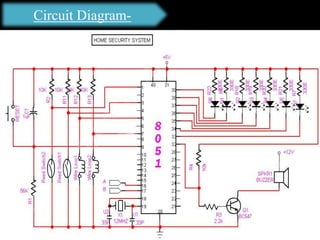
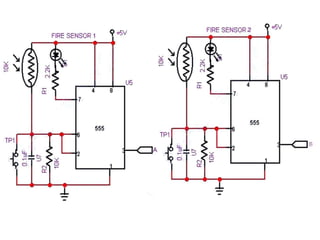
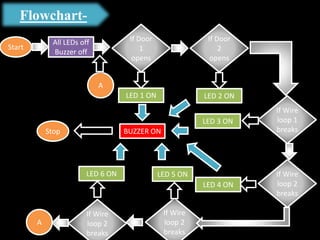
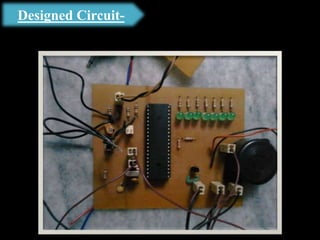
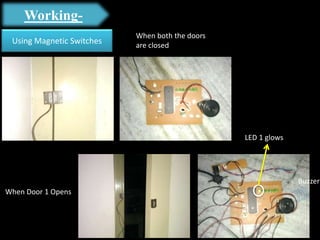
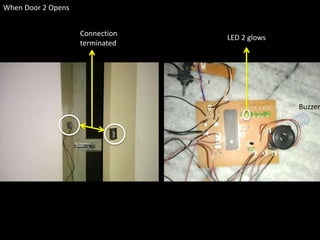
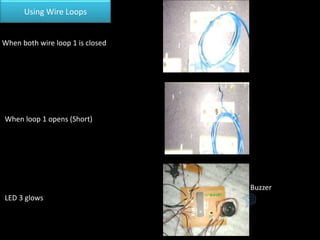
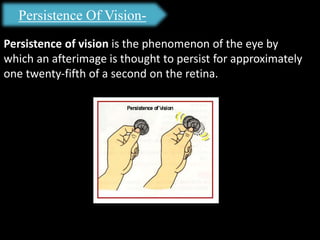
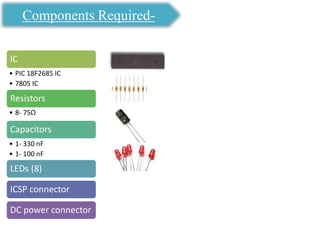
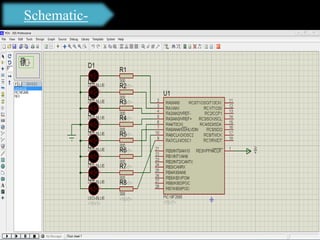
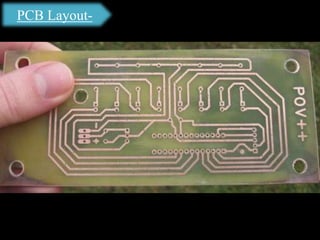
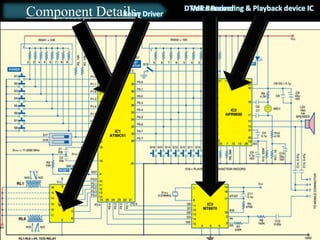
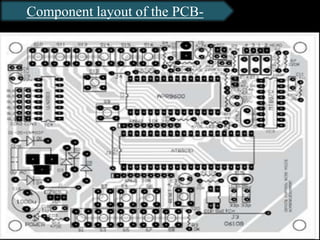
The document presents an overview of microcontrollers, specifically focusing on PIC microcontrollers, and highlights their differences from microprocessors. It covers the history, applications, limitations, and components required for various projects using PIC microcontrollers, including home security systems and digital persistence of vision displays. The presentation also discusses development tools and includes schematic diagrams for the designed circuits.