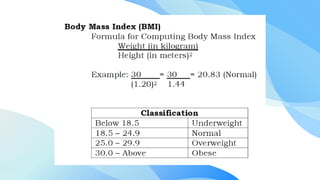
This document discusses physical fitness and healthy eating habits. It defines physical fitness as being able to do physical activities without getting tired. It identifies the different components of health-related fitness like cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength, and flexibility. It also discusses the barriers to physical activity like lack of time and motivation. Regarding eating habits, it explains that they are influenced by cultural, social, economic and other factors. It emphasizes that improving eating habits requires reflecting on current habits, replacing unhealthy ones with healthier alternatives, and reinforcing the new habits.