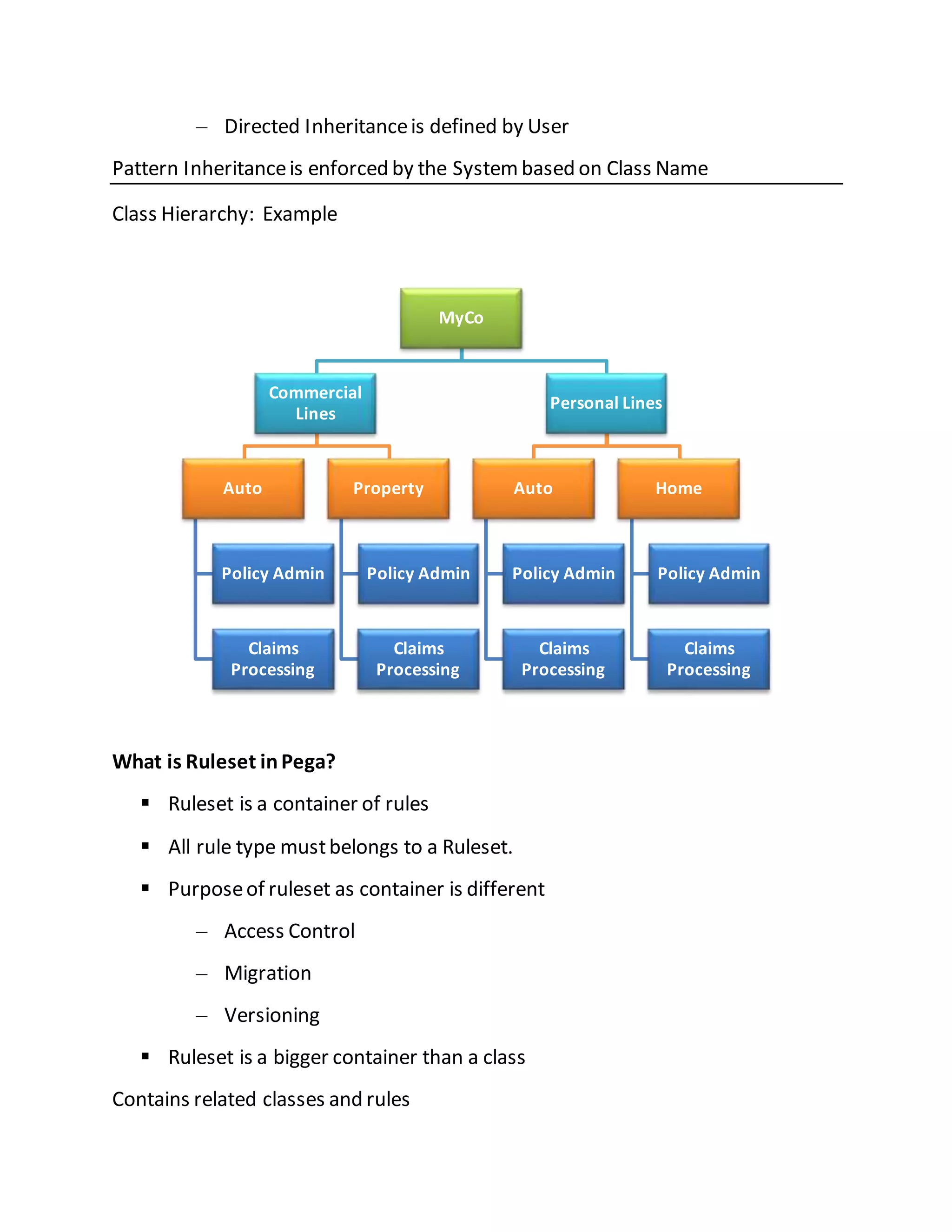
The document outlines key concepts in Pega, including rules as the foundational elements of applications, cases as business transactions, processes represented as flows, and classes that contain rules. It explains rule resolution and inheritance within Pega, the structure and purpose of rulesets, and components of the Pega designer studio, which is a high-productivity portal for developers. Additionally, it covers various explorers in the designer studio and introduces debugging and performance tools available in Pega.