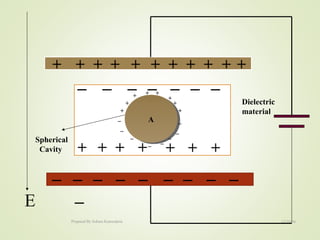
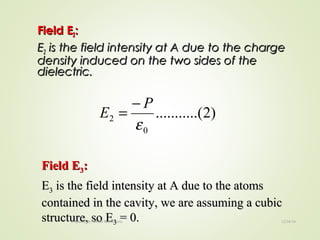
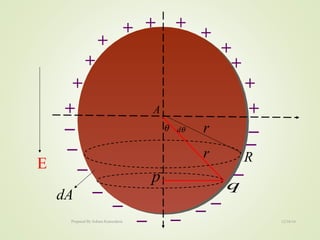
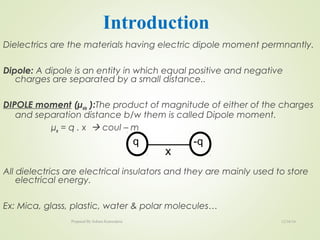
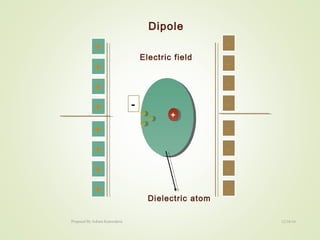
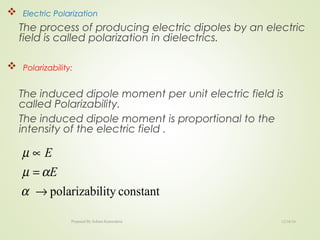
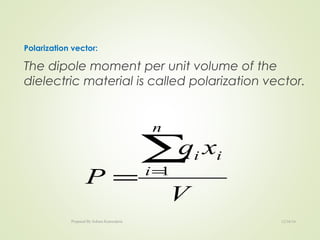
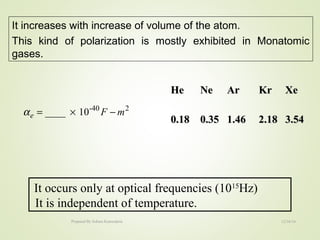
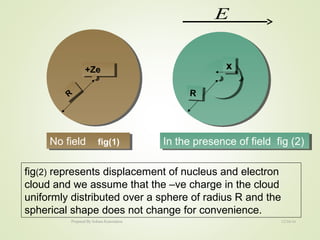
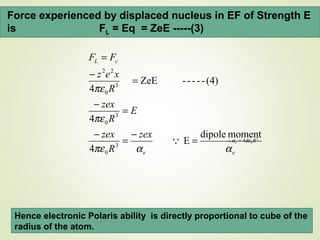
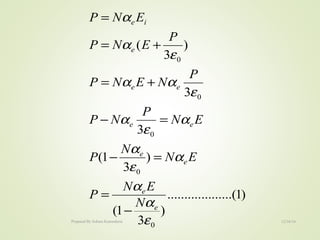The document discusses key concepts related to dielectrics and polarization. It defines that dielectrics have a permanent electric dipole moment and are electrical insulators that can store electrical energy. It describes different types of polarization that can occur in dielectrics, including electronic, ionic, orientational, and space charge polarization. It also discusses dipole moment, dielectric constant, electric flux density, electric susceptibility, local fields, and the Clausius-Mossotti relation.









![Restoring force constant depend upon the mass of the ion and
natural frequency and is given by
[ ]Mm
w
eE
xx
wm
eE
x
xwmeEF
11
2
0
21
2
0
2
0
.
or
.
+=+∴
=
==
12/16/16Prepared By Soham Kansodaria](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slidesharephysics-161216064730/85/Physics-Dielectric-19-320.jpg)
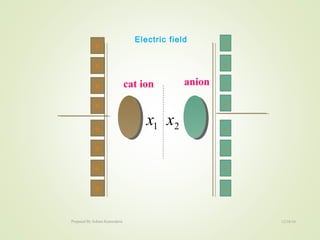
![Where ‘M’ mass of anion and ‘m’ is mass of cat ion
[ ]
[ ]Mm
ionic
ionic
Mmionic
w
e
E
w
Ee
xx
11
2
0
2
11
2
0
2
21
or
)e(
+⇒=
+=+=∴
µ
α
µ
This polarization occurs at frequency 1013
Hz (IR).
It is a slower process compared to electronic
polarization.
It is independent of temperature.
12/16/16Prepared By Soham Kansodaria](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slidesharephysics-161216064730/85/Physics-Dielectric-20-320.jpg)


![[ ] kTw
e
R
kT
EN
kT
EN
NP
ori
mMooriionicelec
orie
o
o
orie
orieo
3
4
3
..
3
..
.
2
11
2
0
2
3
2
2
µ
πεαααα
µ
α
α
µ
µ
+++=++=∴
=
=⇒=
Expression for orientation polarization
This is called Langevin–Debye equation for total Polaris ability in
dielectrics.
12/16/16Prepared By Soham Kansodaria](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slidesharephysics-161216064730/85/Physics-Dielectric-23-320.jpg)