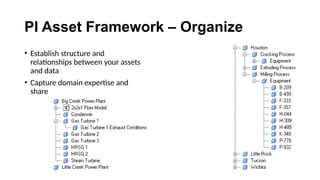
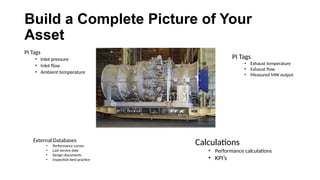
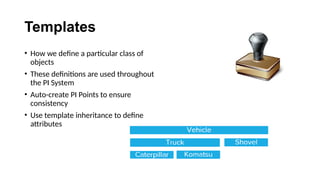
The document explains the PI Asset Framework, a hierarchical structure that organizes and simplifies data related to assets, allowing users to interpret information from both data and user models. It enables integration of diverse data sources, supports analytics, and enhances asset management by utilizing templates and standardization. Benefits include improved data accessibility, the ability to conduct comprehensive analyses, and seamless deployment across an enterprise.