The document is a presentation on dielectrics that covers:
- The basic terms related to dielectrics including electric field, flux, and dielectric constant.
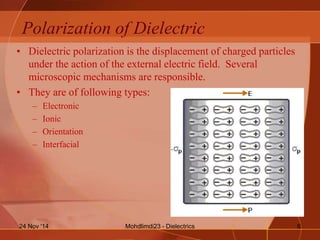
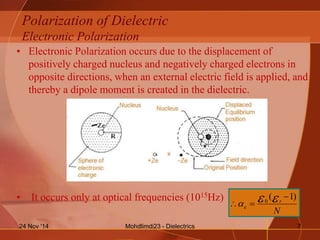
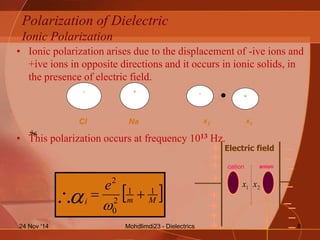
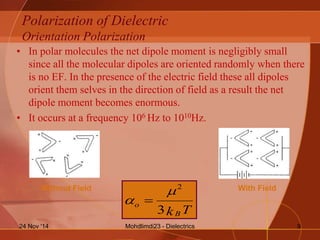
- The different types of polarization that can occur in dielectrics including electronic, ionic, orientation, and interfacial polarization.
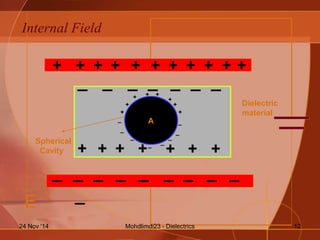
- How the internal electric field is calculated for a dielectric material placed between the plates of a capacitor.
- The various types of dielectric materials including solid, liquid, and gaseous dielectrics.
- The key properties desired in a good dielectric material and examples of applications for dielectrics such as in capacitors and transformers.